28F640W30 NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V], 28F640W30 Datasheet - Page 50

28F640W30
Manufacturer Part Number
28F640W30
Description
Numonyx Wireless Flash Memory (W30)
Manufacturer
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet
1.28F640W30.pdf
(102 pages)
- Current page: 50 of 102
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
9.1.4
9.1.5
9.2
Datasheet
50
Reset
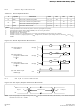
The flash device enters a reset mode when RST# is asserted. In reset mode, internal
circuitry is turned off and outputs are placed in a high-impedance state.
After returning from reset, a time t
(t
interval, normal operation is restored. The flash device defaults to read-array mode,
the status register is set to 80h, and the Read Configuration Register defaults to
asynchronous page-mode reads.
If RST# is asserted during an erase or program operation, the operation aborts and the
memory contents at the aborted block or address are invalid. See
Operations Waveforms” on page 46
As on any automated device, RST# must be asserted during system reset. When the
system comes out of reset, the processor expects to read from the flash memory array.
Automated flash memory devices provide status information when read during program
or erase operations. If a CPU reset occurs with no flash memory reset, the CPU might
not be properly initialized, because the flash memory device might be providing status
information instead of array data. 1.8 Volt Numonyx Flash memory devices allow
proper CPU initialization following a system reset through the use of the RST# input. In
this application, RST# is controlled by the same CPU reset signal, RESET#.
Write
A write occurs when CE# and WE# are asserted and OE# is deasserted. Flash memory
control commands are written to the CUI using standard microprocessor write timings.
Proper use of the ADV# input is needed for proper latching of the addresses. Refer to
Section 7.3, “AC Write Characteristics” on page 38
latched on the rising edge of WE#. Write operations are asynchronous; CLK is ignored
(but can be kept active/toggling).
The CUI does not occupy an addressable memory location within any partition. The
system processor must access it at the correct address range, depending on the kind of
command executed. Programming or erasing can occur in only one partition at a time.
Other partitions must be in one of the read modes or erase suspend mode.
Table 18, “Command Codes and Descriptions” on page 51
commands.
moving between different operating modes using CUI commands.
Flash Device Commands
The flash device on-chip WSM manages erase and program algorithms. This local CPU
(WSM) controls the flash device in-system read, program, and erase operations. Bus
cycles to or from the flash memory device conform to standard microprocessor bus
cycles. The RST#, CE#, OE#, WE#, and ADV# control signals dictate data flow into and
out of the flash device. WAIT informs the CPU of valid data during burst reads.
Table 17, “Bus Operations Summary” on page 48
To select flash device operations, write specific commands into the flash device CUI.
Table 18, “Command Codes and Descriptions” on page 51
codes and descriptions.
definitions. Because commands are partition-specific, you must issue write commands
within the target address range.
PHWV
) is required before a write sequence can be initiated. After this wake-up
Appendix A, “Write State Machine” on page 86
Table 19, “Bus Cycle Definitions” on page 52
PHQV
for detailed information regarding reset timings.
is required until outputs are valid, and a delay
summarizes bus operations.
for details. The address and data are
Numonyx™ Wireless Flash Memory (W30)
Numonyx™ Wireless Flash Memory (W30)
shows the available
lists all possible command
provides information about
Order Number: 290702-13
Figure 21, “Reset
lists command
November 2007
Related parts for 28F640W30
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Numonyx Wireless Flash Memory (W18)
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Numonyx StrataFlash Wireless Memory
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8 Mbit, low voltage, Page-Erasable Serial Flash memory with byte alterability and a 50 MHz SPI bus interface
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128 Mbit (8 Mb ×16, multiple bank, multilevel interface, burst) 1.8 V supply, secure Flash memories
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
64-Mbit, dual I/O, 4-Kbyte subsector erase, serial flash memory with 75 MHz SPI bus interface
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
512 Kbit, serial Flash memory, 50 MHz SPI bus interface
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
1 Mbit, serial Flash memory, 50 MHz SPI bus interface
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
16 Mbit, serial Flash memory, 75 MHz SPI bus interface
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Wireless Flash Memory (W18/W30 SCSP)
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
StrataFlash® Cellular Memory
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128 Mbit (16Mb x8 or 8Mb x16, Multiple Bank, Page, Boot Block) 3V supply Flash memory
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128 Mbit (8 Mb x 16, multiple bank, page, dual boot) 3 V supply Flash memory
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32 Mbit (4Mb x8 or 2Mb x16, Dual Bank 8:24, Boot Block) 3V Supply Flash Memory
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32 Mbit (4Mb x8 or 2Mb x16, Dual Bank 16:16, Boot Block) 3V Supply Flash Memory
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
64 Mbit (8Mb x8 or 4Mb x16, Multiple Bank, Page, Boot Block) 3V Supply Flash Memory
Manufacturer:
NUMONYX [Numonyx B.V]
Datasheet: