DSPIC30F3013-30I/SO Microchip Technology, DSPIC30F3013-30I/SO Datasheet - Page 45
DSPIC30F3013-30I/SO
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC30F3013-30I/SO
Description
IC DSPIC MCU/DSP 24K 28SOIC
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
dsPIC™ 30Fr
Datasheets
1.DSPIC30F2011-20ISO.pdf
(210 pages)
2.DSPIC30F2011-20ISO.pdf
(6 pages)
3.DSPIC30F3012-20ISO.pdf
(14 pages)
4.DSPIC30F3012-20ISO.pdf
(20 pages)
5.DSPIC30F3014-30IP.pdf
(244 pages)
Specifications of DSPIC30F3013-30I/SO
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
24KB (8K x 24)
Package / Case
28-SOIC (7.5mm Width)
Core Processor
dsPIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
30 MIPs
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
20
Eeprom Size
1K x 8
Ram Size
2K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 10x12b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Product
DSCs
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Processor Series
DSPIC30F
Core
dsPIC
Maximum Clock Frequency
30 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
30
Data Ram Size
2 KB
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
52713-733, 52714-737, 53276-922, EWDSPIC
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120, ICE4000, DM240002, DM300018, DM330011
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
XLT28SO-1 - SOCKET TRANSITION 28SOIC 300MILDV164005 - KIT ICD2 SIMPLE SUIT W/USB CABLE
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
DSPIC30F301330ISO
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F3013-30I/SO
Manufacturer:
NSC
Quantity:
340
Part Number:
DSPIC30F3013-30I/SO
Manufacturer:
PIC
Quantity:
20 000
4.0
The dsPIC core contains two independent address
generator units: the X AGU and Y AGU. Further, the X
AGU has two parts: X RAGU (Read AGU) and X
WAGU (Write AGU). The X RAGU and X WAGU sup-
port byte and respectively, for both MCU and DSP
instructions. The Y AGU supports word sized data
reads for the DSP MAC class of instructions only. They
are each capable of supporting two types of data
addressing:
• Linear Addressing
• Modulo (Circular) Addressing
In addition, the X WAGU can support:
• Bit-Reversed Addressing
Linear and Modulo Data Addressing modes can be
applied to data space or program space. Bit-Reversed
addressing is only applicable to data space addresses.
4.1
Although the data space memory is organized as 16-bit
words, all effective addresses (EAs) are byte
addresses. Instructions can thus access individual
bytes, as well as properly aligned words. Word
addresses must be aligned at even boundaries. Mis-
aligned word accesses are not supported, and if
attempted, will initiate an address error trap.
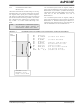
TABLE 4-1:
2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
File Register Direct
Register Direct
Register Indirect
Register Indirect Post-modified
Register Indirect Pre-modified
Register Indirect with Register Offset The sum of Wn and Wb forms the EA.
Register Indirect with Literal Offset
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this group
of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be a complete
reference source. For more information on the CPU,
peripherals, register descriptions and general device
functionality, refer to the dsPIC30F Family Reference
Manual (DS70046). For more information on the device
instruction set and programming, refer to the dsPIC30F
Programmer’s Reference Manual (DS70030).
ADDRESS GENERATOR UNITS
Data Space Organization
Addressing Mode
FUNDAMENTAL ADDRESSING MODES SUPPORTED
The address of the file register is specified explicitly.
The contents of a register are accessed directly.
The contents of Wn forms the EA.
The contents of Wn forms the EA. Wn is post-modified (incremented or
decremented) by a constant value.
Wn is pre-modified (incremented or decremented) by a signed constant value
to form the EA.
The sum of Wn and a literal forms the EA.
Preliminary
When executing instructions which require just one
source operand to be fetched from data space, the X
RAGU and X WAGU are used to calculate the effective
address. The X RAGU and X WAGU can generate any
address in the 64 Kbyte data space. They support all
MCU Addressing modes and Modulo Addressing for
low overhead circular buffers. The X WAGU also sup-
ports Bit-Reversed Addressing to facilitate FFT data
reorganization.
When executing instructions which require two source
operands to be concurrently fetched (i.e., the MAC class
of DSP instructions), both the X RAGU and Y AGU are
used simultaneously and the data space is split into 2
independent address spaces, X and Y. The Y AGU sup-
ports Register Indirect Post-Modified and Modulo
Addressing only. Note that the data write phase of the
MAC class of instruction does not split X and Y address
space. The write EA is calculated using the X WAGU
and the data space is configured for full 64 Kbyte
access.
In the Split Data Space mode, some W register address
pointers are dedicated to X RAGU, and others to Y
AGU. The EAs of each operand must, therefore, be
restricted within different address spaces. If they are
not, one of the EAs will be outside the address space
of the corresponding data space (and will fetch the bus
default value, 0x0000).
4.2
The Addressing modes in Table 4-1 form the basis of
the Addressing modes optimized to support the specific
features of individual instructions. The Addressing
modes provided in the MAC class of instructions are
somewhat different from those in the other instruction
types.
Some Addressing mode combinations may lead to a
one-cycle stall during instruction execution, or are not
allowed, as discussed in Section 4.3.
Description
Instruction Addressing Modes
dsPIC30F
DS70082G-page 43