DSPIC30F2023 Microchip Technology Inc., DSPIC30F2023 Datasheet - Page 141

DSPIC30F2023
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC30F2023
Description
28/44-pin Dspic30f1010/202x Enhanced Flash Smps 16-bit Digital Signal Controller
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet
1.DSPIC30F2023.pdf
(286 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-20E/ML
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-20E/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
135
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-20E/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-20E/PT
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-30I/ML
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-30I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-30I/PT
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-30I/PTD32
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
135
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023-30I/PTD32
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023T-20E/PT
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC30F2023T-30I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
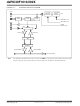
12.34.5 APPLICATION OF VARIABLE PHASE PWM
Variable phase PWM is used in newer power conver-
sion topologies that are designed to reduce switching
losses. In standard PWM methods, any time a transis-
tor switches between the conducting state and the
nonconducting state (and vice versa), the transistor is
exposed to the full current and voltage condition for
the period of time it takes the transistor to turn on or
off. The power loss (V * I * Tsw * FPWM) becomes
appreciable at high frequencies. The Zero Voltage
Switching (ZVS) and Zero Current Switching (ZVC) cir-
cuit topologies attempt to use quasi-resonant tech-
niques to shift either the voltage or current waveforms
relative to each other. This action either makes the
voltage or the current zero at the time the transistor
turns on or off. If either the current or the voltage is
zero, then there is no switching loss generated.
In variable phase PWM modes, the duty cycle is fixed
at 50%, and the power flow is controlled by varying the
phase relationship between the PWM channels, as
shown in Figure 12-26.
FIGURE 12-26:
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
PWM1H
PWM1H
PWM2L
+V
PWM1L
PWM2H
PWM1H
IN
MODE
Variable Phase Shift
PWM1H
PWM1H
APPLICATION OF
VARIABLE PHASE PWM
MODE
Full Bridge ZVT Converter
T1
V
+
OUT
Preliminary
12.34.6 APPLICATION OF CURRENT RESET PWM
In Current Reset PWM mode, the PWM frequency var-
ies with the load current. This mode is different than
most PWM modes because the user sets the maxi-
mum PWM period, but an external circuit measures
the inductor current. When the inductor current falls
below a specified value, the external current compara-
tor circuit generates a signal that resets the PWM time
base counter. The user specifies a PWM “on” time,
and then some time after the PWM signal becomes
inactive, the inductor current falls below a specified
value and the PWM counter is reset earlier than the
programmed PWM period. This mode is sometimes
called Constant On-Time.
This mode should not be confused with cycle-by-cycle
current-limiting PWM, where the PWM is asserted, an
external circuit generates a current Fault and the PWM
signal is turned off before its programmed duty cycle
would normally turn it off. In this mode, shown in
Figure 12-27, the PWM frequency is fixed per the time
base period.
FIGURE 12-27:
AC
dsPIC30F1010/202X
IN
PWM1H
PWM1H
External current comparator resets PWM counter
MODE
This is a variable frequency PWM mode
I
L
PWM cycle restarts early
Actual Period
+
Programmed Period
T
ON
C
APPLICATION OF
CURRENT RESET PWM
MODE
IN
PWM1H
L
I
L
T
OFF
DS70178C-page 139
D
+
V
C
OUT
OUT