XC3S1000-4FG456I Xilinx Inc, XC3S1000-4FG456I Datasheet - Page 12

XC3S1000-4FG456I
Manufacturer Part Number
XC3S1000-4FG456I
Description
FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY
Manufacturer
Xilinx Inc
Series
Spartan™-3r
Datasheet
1.XC3S50-4VQG100C.pdf
(217 pages)
Specifications of XC3S1000-4FG456I
Number Of Logic Elements/cells
17280
Number Of Labs/clbs
1920
Total Ram Bits
442368
Number Of I /o
333
Number Of Gates
1000000
Voltage - Supply
1.14 V ~ 1.26 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 100°C
Package / Case
456-BBGA
Package
456FBGA
Family Name
Spartan®-3
Device Logic Units
17280
Device System Gates
1000000
Maximum Internal Frequency
630 MHz
Typical Operating Supply Voltage
1.2 V
Maximum Number Of User I/os
333
Ram Bits
442368
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
XC3S1000-4FG456I
Manufacturer:
XILINX
Quantity:
530
Company:
Part Number:
XC3S1000-4FG456I
Manufacturer:
XILINX
Quantity:
166
Part Number:
XC3S1000-4FG456I
Manufacturer:
XILINX/赛灵思
Quantity:
20 000
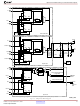
Spartan-3 FPGA Family: Functional Description
IOBs
For additional information, refer to the “Using I/O
Resources” chapter in UG331.
IOB Overview
The Input/Output Block (IOB) provides a programmable,
bidirectional interface between an I/O pin and the FPGA’s
internal logic.
A simplified diagram of the IOB’s internal structure appears
in
IOB: the output path, input path, and 3-state path. Each
path has its own pair of storage elements that can act as
either registers or latches. For more information, see the
Storage Element Functions
nal paths are as follows:
•
•
•
Table 4: Storage Element Signal Description
12
54
D
Q
CK
CE
SR
REV
Element
Storage
Signal
Figure
The input path carries data from the pad, which is
bonded to a package pin, through an optional
programmable delay element directly to the I line.
There are alternate routes through a pair of storage
elements to the IQ1 and IQ2 lines. The IOB outputs I,
IQ1, and IQ2 all lead to the FPGA’s internal logic. The
delay element can be set to ensure a hold time of zero.
The output path, starting with the O1 and O2 lines,
carries data from the FPGA’s internal logic through a
multiplexer and then a three-state driver to the IOB
pad. In addition to this direct path, the multiplexer
provides the option to insert a pair of storage elements.
The 3-state path determines when the output driver is
high impedance. The T1 and T2 lines carry data from
the FPGA’s internal logic through a multiplexer to the
5. There are three main signal paths within the
Data input
Data output
Clock input
Clock Enable input
Set/Reset
Reverse
Description
section. The three main sig-
Data at this input is stored on the active edge of CK enabled by CE. For latch operation when the
input is enabled, data passes directly to the output Q.
The data on this output reflects the state of the storage element. For operation as a latch in
transparent mode, Q will mirror the data at D.
A signal’s active edge on this input with CE asserted, loads data into the storage element.
When asserted, this input enables CK. If not connected, CE defaults to the asserted state.
Forces storage element into the state specified by the SRHIGH/SRLOW attributes. The
SYNC/ASYNC attribute setting determines if the SR input is synchronized to the clock or not.
Used together with SR. Forces storage element into the state opposite from what SR does.
www.xilinx.com
•
Storage Element Functions
There are three pairs of storage elements in each IOB, one
pair for each of the three paths. It is possible to configure
each of these storage elements as an edge-triggered
D-type flip-flop (FD) or a level-sensitive latch (LD).
The storage-element-pair on either the Output path or the
Three-State path can be used together with a special multi-
plexer to produce Double-Data-Rate (DDR) transmission.
This is accomplished by taking data synchronized to the
clock signal’s rising edge and converting them to bits syn-
chronized on both the rising and the falling edge. The com-
bination of two registers and a multiplexer is referred to as a
Double-Data-Rate D-type flip-flop (FDDR).
See
information.
The signal paths associated with the storage element are
described in
output driver. In addition to this direct path, the
multiplexer provides the option to insert a pair of
storage elements. When the T1 or T2 lines are
asserted High, the output driver is high-impedance
(floating, Hi-Z). The output driver is active-Low
enabled.
All signal paths entering the IOB, including those
associated with the storage elements, have an inverter
option. Any inverter placed on these paths is
automatically absorbed into the IOB.
Double-Data-Rate Transmission, page 14
Function
Table
4.
DS099-2 (v2.5) December 4, 2009
Product Specification
for more
R