SAM9G45 Atmel Corporation, SAM9G45 Datasheet - Page 167

SAM9G45
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM9G45
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Datasheets
1.SAM9261.pdf
(248 pages)
2.SAM9261.pdf
(1274 pages)
3.SAM9261.pdf
(43 pages)
4.SAM9G45.pdf
(10 pages)
5.SAM9G45.pdf
(55 pages)
6.SAM9G45.pdf
(1196 pages)
Specifications of SAM9G45
Flash (kbytes)
0 Kbytes
Pin Count
324
Max. Operating Frequency
400 MHz
Cpu
ARM926
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
160
Ext Interrupts
160
Usb Transceiver
3
Usb Speed
Hi-Speed
Usb Interface
Host, Device
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
2
Uart
5
Lin
4
Ssc
2
Ethernet
1
Sd / Emmc
2
Graphic Lcd
Yes
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
Yes
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
440
Resistive Touch Screen
Yes
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
64
Self Program Memory
NO
External Bus Interface
2
Dram Memory
DDR2/LPDDR, SDRAM/LPSDR
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
0.9 to 1.1
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
No/Yes
Timers
6
Output Compare Channels
6
Input Capture Channels
6
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
No
- SAM9261 PDF datasheet
- SAM9261 PDF datasheet #2
- SAM9261 PDF datasheet #3
- SAM9G45 PDF datasheet #4
- SAM9G45 PDF datasheet #5
- SAM9G45 PDF datasheet #6
- Current page: 167 of 1196
- Download datasheet (20Mb)
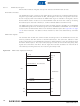
Table 20-7.
6438G–ATARM–19-Apr-11
Mode
Attribute Memory
Common Memory
I/O Mode
Alternate True IDE Mode
Standby Mode or
Address Space is not
assigned to CF
Alternate Status Read
CFCE1 and CFCE2 Signals
Read/Write Signals
Control Register
Drive Address
Data Register
Task File
CFCE1 and CFCE2 Truth Table
To cover all types of access, the SMC must be alternatively set to drive 8-bit data bus or 16-bit
data bus. The odd byte access on the D[7:0] bus is only possible when the SMC is configured to
drive 8-bit memory devices on the corresponding NCS pin (NCS4 or NCS5). The Chip Select
Register (DBW field in the corresponding Chip Select Register) of the NCS4 and/or NCS5
address space must be set as shown in
NBS1 and NBS0 are the byte selection signals from SMC and are available when the SMC is set
in Byte Select mode on the corresponding Chip Select.
The CFCE1 and CFCE2 waveforms are identical to the corresponding NCSx waveform. For
details on these waveforms and timings, refer to the Static Memory Controller section.
In I/O mode and True IDE mode, the CompactFlash logic drives the read and write command
signals of the SMC on CFIOR and CFIOW signals, while the CFOE and CFWE signals are deac-
tivated. Likewise, in common memory mode and attribute memory mode, the SMC signals are
driven on the CFOE and CFWE signals, while the CFIOR and CFIOW are deactivated.
20-6 on page 168
Attribute memory mode, common memory mode and I/O mode are supported by setting the
address setup and hold time on the NCS4 (and/or NCS5) chip select to the appropriate values.
For details on these signal waveforms, please refer to the section: Setup and Hold Cycles of the
Static Memory Controller section.
CFCE2
NBS1
NBS1
NBS1
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
CFCE1
demonstrates a schematic representation of this logic.
NBS0
NBS0
NBS0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
True IDE Mode
16 bits
16 bits
16 bits
16bits
DBW
8 bits
8 bits
8 bits
8 bits
Don’t
Care
–
Table 20-7
Comment
Access to Even Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Even Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Odd Byte on D[15:8]
Access to Odd Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Even Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Odd Byte on D[15:8]
Access to Odd Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Even Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Odd Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Even Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Odd Byte on D[15:8]
Access to Even Byte on D[7:0]
Access to Odd Byte on D[7:0]
to enable the required access type.
–
SMC Access Mode
Byte Select
Byte Select
Byte Select
Byte Select
Don’t Care
SAM9G45
–
Figure
167
Related parts for SAM9G45
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: