P87LPC768BD,512 NXP Semiconductors, P87LPC768BD,512 Datasheet - Page 12
P87LPC768BD,512
Manufacturer Part Number
P87LPC768BD,512
Description
IC 80C51 MCU 4K OTP 20-SOIC
Manufacturer
NXP Semiconductors
Series
LPC700r
Datasheet
1.P87LPC768BD512.pdf
(65 pages)
Specifications of P87LPC768BD,512
Core Processor
8051
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
20MHz
Connectivity
I²C, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, LED, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
18
Program Memory Size
4KB (4K x 8)
Program Memory Type
OTP
Ram Size
128 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 6 V
Data Converters
A/D 4x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Package / Case
20-SOIC (7.5mm Width)
Processor Series
P87LPC7x
Core
80C51
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
128 B
Interface Type
I2C, UART
Maximum Clock Frequency
10 MHz, 20 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
18
Number Of Timers
2
Operating Supply Voltage
2.7 V to 6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
PK51, CA51, A51, ULINK2
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
On-chip Adc
8 bit, 4 Channel
For Use With
OM10063 - PROGRAMMER LPC700 P76XLCPOM10050 - EMULATOR LPC700 PDS76X
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Other names
568-3218-5
935267360512
P87LPC768BD
935267360512
P87LPC768BD
Philips Semiconductors
A/D Timing
The A/D may be clocked in one of two ways. The default is to use
the CPU clock as the A/D clock source. When used in this manner,
the A/D completes a conversion in 31 machine cycles. The A/D may
be operated up to the maximum CPU clock rate of 20 MHz, giving a
conversion time of 9.3 s. The formula for calculating A/D
conversion time when the CPU clock runs the A/D is: 186 s / CPU
clock rate (in MHZ). To obtain accurate A/D conversion results, the
CPU clock must be at least 1 MHz.
The A/D may also be clocked by the on-chip RC oscillator, even if
the RC oscillator is not used as the CPU clock. This is accomplished
by setting the RCCLK bit in ADCON. This arrangement has several
advantages. First, the A/D conversion time is faster at lower CPU
clock rates. Also, the CPU may be run at speeds below 1 MHz
without affecting A/D accuracy. Finally, the Power Down mode may
be used to completely shut down the CPU and its oscillator, along
2002 Mar 12
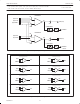
ADCON
Bit addressable
Reset Value: 00h
BIT
ADCON.7
ADCON.6
ADCON.5
ADCON.4
ADCON.3
ADCON.2
ADCON.1, 0
Low power, low price, low pin count (20 pin) microcontroller
with 4 kB OTP 8-bit A/D, Pulse Width Modulator
Address: C0h
AADR1, AADR0
ADCI, ADCS
SYMBOL
AADR1,0
ENADC
RCCLK
ADCS
ADCI
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
-
-
FUNCTION
When ENADC = 1, the A/D is enabled and conversions may take place. Must be set 10
microseconds before a conversion is started. ENADC cannot be cleared while ADCS or ADCI
are 1.
Reserved for future use. Should not be set to 1 by user programs.
Reserved for future use. Should not be set to 1 by user programs.
A/D conversion complete/interrupt flag. This flag is set when an A/D conversion is completed.
This bit will cause a hardware interrupt if enabled and of sufficient priority. Must be cleared by
software.
A/D start. Setting this bit by software starts the conversion of the selected A/D input. ADCS
remains set while the A/D conversion is in progress and is cleared automatically upon
completion. While ADCS or ADCI are one, new start commands are ignored.
A/D Status
A/D not busy, a conversion can be started.
A/D busy, the start of a new conversion is blocked.
An A/D conversion is complete. ADCI must be cleared prior to starting a new conversion.
An A/D conversion is complete. ADCI must be cleared prior to starting a new conversion. This
state exists for one machine cycle as an A/D conversion is completed.
When RCCLK = 0, the CPU clock is used as the A/D clock. When RCCLK = 1, the internal RC
oscillator is used as the A/D clock. This bit is writable while ADCS and ADCI are 0.
Along with AADR0, selects the A/D channel to be converted. These bits can only be written
while ADCS and ADCI are 0.
A/D Input Selected
AD0 (P0.3).
AD1 (P0.4).
AD2 (P0.5).
AD3 (P0.6).
ENADC
7
Figure 2. A/D Control Register (ADCON)
6
-
10
5
-
When the A/D is operated from the RCCLK while the CPU is running
synchronize A/D operation. The time can range from a minimum of 3
with other peripheral functions, in order to obtain the best possible
A/D accuracy. This should not be used if the MCU uses an external
clock source greater than 4 MHz.
from another clock source, 3 or 4 machine cycles are used to
machine cycles (at the CPU clock rate) + 108 RC clocks to a
maximum of 4 machine cycles (at the CPU clock rate) + 112 RC
clocks.
Example A/D conversion times at various CPU clock rates are
shown in Table 1. In Table 1, maximum times for RCCLK = 1 use an
RC clock frequency of 4.5 MHz (6 MHz - 25%). Minimum times for
RCCLK = 1 use an RC clock frequency of 7.5 MHz (6 MHz + 25%).
Nominal time assume an ideal RC clock frequency of 6 MHz and an
average of 3.5 machine cycles at the CPU clock rate.
ADCI
4
ADCS
3
RCCLK
2
AADR1
1
P87LPC768
AADR0
SU01354
Preliminary data
0