A3P125-QNG132 MICROSEMI, A3P125-QNG132 Datasheet - Page 63

A3P125-QNG132
Manufacturer Part Number
A3P125-QNG132
Description
Manufacturer
MICROSEMI
Datasheet
1.A3P125-QNG132.pdf
(144 pages)
Specifications of A3P125-QNG132
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
A3P125-QNG132
Manufacturer:
ACT
Quantity:
343
Company:
Part Number:
A3P125-QNG132I
Manufacturer:
ACT
Quantity:
265
Part Number:
A3P125-QNG132I
Manufacturer:
MICROSEMI/美高森美
Quantity:
20 000
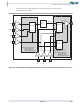
Figure 2-13 • B-LVDS/M-LVDS Multipoint Application Using LVDS I/O Buffers
R
T
Z
Z
Z
0
0
stub
Receiver
+
R
R
S
B-LVDS/M-LVDS
Bus LVDS (B-LVDS) and Multipoint LVDS (M-LVDS) specifications extend the existing LVDS standard to
high-performance multipoint bus applications. Multidrop and multipoint bus configurations may contain
any combination of drivers, receivers, and transceivers. Actel LVDS drivers provide the higher drive
current required by B-LVDS and M-LVDS to accommodate the loading. The drivers require series
terminations for better signal quality and to control voltage swing. Termination is also required at both
ends of the bus since the driver can be located anywhere on the bus. These configurations can be
implemented using the TRIBUF_LVDS and BIBUF_LVDS macros along with appropriate terminations.
Multipoint designs using Actel LVDS macros can achieve up to 200 MHz with a maximum of 20 loads. A
sample application is given in
section in
Example: For a bus consisting of 20 equidistant loads, the following terminations provide the required
differential voltage, in worst-case Industrial operating conditions, at the farthest receiver: R
R
LVPECL
Low-Voltage Positive Emitter-Coupled Logic (LVPECL) is another differential I/O standard. It requires
that one data bit be carried through two signal lines. Like LVDS, two pins are needed. It also requires
external resistor termination.
The full implementation of the LVDS transmitter and receiver is shown in an example in
page
receiver macro, three board resistors at the transmitter end, and one resistor at the receiver end. The
values for the three driver resistors are different from those used in the LVDS implementation because
the output standard specifications are different.
-
T
EN
R
Z
= 70 Ω, given Z
S
stub
2-52. The building blocks of the LVPECL transmitter-receiver are one transmitter macro, one
Table 2-84 on page
Z
Z
Z
0
0
stub
Transceiver
+
R
T
0
S
-
= 50 Ω (2") and Z
EN
R
Z
stub
S
Z
Z
Z
0
0
2-50.
Figure
stub
Driver
+
R
D
S
2-13. The input and output buffer delays are available in the LVDS
stub
-
EN
R
Z
S
stub
= 50 Ω (~1.5").
R e v i s i o n 1
Z
Z
Z
0
0
stub
Receiver
+
R
R
S
-
EN
R
Z
S
stub
Automotive ProASIC3 Flash Family FPGAs
...
Z
Z
0
0
Transceiver
+
R
T
S
-
EN
R
S
Figure 2-14 on
S
BIBUF_LVDS
= 60 Ω and
Z
Z
0
0
2- 51
R
T