5AGXBA1D4F31C4N Altera Corporation, 5AGXBA1D4F31C4N Datasheet - Page 29

5AGXBA1D4F31C4N
Manufacturer Part Number
5AGXBA1D4F31C4N
Description
FPGA - Field Programmable Gate Array FPGA - Arria V GX 2830 LABS 416 IOs
Manufacturer
Altera Corporation
Series
Arria V GXr
Datasheet
1.5AGXFB3H4F40C5N.pdf
(33 pages)
Specifications of 5AGXBA1D4F31C4N
Rohs
yes
Number Of Logic Blocks
2830
Number Of I/os
416
Maximum Operating Frequency
800 MHz
Operating Supply Voltage
1.2 V to 1.8 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
FBGA-896
Distributed Ram
8463 kbit
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
AV-51001
2013.01.11
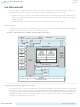
Arria V Device Overview
HPS–FPGA AXI Bridges
HPS SDRAM Controller Subsystem
FPGA Configuration and Processor Booting
The debug access port provides interfaces to industry standard JTAG debug probes and supports ARM
CoreSight debug and core traces to facilitate software development.
The HPS–FPGA bridges, which support the Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA
eXtensible Interface (AXI
The HPS–FPGA AXI bridges allow masters in the FPGA fabric to communicate with slaves in the HPS logic,
and vice versa. For example, the HPS-to-FPGA AXI bridge allows you to share memories instantiated in the
FPGA fabric with one or both microprocessors in the HPS, while the FPGA-to-HPS AXI bridge allows logic
in the FPGA fabric to access the memory and peripherals in the HPS.
Each HPS–FPGA bridge also provides asynchronous clock crossing for data transferred between the FPGA
fabric and the HPS.
The HPS SDRAM controller subsystem contains a multiport SDRAM controller and DDR PHY that are
shared between the FPGA fabric (through the FPGA-to-HPS SDRAM interface), the level 2 (L2) cache, and
the level 3 (L3) system interconnect. The FPGA-to-HPS SDRAM interface supports AMBA AXI and Avalon
Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) interface standards, and provides up to six individual ports for access by
masters implemented in the FPGA fabric.
To maximize memory performance, the SDRAM controller subsystem supports command and data
reordering, deficit round-robin arbitration with aging, and high-priority bypass features. The SDRAM
controller subsystem supports DDR2, DDR3, or LPDDR2 devices up to 4 Gb in density operating at up to
533 MHz (1066 Mbps data rate).
The FPGA fabric and HPS in the SoC FPGA are powered independently. You can reduce the clock frequencies
or gate the clocks to reduce dynamic power, or shut down the entire FPGA fabric to reduce total system
power.
You can configure the FPGA fabric and boot the HPS independently, in any order, providing you with more
design flexibility:
Note:
FPGA-to-HPS AXI bridge—a high-performance bus supporting 32, 64, and 128 bit data widths that
allows the FPGA fabric to issue transactions to slaves in the HPS.
HPS-to-FPGA AXI bridge—a high-performance bus supporting 32, 64, and 128 bit data widths that
allows the HPS to issue transactions to slaves in the FPGA fabric.
Lightweight HPS-to-FPGA AXI bridge—a lower performance 32 bit width bus that allows the HPS to
issue transactions to slaves in the FPGA fabric. This bridge is primarily used for control and status register
(CSR) accesses to peripherals in the FPGA fabric.
You can boot the HPS independently. After the HPS is running, the HPS can fully or partially reconfigure
the FPGA fabric at any time under software control. The HPS can also configure other FPGAs on the
board through the FPGA configuration controller.
You can power up both the HPS and the FPGA fabric together, configure the FPGA fabric first, and then
boot the HPS from memory accessible to the FPGA fabric.
Although the FPGA fabric and HPS are on separate power domains, the HPS must remain powered
up during operation while the FPGA fabric can be powered up or down as required.
™
) specifications, consist of the following bridges:
Arria V Device Overview
Altera Corporation
®
) Advanced
29
®