DSPIC30F6011-30I/PF Microchip Technology, DSPIC30F6011-30I/PF Datasheet - Page 42

DSPIC30F6011-30I/PF
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC30F6011-30I/PF
Description
IC DSPIC MCU/DSP 132K 64TQFP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
dsPIC™ 30Fr
Datasheets
1.DSPIC30F6014-20IPF.pdf
(228 pages)
2.DSPIC30F6014-20IPF.pdf
(22 pages)
3.DSPIC30F6014-20IPF.pdf
(28 pages)
Specifications of DSPIC30F6011-30I/PF
Core Processor
dsPIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
30 MIPs
Connectivity
CAN, I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, LVD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
52
Program Memory Size
132KB (44K x 24)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
2K x 8
Ram Size
6K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 16x12b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-TQFP, 64-VQFP
Core Frequency
40MHz
Core Supply Voltage
5.5V
Embedded Interface Type
CAN, I2C, SPI, UART
No. Of I/o's
52
Flash Memory Size
132KB
Supply Voltage Range
2.5V To 5.5V
Package
64TQFP
Device Core
dsPIC
Family Name
dsPIC30
Maximum Speed
30 MHz
Operating Supply Voltage
3.3|5 V
Data Bus Width
16 Bit
Number Of Programmable I/os
52
Interface Type
3-Wire/CAN/I2C/SPI/UART
On-chip Adc
16-chx12-bit
Number Of Timers
5
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
XLT64PT4 - SOCKET TRAN ICE 64MQFP/TQFPAC164313 - MODULE SKT FOR PM3 64PFAC30F002 - MODULE SOCKET DSPIC30F 64TQFPDV164005 - KIT ICD2 SIMPLE SUIT W/USB CABLE
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant, Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
DSPIC30F601130IPF
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F6011-30I/PF
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
dsPIC30F6011/6012/6013/6014
4.1.3
Move instructions and the DSP accumulator class of
instructions provide a greater degree of addressing
flexibility than other instructions. In addition to the
addressing modes supported by most MCU instruc-
tions, move and accumulator instructions also support
Register Indirect with Register Offset Addressing
mode, also referred to as Register Indexed mode.
In summary, the following addressing modes are
supported by move and accumulator instructions:
• Register Direct
• Register Indirect
• Register Indirect Post-modified
• Register Indirect Pre-modified
• Register Indirect with Register Offset (Indexed)
• Register Indirect with Literal Offset
• 8-bit Literal
• 16-bit Literal
4.1.4
The dual source operand DSP instructions (CLR, ED,
EDAC, MAC, MPY, MPY.N, MOVSAC and MSC), also
referred to as MAC instructions, utilize a simplified set of
addressing modes to allow the user to effectively
manipulate the data pointers through register indirect
tables.
The 2 source operand prefetch registers must be a
member of the set {W8, W9, W10, W11}. For data
reads, W8 and W9 will always be directed to the X
RAGU and W10 and W11 will always be directed to the
Y AGU. The effective addresses generated (before and
after modification) must, therefore, be valid addresses
within X data space for W8 and W9 and Y data space
for W10 and W11.
DS70117F-page 40
Note:
Note:
Note:
MOVE AND ACCUMULATOR
INSTRUCTIONS
For the MOV instructions, the addressing
mode specified in the instruction can differ
for the source and destination EA.
However, the 4-bit Wb (register offset)
field is shared between both source and
destination (but typically only used by
one).
Not all instructions support all the address-
ing modes given above. Individual instruc-
tions may support different subsets of
these addressing modes.
MAC INSTRUCTIONS
Register indirect with register offset
addressing is only available for W9 (in X
space) and W11 (in Y space).
In summary, the following addressing modes are
supported by the MAC class of instructions:
• Register Indirect
• Register Indirect Post-modified by 2
• Register Indirect Post-modified by 4
• Register Indirect Post-modified by 6
• Register Indirect with Register Offset (Indexed)
4.1.5
Besides the various addressing modes outlined above,
some instructions use literal constants of various sizes.
For example, BRA (branch) instructions use 16-bit
signed literals to specify the branch destination directly,
whereas the DISI instruction uses a 14-bit unsigned
literal field. In some instructions, such as ADD Acc, the
source of an operand or result is implied by the opcode
itself. Certain operations, such as NOP, do not have any
operands.
4.2
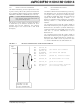
Modulo Addressing is a method of providing an auto-
mated means to support circular data buffers using
hardware. The objective is to remove the need for soft-
ware to perform data address boundary checks when
executing tightly looped code, as is typical in many
DSP algorithms.
Modulo Addressing can operate in either data or pro-
gram space (since the data pointer mechanism is
essentially the same for both). One circular buffer can
be supported in each of the X (which also provides the
pointers into program space) and Y data spaces. Mod-
ulo Addressing can operate on any W register pointer.
However, it is not advisable to use W14 or W15 for Mod-
ulo Addressing since these two registers are used as
the Stack Frame Pointer and Stack Pointer,
respectively.
In general, any particular circular buffer can only be
configured to operate in one direction, as there are cer-
tain restrictions on the buffer start address (for incre-
menting buffers), or end address (for decrementing
buffers) based upon the direction of the buffer.
The only exception to the usage restrictions is for buff-
ers which have a power-of-2 length. As these buffers
satisfy the start and end address criteria, they may
operate in a Bidirectional mode (i.e., address boundary
checks will be performed on both the lower and upper
address boundaries).
Modulo Addressing
OTHER INSTRUCTIONS
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.