PIC16F724-E/MV Microchip Technology, PIC16F724-E/MV Datasheet - Page 80

PIC16F724-E/MV
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC16F724-E/MV
Description
7KB Flash Program, 1.8V-5.5V, 16MHz Internal Oscillator, 8b ADC, CCP, I2C/SPI, A
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® XLP™ 16Fr
Datasheet
1.AC164112.pdf
(302 pages)
Specifications of PIC16F724-E/MV
Processor Series
PIC16F
Core
PIC
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
7 KB
Data Ram Size
192 B
Interface Type
I2C, SPI, AUSART
Number Of Timers
3
Operating Supply Voltage
1.8 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
UQFN-40
Development Tools By Supplier
MPLAB IDE Software
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Core Processor
PIC
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
20MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
36
Eeprom Size
-
Ram Size
192 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.8 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 14x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
- Current page: 80 of 302
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
PIC16F72X/PIC16LF72X
6.5
PORTD
corresponding
(Register 6-13). Setting a TRISD bit (= 1) will make the
corresponding PORTD pin an input (i.e., put the
corresponding output driver in a High-Impedance mode).
Clearing a TRISD bit (= 0) will make the corresponding
PORTD pin an output (i.e., enable the output driver and
put the contents of the output latch on the selected pin).
Example 6-4 shows how to initialize PORTD.
Reading the PORTD register (Register 6-12) reads the
status of the pins, whereas writing to it will write to the
PORT latch. All write operations are read-modify-write
operations. Therefore, a write to a port implies that the
port pins are read, this value is modified and then written
to the PORT data latch.
The TRISD register (Register 6-13) controls the
PORTD pin output drivers, even when they are being
used as analog inputs. The user should ensure the bits
in the TRISD register are maintained set when using
them as analog inputs. I/O pins configured as analog
input always read ‘0’.
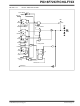
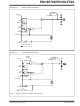
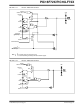
REGISTER 6-12:
DS41341E-page 80
bit 7
Legend:
R = Readable bit
-n = Value at POR
bit 7-0
Note 1:
Note 1: PORTD is available on PIC16F724/LF724
R/W-x
RD7
(1)
PORTD and TRISD Registers
is a 8-bit wide, bidirectional port. The
PORTD is not implemented on PIC16F722/723/726/PIC16LF722/723/726 devices, read as ‘0’.
and PIC16F727/LF727 only.
data
RD<7:0>: PORTD General Purpose I/O Pin bits
1 = Port pin is > V
0 = Port pin is < V
R/W-x
RD6
PORTD: PORTD REGISTER
direction
W = Writable bit
‘1’ = Bit is set
register
R/W-x
IH
IL
RD5
is
TRISD
R/W-x
RD4
(1)
U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
‘0’ = Bit is cleared
R/W-x
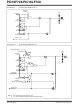
EXAMPLE 6-4:
6.5.1
The ANSELD register (Register 6-9) is used to
configure the Input mode of an I/O pin to analog.
Setting the appropriate ANSELD bit high will cause all
digital reads on the pin to be read as ‘0’ and allow
analog functions on the pin to operate correctly.
The state of the ANSELD bits has no affect on digital
output functions. A pin with TRIS clear and ANSEL set
will still operate as a digital output, but the Input mode
will be analog. This can cause unexpected behavior
when executing read-modify-write instructions on the
affected port.
RD3
BANKSEL PORTD
CLRF
BANKSEL ANSELD
CLRF
BANKSEL TRISD
MOVLW
MOVWF
Note:
PORTD
ANSELD
B‘00001100’
TRISD
ANSELD REGISTER
The ANSELD register must be initialized
to configure an analog channel as a digital
input. Pins configured as analog inputs will
read ‘0’.
R/W-x
RD2
INITIALIZING PORTD
© 2009 Microchip Technology Inc.
;
;Init PORTD
;Make PORTD digital
;
;Set RD<3:2> as inputs
;and set RD<7:4,1:0>
;as outputs
x = Bit is unknown
R/W-x
RD1
R/W-x
RD0
bit 0
Related parts for PIC16F724-E/MV
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 4KX14 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 4KX14 44TQFP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 4KX14 40-DIP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
7KB Flash Program, 1.8V-5.5V, 16MHz Internal Oscillator, 8b ADC, CCP, I2C/SPI, A
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
7KB Flash Program, 1.8V-5.5V, 16MHz Internal Oscillator, 8b ADC, CCP, I2C/SPI, A
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
7KB Flash Program, 1.8V-5.5V, 16MHz Internal Oscillator, 8b ADC, CCP, I2C/SPI, A
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
7KB Flash Program, 1.8V-5.5V, 16MHz Internal Oscillator, 8b ADC, CCP, I2C/SPI, A
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28-QFN
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28-SOIC
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28DIP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28-SOIC
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28QFN
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28SSOP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 8-SSOP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28-SSOP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet: