MC68HC908GP32CB Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC908GP32CB Datasheet - Page 136
MC68HC908GP32CB
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC908GP32CB
Description
IC MCU 32K FLASH 8MHZ 42-SDIP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC08r
Datasheet
1.MC908GP32CFBE.pdf
(266 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC908GP32CB
Core Processor
HC08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Connectivity
SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM
Number Of I /o
33
Program Memory Size
32KB (32K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
512 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
42-DIP (0.600", 15.24mm)
For Use With
M68EVB908GP32 - BOARD EVALUATION FOR HC908GP32
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
- Current page: 136 of 266
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
Serial Communications Interface Module (SCI)
13.4.2.2 Character Transmission
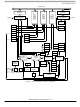
During an SCI transmission, the transmit shift register shifts a character out to the PTE0/TxD pin. The SCI
data register (SCDR) is the write-only buffer between the internal data bus and the transmit shift register.
To initiate an SCI transmission:
At the start of a transmission, transmitter control logic automatically loads the transmit shift register with
a preamble of logic 1s. After the preamble shifts out, control logic transfers the SCDR data into the
transmit shift register. A logic 0 start bit automatically goes into the least significant bit position of the
transmit shift register. A logic 1 stop bit goes into the most significant bit position.
The SCI transmitter empty bit, SCTE, in SCS1 becomes set when the SCDR transfers a byte to the
transmit shift register. The SCTE bit indicates that the SCDR can accept new data from the internal data
bus. If the SCI transmit interrupt enable bit, SCTIE, in SCC2 is also set, the SCTE bit generates a
transmitter CPU interrupt request.
When the transmit shift register is not transmitting a character, the PTE0/TxD pin goes to the idle
condition, logic 1. If at any time software clears the ENSCI bit in SCI control register 1 (SCC1), the
transmitter and receiver relinquish control of the port E pins.
13.4.2.3 Break Characters
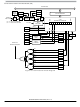
Writing a logic 1 to the send break bit, SBK, in SCC2 loads the transmit shift register with a break
character. A break character contains all logic 0s and has no start, stop, or parity bit. Break character
length depends on the M bit in SCC1. As long as SBK is at logic 1, transmitter logic continuously loads
break characters into the transmit shift register. After software clears the SBK bit, the shift register finishes
transmitting the last break character and then transmits at least one logic 1. The automatic logic 1 at the
end of a break character guarantees the recognition of the start bit of the next character.
The SCI recognizes a break character when a start bit is followed by eight or nine logic 0 data bits and a
logic 0 where the stop bit should be.
Receiving a break character has these effects on SCI registers:
13.4.2.4 Idle Characters
An idle character contains all logic 1s and has no start, stop, or parity bit. Idle character length depends
on the M bit in SCC1. The preamble is a synchronizing idle character that begins every transmission.
136
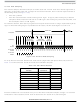
1. Enable the SCI by writing a logic 1 to the enable SCI bit (ENSCI) in SCI control register 1 (SCC1).
2. Enable the transmitter by writing a logic 1 to the transmitter enable bit (TE) in SCI control register
3. Clear the SCI transmitter empty bit by first reading SCI status register 1 (SCS1) and then writing
4. Repeat step 3 for each subsequent transmission.
•
•
•
•
•
•
2 (SCC2).
to the SCDR.
Sets the framing error bit (FE) in SCS1
Sets the SCI receiver full bit (SCRF) in SCS1
Clears the SCI data register (SCDR)
Clears the R8 bit in SCC3
Sets the break flag bit (BKF) in SCS2
May set the overrun (OR), noise flag (NF), parity error (PE), or reception in progress flag (RPF) bits
MC68HC908GP32 Data Sheet, Rev. 10
Freescale Semiconductor
Related parts for MC68HC908GP32CB
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: