NAU8812EVB Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America, NAU8812EVB Datasheet - Page 57

NAU8812EVB
Manufacturer Part Number
NAU8812EVB
Description
BOARD EVAL FOR NAU8812
Manufacturer
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Series
emPowerAudio™r
Datasheet
1.NAU8812EVB.pdf
(109 pages)
Specifications of NAU8812EVB
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 57 of 109
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
Companding is used in digital communication systems to optimize signal-to-noise ratios with reduced data bit rates,
and make use of non-linear algorithms. NAU8812 supports two different types of companding A-law and µ-law on
both transmit and receive sides. A-law algorithm is used in European communication systems and µ-law algorithm is
used by North America, Japan, and Australia. This feature is enabled by setting DACCM[4:3] address (0x05) or
ADCCM[2:1] address (0x05) register bits. Companding converts 13 bits (µ-law) or 12 bits (A-law) to 8 bits using non-
linear quantization. The companded signal is an 8-bit word containing sign (1-bit), exponent (3-bits) and mantissa (4-
bits). As recommended by the G.711 standard (all 8-bits are inverted for µ-law, all even data bits are inverted for A-
law).
Setting CMB8[5] address 0x05 to 1 will cause the PCM interface to use 8-bit word length for data transfer, overriding
the word length configuration setting in WLEN[6:5] address 0x04.
The following equations for data compression (as set out by ITU-T G.711 standard):
µ-law (where µ=255 for the U.S. and Japan):
F(x) = ln( 1 + µ|x|) / ln( 1 + µ)
A-law (where A=87.6 for Europe):
F(x) = A|x| / ( 1 + lnA)
F(x) = ( 1 + lnA|x|) / (1 + lnA)
emPowerAudio
Datasheet Revision 2.0
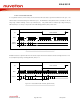
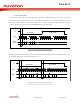
0x05
Addr
12.10.6. Companding
D8
0
™
f or x ≤ 1/A
D7
0
f or 1/A ≤ x ≤ 1
D6
0
-1 ≤ x ≤ 1
Table 29: Companding Control
CMB8
D5
Page 57 of 109
D4
DACCM[1:0]
D3
D2
ADCCM[1:0]
D1
NAU8812
January 2011
ADDAP
D0
Default
0x000
Related parts for NAU8812EVB
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Nuvoton Technology Corporation of America
Datasheet: