MC68HC711E20CFS2 MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc], MC68HC711E20CFS2 Datasheet - Page 101

MC68HC711E20CFS2
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC711E20CFS2
Description
Microcontrollers
Manufacturer
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet
1.MC68HC711E20CFS2.pdf
(268 pages)
- Current page: 101 of 268
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
5.5.3 Illegal Opcode Trap
5.5.4 Software Interrupt (SWI)
5.5.5 Maskable Interrupts
5.5.6 Reset and Interrupt Processing
M68HC11E Family — Rev. 5
MOTOROLA
stacking the CCR. A return-from-interrupt instruction restores the X and I bits to
their pre-interrupt request state.
Because not all possible opcodes or opcode sequences are defined, the MCU
includes an illegal opcode detection circuit, which generates an interrupt request.
When an illegal opcode is detected and the interrupt is recognized, the current
value of the program counter is stacked. After interrupt service is complete,
reinitialize the stack pointer so repeated execution of illegal opcodes does not
cause stack underflow. Left uninitialized, the illegal opcode vector can point to a
memory location that contains an illegal opcode. This condition causes an infinite
loop that causes stack underflow. The stack grows until the system crashes.
The illegal opcode trap mechanism works for all unimplemented opcodes on all
four opcode map pages. The address stacked as the return address for the illegal
opcode interrupt is the address of the first byte of the illegal opcode. Otherwise, it
would be almost impossible to determine whether the illegal opcode had been one
or two bytes. The stacked return address can be used as a pointer to the illegal
opcode so the illegal opcode service routine can evaluate the offending opcode.
SWI is an instruction, and thus cannot be interrupted until complete. SWI is not
inhibited by the global mask bits in the CCR. Because execution of SWI sets the I
mask bit, once an SWI interrupt begins, other interrupts are inhibited until SWI is
complete, or until user software clears the I bit in the CCR.
The maskable interrupt structure of the MCU can be extended to include additional
external interrupt sources through the IRQ pin. The default configuration of this pin
is a low-level sensitive wired-OR network. When an event triggers an interrupt, a
software accessible interrupt flag is set. When enabled, this flag causes a constant
request for interrupt service. After the flag is cleared, the service request is
released.
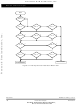
Figure 5-5
illustrates how the CPU begins from a reset and how interrupt detection relates to
normal opcode fetches.
illustrates interrupt priorities.
within the SCI subsystem.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
and
Figure 5-6
Go to: www.freescale.com
Resets and Interrupts
Figure 5-6
illustrate the reset and interrupt process.
Figure 5-7
is an expansion of a block in
shows the resolution of interrupt sources
Resets and Interrupts
Figure 5-5
Figure 5-5
Data Sheet
Interrupts
and
101
Related parts for MC68HC711E20CFS2
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
APPENDIX A ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE [Freescale Semiconductor, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola, Inc [VOLTAGE REGULATOR]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
6367254 MOTOROLA SC (XSTRS/R F)
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MC1494LMotorola, Inc [MONOLITHIC FOUR-QUADRANT MULTIPLIER]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MC1466LMotorola, Inc [PRECISION WIDE RANGE VOLTAGE AND CURRENT REGULATOR]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MC145532DWMotorola, Inc [ADPCM Transcoder]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon Controlled Rectifiers
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
RF Power Field Effect Transistors N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Lateral MOSFETs
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
RF POWER FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
LATERAL N-CHANNEL BROADBAND RF POWER MOSFETs
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
RF POWER FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
RF LOW POWER TRANSISTOR NPN SILICON
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PLASTIC SURFACE MOUNT ZENER DIODES 1.5 WATTS 3.3-68 VOLTS
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
OVERVOLTAGE TRANSIENT SUPPRESSOR
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TMOS POWER FET 15 AMPERES 60 VOLTS
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc]
Datasheet: