PIC32MX575F512LT-80I/BG Microchip Technology, PIC32MX575F512LT-80I/BG Datasheet - Page 160

PIC32MX575F512LT-80I/BG
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC32MX575F512LT-80I/BG
Description
512KB Flash, 64KB RAM, 80 MHz, USB, 1xCAN, 8 DMA 121 XBGA 10x10x1.20mm T/R
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® 32MXr
Datasheet
1.PIC32MX575F256H-80IMR.pdf
(254 pages)
Specifications of PIC32MX575F512LT-80I/BG
Core Processor
MIPS32® M4K™
Core Size
32-Bit
Speed
80MHz
Connectivity
CAN, I²C, SPI, UART/USART, USB OTG
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, POR, PWM, WDT
Program Memory Size
512KB (512K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
64K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.3 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 16x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
121-TFBGA
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Number Of I /o
-
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC32MX575F512LT-80I/BG
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 160 of 254
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
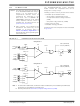
PIC32MX5XX/6XX/7XX
The processor will exit, or ‘wake-up’, from Sleep on one
of the following events:
• On any interrupt from an enabled source that is
• On any form of device Reset.
• On a WDT time-out.
If the interrupt priority is lower than or equal to the
current priority, the CPU will remain Halted, but the
PBCLK will start running and the device will enter into
Idle mode.
27.3.2
In Idle mode, the CPU is Halted but the System Clock
(SYSCLK) source is still enabled. This allows peripher-
als to continue operation when the CPU is Halted.
Peripherals can be individually configured to Halt when
entering Idle by setting their respective SIDL bit.
Latency, when exiting Idle mode, is very low due to the
CPU oscillator source remaining active.
The device enters Idle mode when the SLPEN bit
(OSCCON<4>) is clear and a WAIT instruction is
executed.
DS61156F-page 160
operating in Sleep. The interrupt priority must be
greater than the current CPU priority.
Note 1: Changing
2: Oscillator start-up and PLL lock delays
IDLE MODE
requires recalculation of peripheral tim-
ing. For example, assume the UART is
configured for 9600 baud with a PB clock
ratio of 1:1 and a P
the PB clock divisor of 1:2 is used, the
input frequency to the baud clock is cut in
half; therefore, the baud rate is reduced
to 1/2 its former value. Due to numeric
truncation in calculations (such as the
baud rate divisor), the actual baud rate
may be a tiny percentage different than
expected. For this reason, any timing cal-
culation required for a peripheral should
be performed with the new PB clock fre-
quency instead of scaling the previous
value based on a change in the PB divisor
ratio.
are applied when switching to a clock
source that was disabled and that uses a
crystal and/or the PLL. For example,
assume the clock source is switched from
P
in order to save power. No oscillator start-
up delay would be applied when exiting
Idle. However, when switching back to
P
oscillator start-up/lock delays would be
applied.
OSC
OSC
,
to LPRC just prior to entering Sleep
the
the
appropriate
PBCLK
OSC
of 8 MHz. When
divider
PLL
and/or
ratio
The processor will wake or exit from Idle mode on the
following events:
• On any interrupt event for which the interrupt
• On any form of device Reset
• On a WDT time-out interrupt
27.3.3
Most of the peripherals on the device are clocked using
the PBCLK. The peripheral bus can be scaled relative to
the SYSCLK to minimize the dynamic power consumed
by the peripherals. The PBCLK divisor is controlled by
PBDIV<1:0> (OSCCON<20:19>), allowing SYSCLK to
PBCLK ratios of 1:1, 1:2, 1:4 and 1:8. All peripherals
using PBCLK are affected when the divisor is changed.
Peripherals such as USB, interrupt controller, DMA, bus
matrix and prefetch cache are clocked directly from
SYSCLK. As a result, they are not affected by PBCLK
divisor changes.
Changing the PBCLK divisor affects:
• The CPU to peripheral access latency. The CPU
• The power consumption of the peripherals. Power
To minimize dynamic power, the PB divisor should be
chosen to run the peripherals at the lowest frequency
that provides acceptable system performance. When
selecting a PBCLK divider, peripheral clock require-
ments, such as baud rate accuracy, should be taken
into account. For example, the UART peripheral may
not be able to achieve all baud rate values at some
PBCLK divider depending on the SYSCLK value.
source is enabled. The priority of the interrupt
event must be greater than the current priority of
the CPU. If the priority of the interrupt event is
lower than or equal to current priority of the CPU,
the CPU will remain Halted and the device will
remain in Idle mode.
has to wait for next PBCLK edge for a read to
complete. In 1:8 mode, this results in a latency of
one to seven SYSCLKs.
consumption is directly proportional to the fre-
quency at which the peripherals are clocked. The
greater the divisor, the lower the power consumed
by the peripherals.
PERIPHERAL BUS SCALING
METHOD
© 2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Related parts for PIC32MX575F512LT-80I/BG
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: