FL7930BM Fairchild Semiconductor, FL7930BM Datasheet - Page 14
FL7930BM
Manufacturer Part Number
FL7930BM
Description
Power Factor Correction ICs PFC Controller for Lighting; 2nd OVP
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FL7930BM.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of FL7930BM
Switching Frequency
300 KHz
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
SOP-8
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
© 2011 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FL7930 • Rev. 1.0.0
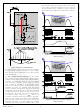
Because auxiliary winding voltage can swing from
negative voltage to positive voltage, the internal block in
the ZCD pin has both positive and negative voltage
clamping circuits. When the auxiliary voltage is
negative, an internal circuit clamps the negative voltage
at the ZCD pin around 0.65V by sourcing current to the
serial resistor between the ZCD pin and the auxiliary
winding. When the auxiliary voltage is higher than 6.5V,
current is sinked through a resistor from the auxiliary
winding to the ZCD pin.
To check the boost inductor current zero instance,
auxiliary winding voltage is used. When boost inductor
current becomes zero, there is a resonance between
boost inductor and all capacitors at MOSFET drain pin,
including C
the D-S pin to reduce the voltage rising and falling slope
of the MOSFET; a parasitic capacitor at inductor; and so
on to improve performance. Resonated voltage is
reflected to the auxiliary winding and can be used for
detecting zero current of boost inductor and valley
position of MOSFET voltage stress. For valley detection,
a minor delay by the resistor and capacitor is needed. A
capacitor increases the noise immunity at the ZCD pin.
If ZCD voltage is higher than 1.5V, an internal ZCD
comparator output becomes HIGH and LOW when the
ZCD goes below 1.4V. At the falling edge of comparator
output, internal logic turns on the MOSFET.
Figure 33. Auxiliary Voltage Threshold
Figure 32. Auxiliary Voltage Depends
OSS
of the MOSFET; an external capacitor at
on MOSFET Switching
14
When no ZCD signal is available, the PFC controller
cannot turn on the MOSFET, so the controller checks
every switching off time and forces MOSFET turn on
when the off time is longer than 150μs. This is called
restart timer. The restart timer triggers MOSFET turn-on
at startup and may be used at the input voltage-zero
cross period.
Because the MOSFET turn on depends on the ZCD
input, switching frequency may increase to higher than
several megahertz due to mis-triggering or noise on the
nearby ZCD pin. If the switching frequency is higher
than needed for critical conduction mode (CRM),
operation mode shifts to continuous conduction mode
(CCM). In CCM, unlike CRM where the boost inductor
current is reset to zero at the next switch on; inductor
current builds up at every switching cycle and can be
raised to high current that exceeds the current rating of
the power switch or diode. This can seriously damage
the power switch and result in burn down. To avoid this,
maximum switching frequency limitation is embedded. If
ZCD signal is applied again within 3.3μs after the
previous rising edge of the gate signal, this signal is
ignored internally and FL7930 waits for another ZCD
signal.
performance at light load and high input voltage.
7. Control: The scaled output is compared with the
internal reference voltage and sinking or sourcing
current is generated from the COMP pin by the
transconductance amplifier. The error amplifier output is
compared with the internal sawtooth waveform to give
proper turn-on time based on the controller.
Figure 35. Maximum Switching Frequency
This
Figure 34. Restart Timer at Startup
150
s
slightly
Limit Operation
degrades
the
power
www.fairchildsemi.com
factor