DSPD56367PV150 Freescale Semiconductor, DSPD56367PV150 Datasheet - Page 15
DSPD56367PV150
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPD56367PV150
Description
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.DSPD56367PV150.pdf
(100 pages)
Specifications of DSPD56367PV150
Device Core Size
24b
Format
Fixed Point
Clock Freq (max)
150MHz
Mips
150
Device Input Clock Speed
150MHz
Ram Size
69KB
Program Memory Size
120KB
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
1.8/3.3V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
1.71/3.14V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
1.89/3.46V
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 95C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
144
Package Type
LQFP
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DSPD56367PV150
Manufacturer:
MOT
Quantity:
60
Company:
Part Number:
DSPD56367PV150K41R
Manufacturer:
DSP
Quantity:
59
2.11
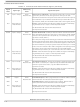
The SHI has five I/O signals that can be configured to allow the SHI to operate in either SPI or I
Freescale Semiconductor
Signal
Name
MISO
SCK
SCL
SDA
Serial Host Interface
Open-Drain
Input or
Input or
Input or
Input or
Signal
Output
Output
Output
Output
Type
State During
Tri-Stated
Tri-Stated
Reset
Table 2-10 Serial Host Interface Signals
SPI Serial Clock—The SCK signal is an output when the SPI is configured as a
master and a Schmitt-trigger input when the SPI is configured as a slave. When the
SPI is configured as a master, the SCK signal is derived from the internal SHI clock
generator. When the SPI is configured as a slave, the SCK signal is an input, and
the clock signal from the external master synchronizes the data transfer. The SCK
signal is ignored by the SPI if it is defined as a slave and the slave select (SS) signal
is not asserted. In both the master and slave SPI devices, data is shifted on one
edge of the SCK signal and is sampled on the opposite edge where data is stable.
Edge polarity is determined by the SPI transfer protocol.
I
SCL is a Schmitt-trigger input when configured as a slave and an open-drain output
when configured as a master. SCL should be connected to V
resistor.
This signal is tri-stated during hardware, software, and individual reset. Thus, there
is no need for an external pull-up in this state.
This input is 3.3V tolerant.
SPI Master-In-Slave-Out—When the SPI is configured as a master, MISO is the
master data input line. The MISO signal is used in conjunction with the MOSI signal
for transmitting and receiving serial data. This signal is a Schmitt-trigger input when
configured for the SPI Master mode, an output when configured for the SPI Slave
mode, and tri-stated if configured for the SPI Slave mode when SS is deasserted.
An external pull-up resistor is not required for SPI operation.
I
receiving and an open-drain output when transmitting. SDA should be connected to
V
in SDA must be stable during the high period of SCL. The data in SDA is only
allowed to change when SCL is low. When the bus is free, SDA is high. The SDA
line is only allowed to change during the time SCL is high in the case of start and
stop events. A high-to-low transition of the SDA line while SCL is high is a unique
situation, and is defined as the start event. A low-to-high transition of SDA while
SCL is high is a unique situation defined as the stop event.
This signal is tri-stated during hardware, software, and individual reset. Thus, there
is no need for an external pull-up in this state.
This input is 3.3V tolerant.
2
2
CC
C Serial Clock—SCL carries the clock for I
C Data and Acknowledge—In I
DSP56367 Technical Data, Rev. 2.1
through a pull-up resistor. SDA carries the data for I
Signal Description
2
C mode, SDA is a Schmitt-trigger input when
2
C bus transactions in the I
2
C transactions. The data
CC
Serial Host Interface
through a pull-up
2
2
C mode.
C mode.
2-11