ADUC7122 Analog Devices, ADUC7122 Datasheet - Page 41

ADUC7122
Manufacturer Part Number
ADUC7122
Description
Precision Analog Microcontroller, 12-Bit Analog I/O, ARM7TDMI® MCU
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.ADUC7122.pdf
(96 pages)
Specifications of ADUC7122
Mcu Core
ARM7 TDMI
Mcu Speed (mips)
40
Sram (bytes)
8192Bytes
Gpio Pins
32
Adc # Channels
13
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ADUC7122BBCZ
Manufacturer:
MICREL
Quantity:
231
Company:
Part Number:
ADUC7122BBCZ
Manufacturer:
Analog Devices Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADUC7122BBCZ-RL
Manufacturer:
Analog Devices Inc
Quantity:
10 000
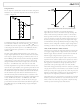
RESET AND REMAP
The ARM exception vectors are all situated at the bottom of the
memory array, from Address 0x00000000 to Address 0x00000020,
as shown in Figure 26.
By default and after any reset, the Flash/EE is mirrored at the
bottom of the memory array. The remap function allows the
programmer to mirror the SRAM at the bottom of the memory
array, facilitating execution of exception routines from SRAM
instead of from Flash/EE. This means exceptions are executed
twice as fast, with the exception being executed in ARM mode
(32 bits), and the SRAM being 32 bits wide instead of a 16-bit
wide Flash/EE memory.
Remap Operation
When a reset occurs on the ADuC7122, execution starts
automatically in factory-programmed internal configuration
Table 60. REMAP MMR Bit Designations (Address = 0xFFFF0220, Default Value = 0x00)
Bit
0
Table 61. RSTSTA MMR Bit Designations (Address = 0xFFFF0230, Default Value = 0x0X)
Bit
7:3
2
1
0
KERNEL
INTERRUPT
SERVICE ROUTINES
INTERRUPT
SERVICE ROUTINES
ARM EXCEPTION
VECTOR ADDRESSES
Name
Remap
Figure 26. Remap for Exception Execution
0x00000020
0x00000000 0x00000000
Description
Reserved.
Software reset.
Set by the user to force a software reset.
Cleared by setting the corresponding bit in RSTCLR.
Watchdog timeout.
Set automatically when a watchdog timeout occurs.
Cleared by setting the corresponding bit in RSTCLR.
Power-on reset.
Set automatically when a power-on reset occurs.
Cleared by setting the corresponding bit in RSTCLR.
Description
Remap bit.
Set by the user to remap the SRAM to Address 0x00000000.
Cleared automatically after reset to remap the Flash/EE memory to Address 0x00000000.
0x00080000
0x00040000
0xFFFFFFFF
0x00041FFF
0x0009F800
FLASH/EE
SRAM
MIRROR SPACE
Rev. 0 | Page 41 of 96
code. This kernel is hidden and cannot be accessed by user
code. If the ADuC7122 is in normal mode (the BM pin is high),
it executes the power-on configuration routine of the kernel
and then jumps to the reset vector Address 0x00000000 to
execute the reset exception routine of the user. Because the
Flash/EE is mirrored at the bottom of the memory array at
reset, the reset interrupt routine must always be written in
Flash/EE.
The memory remap from Flash/EE is configured by setting Bit 0 of
the REMAP register. Precautions must be taken to execute this
command from Flash/EE, above Address 0x00080020, and not
from the bottom of the array because this is replaced by the SRAM.
This operation is reversible: the Flash/EE can be remapped at
Address 0x00000000 by clearing Bit 0 of the REMAP MMR.
Precaution must again be taken to execute the remap function
from outside the mirrored area. Any kind of reset remaps the
Flash/EE memory at the bottom of the array.
Reset Operation
There are four types of reset: external reset, power-on reset,
watchdog expiration, and software force reset. The RSTSTA
register indicates the source of the last reset and RSTCLR clears
the RSTSTA register. These registers can be used during a reset
exception service routine to identify the source of the reset. If
RSTSTA is null, the reset was external. Note that when clearing
RSTSTA, all bits that are currently 1 must be cleared. Other-
wise, a reset event occurs.
The RSTCFG register allows different peripherals to retain their
state after a watchdog or software reset.
ADuC7122