SC18IS602BIPW,112 NXP Semiconductors, SC18IS602BIPW,112 Datasheet - Page 14
SC18IS602BIPW,112
Manufacturer Part Number
SC18IS602BIPW,112
Description
IC BRIDGE SPI/I2C 16-TSSOP
Manufacturer
NXP Semiconductors
Specifications of SC18IS602BIPW,112
Controller Type
I²C Bus Controller
Interface
I²C
Voltage - Supply
2.4 V ~ 3.6 V
Current - Supply
11mA
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
16-TSSOP
Operating Temperature Classification
Military
Operating Temperature (max)
125C
Package Type
TSSOP
Rad Hardened
No
Maximum Operating Frequency
4.5 MHz
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 55 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Supply Voltage (max)
3.6 V
Supply Voltage (min)
2.4 V
For Use With
568-4705 - DEMO BOARD I2C TO SPI SC18IS602
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
568-4785-5
935286182112
SC18IS602BIPW
SC18IS602BIPW,112
SC18IS602BIPW
935286182112
SC18IS602BIPW
SC18IS602BIPW,112
SC18IS602BIPW
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
SC18IS602BIPW,112
Manufacturer:
NXP
Quantity:
463
NXP Semiconductors
8. I
SC18IS602_602B_603_4
Product data sheet
2
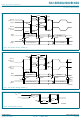
C-bus to SPI communications example
The following example describes a typical sequence of events required to read the
contents of an SPI-based EEPROM. This example assumes that the
SC18IS602/602B/603 is configured to respond to address 50h. A START condition is
shown as ‘ST’, while a STOP condition is ‘SP’. The data is presented in hexadecimal
format.
1. The first message is used to configure the SPI port for mode and frequency.
2. An SPI EEPROM first requires that a Write Enable command be sent before data can
3. Clear the interrupt. This is not required if using a polling method rather than interrupts.
4. Write the 8 data bytes. The first byte (Function ID) tells the SC18IS602/602B/603
5. When an interrupt occurs, do a Clear Interrupt or wait until the SC18IS602/602B/603
6. Read the 8 bytes from the EEPROM. Note that we are writing a command, even
7. The interrupt can be cleared, if needed.
8. Read back the data buffer. Note that we will actually need to read back 11 data bytes
be written.
which Slave Select output to use. This example uses SS2 (shown as 04h). The first
byte sent to the EEPROM is normally 02h for the EEPROM write command. The next
one or two bytes represent the subaddress in the EEPROM. In this example, a
two-byte subaddress is used. Bytes 00 and 30 would cause the EEPROM to write to
subaddress 0030h. The next eight bytes are the eight data bytes that will be written to
subaddresses 0030h through 0037h.
responds to its I
though we are going to perform a read from the SPI port. The Function ID is again
04h, indicating that we are going to use SS2. The EEPROM requires that you send a
03h for a read, followed by the subaddress you would like to read. We are going to
read back the same data previously written, so this means that the subaddress should
be 0030h. We would like to read back 8 bytes so we can send eight bytes of FFh to
tell the SC18IS602/602B/603 to send eight more bytes on MOSI. While it is sending
these eight data bytes, it is also reading the MISO pin and saving the data in the
buffer.
since the first three bytes sent on the SPI port were the read code (03h) and the two
subaddress bytes.
ST,50,F0,02,SP
ST,50,04,06,SP
06h
ST,50,F1,SP
ST,50,04,02,00,30,01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,SP
ST,50,F1,SP
ST,50,04,03,00,30,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,FF,SP
ST,50,F1,SP
ST,50,00,00,00,01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,SP
2
C-bus address.
Rev. 04 — 11 March 2008
SPI frequency 115 kHz using Mode 0
EEPROM write enable using SS2, assuming the Write Enable is
Clear interrupt
Clear interrupt
Clear interrupt
SC18IS602/602B/603
Write 8 bytes using SS2
Read 8 bytes using SS2
Read the data buffer
I
2
C-bus to SPI bridge
© NXP B.V. 2008. All rights reserved.
14 of 25