C8051F018-GQR Silicon Laboratories Inc, C8051F018-GQR Datasheet - Page 108
C8051F018-GQR
Manufacturer Part Number
C8051F018-GQR
Description
IC 8051 MCU 16K FLASH 64TQFP
Manufacturer
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Series
C8051F018r
Specifications of C8051F018-GQR
Core Processor
8051
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
25MHz
Connectivity
SMBus (2-Wire/I²C), SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, Temp Sensor, WDT
Number Of I /o
32
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
1.25K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.8 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-TQFP, 64-VQFP
Processor Series
C8051F0x
Core
8051
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
1.25 KB
Interface Type
I2C, SMBus, SPI, UART
Maximum Clock Frequency
25 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
32
Number Of Timers
4 bit
Operating Supply Voltage
2.8 V to 3.6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
PK51, CA51, A51, ULINK2
Development Tools By Supplier
C8051F005DK
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 8 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F018-GQR
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
15.2.
Only a SPI master device can initiate a data transfer. The SPI is placed in master mode by setting the Master Enable
flag (MSTEN, SPI0CN.1). Writing a byte of data to the SPI data register (SPI0DAT) when in Master Mode starts a
data transfer. The SPI master immediately shifts out the data serially on the MOSI line while providing the serial
clock on SCK. The SPIF (SPI0CN.7) flag is set to logic 1 at the end of the transfer. If interrupts are enabled, an
interrupt request is generated when the SPIF flag is set. The SPI master can be configured to shift in/out from one
to eight bits in a transfer operation in order to accommodate slave devices with different word lengths. The SPIFRS
bits in the SPI Configuration Register (SPI0CFG.[2:0]) are used to select the number of bits to shift in/out in a
transfer operation.
While the SPI master transfers data to a slave on the MOSI line, the addressed SPI slave device simultaneously
transfers the contents of its shift register to the SPI master on the MISO line in a full-duplex operation. The data
byte received from the slave replaces the data in the master’s data register. Therefore, the SPIF flag serves as both a
transmit-complete and receive-data-ready flag. The data transfer in both directions is synchronized with the serial
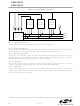
clock generated by the master. Figure 15.3 illustrates the full-duplex operation of an SPI master and an addressed
slave.
The SPI data register is double buffered on reads, but not on a write. If a write to SPI0DAT is attempted during a
data transfer, the WCOL flag (SPI0CN.6) will be set to logic 1 and the write is ignored. The current data transfer
will continue uninterrupted. A read of the SPI data register by the system controller actually reads the receive
buffer. If the receive buffer still holds unread data from a previous transfer when the last bit of the current transfer
is shifted into the SPI shift register, a receive overrun occurs and the RXOVRN flag (SPI0CN.4) is set to logic 1.
The new data is not transferred to the receive buffer, allowing the previously received data byte to be read. The data
byte causing the overrun is lost.
When the SPI is enabled and not configured as a master, it will operate as an SPI slave. Another SPI device acting
as a master will initiate a transfer by driving the NSS signal low. The master then shifts data out of the shift register
on the MOSI pin using the its serial clock. The SPIF flag is set to logic 1 at the end of a data transfer (when the
NSS signal goes high). The slave can load its shift register for the next data transfer by writing to the SPI data
register. The slave must make the write to the data register at least one SPI serial clock cycle before the master
starts the next transmission. Otherwise, the byte of data already in the slave’s shift register will be transferred.
Multiple masters may reside on the same bus. A Mode Fault flag (MODF, SPI0CN.5) is set to logic 1 when the SPI
is configured as a master (MSTEN = 1) and its slave select signal NSS is pulled low. When the Mode Fault flag is
set, the MSTEN and SPIEN bits of the SPI control register are cleared by hardware, thereby placing the SPI module
Operation
7
SPI SHIFT REGISTER
Receive Buffer
6
Baud Rate
Generator
5
MASTER DEVICE
4
3
2
1
Figure 15.3. Full Duplex Operation
0
MOSI
MISO
NSS
SCK
Px.y
Rev. 1.2
VDD
MOSI
MISO
NSS
SCK
SLAVE DEVICE
7
SPI SHIFT REGISTER
Receive Buffer
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
C8051F018
C8051F019
108