MC908QY4ACDWE Freescale Semiconductor, MC908QY4ACDWE Datasheet - Page 139

MC908QY4ACDWE
Manufacturer Part Number
MC908QY4ACDWE
Description
IC MCU 8BIT 4K FLASH 16-SOIC
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC08r
Datasheet
1.MC908QT1ACDWE.pdf
(200 pages)
Specifications of MC908QY4ACDWE
Core Processor
HC08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM
Number Of I /o
13
Program Memory Size
4KB (4K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
128 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 6x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
16-SOIC (0.300", 7.5mm Width)
Processor Series
HC08QY
Core
HC08
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
128 B
Maximum Clock Frequency
8 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
13
Number Of Timers
2
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Development Tools By Supplier
FSICEBASE, M68CBL05AE, DEMO908QB8, DEMO908QC16
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 6 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Connectivity
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MC908QY4ACDWE
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MC908QY4ACDWER
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Chapter 15
Development Support
15.1 Introduction
This section describes the break module, the monitor module (MON), and the monitor mode entry
methods.
15.2 Break Module (BRK)
The break module can generate a break interrupt that stops normal program flow at a defined address to
enter a background program.
Features include:
15.2.1 Functional Description
When the internal address bus matches the value written in the break address registers, the break module
issues a breakpoint signal (BKPT) to the system integration module (SIM). The SIM then causes the CPU
to load the instruction register with a software interrupt instruction (SWI). The program counter vectors to
$FFFC and $FFFD ($FEFC and $FEFD in monitor mode).
The following events can cause a break interrupt to occur:
When a CPU generated address matches the contents of the break address registers, the break interrupt
is generated. A return-from-interrupt instruction (RTI) in the break routine ends the break interrupt and
returns the microcontroller unit (MCU) to normal operation.
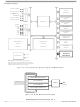
Figure 15-2
When the internal address bus matches the value written in the break address registers or when software
writes a 1 to the BRKA bit in the break status and control register, the CPU starts a break interrupt by:
Freescale Semiconductor
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Accessible input/output (I/O) registers during the break Interrupt
Central processor unit (CPU) generated break interrupts
Software-generated break interrupts
Computer operating properly (COP) disabling during break interrupts
A CPU generated address (the address in the program counter) matches the contents of the break
address registers.
Software writes a 1 to the BRKA bit in the break status and control register.
Loading the instruction register with the SWI instruction
Loading the program counter with $FFFC and $FFFD ($FEFC and $FEFD in monitor mode)
shows the structure of the break module.
MC68HC908QYA/QTA Family Data Sheet, Rev. 3
139