EP9312-CB Cirrus Logic Inc, EP9312-CB Datasheet - Page 337

EP9312-CB
Manufacturer Part Number
EP9312-CB
Description
System-on-Chip Processor
Manufacturer
Cirrus Logic Inc
Series
EP9r
Datasheets
1.EP9307-CRZ.pdf
(824 pages)
2.EP9312-IBZ.pdf
(4 pages)
3.EP9312-CB.pdf
(62 pages)
4.EP9312-CB.pdf
(17 pages)
Specifications of EP9312-CB
Peak Reflow Compatible (260 C)
No
A/d Converter
12 Bits
Leaded Process Compatible
No
No. Of I/o Pins
65
Package / Case
352-BGA
Core Processor
ARM9
Core Size
16/32-Bit
Speed
200MHz
Connectivity
EBI/EMI, EIDE, Ethernet, I²C, IrDA, Keypad/Touchscreen, SPI, UART/USART, USB
Peripherals
AC'97, DMA, I²:S, LCD, LED, MaverickKey, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
16
Program Memory Type
ROMless
Ram Size
32K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.65 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x12b
Oscillator Type
External
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Processor Series
EP93xx
Core
ARM920T
Data Bus Width
32 bit
3rd Party Development Tools
MDK-ARM, RL-ARM, ULINK2
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Program Memory Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
No
Other names
598-1257
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
EP9312-CB
Manufacturer:
CIRRUS
Quantity:
20 000
- EP9307-CRZ PDF datasheet
- EP9312-IBZ PDF datasheet #2
- EP9312-CB PDF datasheet #3
- EP9312-CB PDF datasheet #4
- Current page: 337 of 824
- Download datasheet (13Mb)
DS785UM1
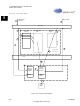
9.2.3.13 Transmit Errors
Refer to
Transmit error conditions are broken into two categories: hard errors and soft errors. A hard
error is generally considered a reliability problem. This includes AHB bus access problems. A
soft error indicates that the frame was not successfully transmitted. The error may be
expected or rare. A soft error needs a graceful recovery by the host driver. Soft errors include:
excessive collisions, SQE error (if connected to a MAU). Hard errors are parity errors (if
enabled), system errors, master and target aborts. These will stop further transmit DMA
activity and require host intervention for recovery.
Hard errors cause the Descriptor Processor to halt operation. This allows the Host to
determine the cause of error and reinitialize and restart the bus master operations.
Most soft errors do not cause the frame processing operations to halt. The Descriptor
Processor simply flags the error and continues on to the next frame. The exception is on a
transmit underrun. By halting the transmit frame processing, the Host has the ability to re-
initialize the transmit Descriptor Processor registers to point to the start of the failed frame
and re-initialize. This will cause the MAC to reattempt the failed frame and allows the order of
frame transmission to be maintained.
Note: Steps 1, 2, 10, and 11 are transparent to the MAC block. Steps 3 through 9, inclusive,
1. Protocol stack initiates a transmit frame.
2. Driver parses protocol stack buffer into Transmit Descriptor Queue.
3. Driver writes number of additional entries to the Transmit Enqueue register.
4. On-chip Descriptor Processor fetches descriptor information.
5. On-chip Descriptor Processor initiates data move.
6. Frame data fetched from system memory into the transmit FIFO.
7. Frame transmitted onto LAN medium. Steps 6 and 7 can overlap.
8. End of frame status written to status queue
9. Driver interrupted if interrupt conditions met.
10.Driver processes the transmit status
11.Driver informs the protocol stack that transmit is complete.
directly involve the MAC.
Figure
9-16. The detailed transmit flow is:
Copyright 2007 Cirrus Logic
1/10/100 Mbps Ethernet LAN Controller
EP93xx User’s Guide
9-35
9
Related parts for EP9312-CB
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
IC ARM920T MCU 200MHZ 352-PBGA
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC ARM9 SOC UNIVERSAL 352PBGA
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC ARM920T MCU 200MHZ 352-PBGA
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC Universal Platform ARM9 SOC Prcessor
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC Universal Platform ARM9 SOC Prcessor
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Development Kit
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Development Kit
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-efficiency PFC + Fluorescent Lamp Driver Reference Design
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Development Kit
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Development Kit
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Development Kit
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Development Kit
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Ref Bd For Speakerbar MSA & DSP Products
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc