CD2231 Intel Corporation, CD2231 Datasheet - Page 42

CD2231
Manufacturer Part Number
CD2231
Description
CD2231 Intelligent Two-channel Lan And Wan Communications Controller
Manufacturer
Intel Corporation
Datasheet
1.CD2231.pdf
(178 pages)
- Current page: 42 of 178
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
CD2231 — Intelligent Two-Channel LAN and WAN Communications Controller
5.3.4
5.3.5
5.3.6
5.4
42
Timers in Synchronous Protocols
In synchronous protocols, the timers have no special significance for the CD2231; they are
available to support the protocols. They are started by host commands or by interrupts generated by
the CD2231. General timers 1 and 2 can be started in either of two ways:
These timers can be disabled by a command through the CCR (Channel Command register).
Timers in Asynchronous Protocols
The receive timer is restarted from the value programmed in RTPR every time a character is
received and loaded into the FIFO, or data is read by the host. For example, the receive FIFO
threshold is set to eight, and six characters are stored in the receive FIFO. If no more characters are
received and the receiver timer times-out, a receive interrupt is asserted (in DMA mode, DMA
transfer occurs). The host is expected to retrieve all six characters from the receive FIFO.
Assuming the host is still enabling this feature (that is, RET bit (IER[5]) from the IER register bit 5
is still set), and if there is no character being received and receiver timer times-out, a receive
exception timeout interrupt (a group 3 interrupt) is asserted. The timer can be disabled if the value
in RTPR is set to ‘0’ or the RET bit is cleared.
Transmit Timer
The TTR (Transmit Timer register) is used only if the embedded transmit command is enabled in
the COR2. The delay transmit command specifies the delay period loaded in the TTR; no further
transmit operations are performed until this timer reaches zero. The current state of the line is held
at either ‘0’ for send break or ‘1’ for inter-character fill.
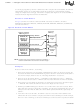
DMA Operation
The CD2231 uses a simple, but powerful, double-buffering method readily compatible with higher-
level buffer control procedures, such as circular queues, link lists, and buffer pools. Each
transmitter and each receiver is assigned an ‘A’ and a ‘B’ buffer. When transmitting, the host
processor alternately fills the A and B buffers, and commands the CD2231 to transmit the buffers
one at a time. When receiving, the CD2231 fills the A and B buffers and informs the host processor
when each is ready.
A simple Ownership Status bit is used for each buffer; this ensures that there are no deadlocks
between the host and the CD2231 regarding the use of a particular buffer.
By using the simple and flexible DMA management of the CD2231, the user host processor is
concerned with transmit/receive data on a block-by-block basis. The user need not be concerned
with character-by-character transfers, or even filling and emptying the FIFOs. The DMA controls
are user-selectable per-channel and operate independently of one another.
1. By loading a new value to GT1 or GT2 when the timer is not running.
2. By setting the SetTm1 or SetTm2 bits in the End of Interrupt register when terminating an
interrupt service routine. In this case, the value should be written to the appropriate Interrupt
Status register (RISR, TISR, or MISR).
Datasheet
Related parts for CD2231
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
CD-ROM, DVD Multimedia IC
Manufacturer:
China Hua Jing Electronics Group Co.

Part Number:
Description:
Cd-rom
Manufacturer:
ROHM Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD-ROM spindle motor driver
Manufacturer:
Rohm
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Digital Signal Processor
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Digital Servo Signal Processor
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Digital Signal Processor
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CD Servo Controller
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Electronic Shockproof Controller
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Servo Controller With Mcu With Interface Supporting Sc9831 Wma/mp3 Encoding/decoding
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Digital Servo Signal Processor Slave Mode
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Cd Digital Servo Signal Processor With Mcu 2/4 Digits Lcd Display And Remote Control
Manufacturer:
Silan
Datasheet: