T89C51RD2-3CBC-L ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation], T89C51RD2-3CBC-L Datasheet - Page 13

T89C51RD2-3CBC-L
Manufacturer Part Number
T89C51RD2-3CBC-L
Description
0 to 40MHz Flash Programmable 8-bit Microcontroller
Manufacturer
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet
1.T89C51RD2-3CBC-L.pdf
(86 pages)
- Current page: 13 of 86
- Download datasheet (934Kb)
6.2. Dual Data Pointer Register Ddptr
The additional data pointer can be used to speed up code execution and reduce code size.
The dual DPTR structure is a way by which the chip will specify the address of an external data memory location.
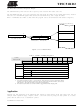
There are two 16-bit DPTR registers that address the external memory, and a single bit called
DPS = AUXR1/bit0 (See Table 3.) that allows the program code to switch between them (Refer to Figure 3).
Application
Software can take advantage of the additional data pointers to both increase speed and reduce code size, for
example, block operations (copy, compare, search ...) are well served by using one data pointer as a ’source’
pointer and the other one as a "destination" pointer.
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE
Rev. F - 15 February, 2001
7
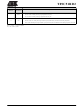
AUXR1(A2H)
Address 0A2H
AUXR1
a.
b. Bit 2 stuck at 0; this allows to use INC AUXR1 to toggle DPS without changing GF3.
Symbol
User software should not write 1s to reserved bits. These bits may be used in future 8051 family
products to invoke new feature. In that case, the reset value of the new bit will be 0, and its active
value will be 1. The value read from a reserved bit is indeterminate.
DPS
GF3
-
DPS
0
Function
Not implemented, reserved for future use.
Data Pointer Selection.
This bit is a general purpose user flag
Reset value
DPS
0
1
Table 3. AUXR1: Auxiliary Register 1
Operating Mode
DPTR0 Selected
DPTR1 Selected
DPH(83H) DPL(82H)
Figure 3. Use of Dual Pointer
X
-
DPTR1
X
-
DPTR0
b
.
X
a
-
X
-
GF3
0
T89C51RD2
External Data Memory
0
0
X
-
DPS
0
13
Related parts for T89C51RD2-3CBC-L
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
0 to 40 MHz Flash Programmable 8-bit Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
0 To 40 Mhz Flash Programmable 8-bit Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
0 to 40MHz Flash Programmable 8-bit Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Atmel CryptoMemory
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Atmel CryptoMemory
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Atmel CryptoMemory, 16Kbit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: