PIC18F4520-I/P Microchip Technology Inc., PIC18F4520-I/P Datasheet - Page 126

PIC18F4520-I/P
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F4520-I/P
Description
40 Pin, 32 KB Flash, 1536 RAM, 36 I/O
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet
1.PIC18F4520-IP.pdf
(390 pages)
Specifications of PIC18F4520-I/P
A/d Inputs
13-Channel, 10-Bit
Comparators
2
Cpu Speed
10 MIPS
Eeprom Memory
256 Bytes
Input Output
36
Interface
I2C/SPI/USART
Memory Type
Flash
Number Of Bits
8
Package Type
40-pin PDIP
Programmable Memory
32K Bytes
Ram Size
1.5K Bytes
Speed
40 MHz
Timers
1-8-bit, 3-16-bit
Voltage, Range
2-5.5 V
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
RoHS Compliant part
Electrostatic Device
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F4520-I/P
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
104
Part Number:
PIC18F4520-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCH
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F4520-I/PT
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
14 300
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F4520-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
33 055
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F4520-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
PIC18F4520-I/PT
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 126 of 390
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
PIC18F2420/2520/4420/4520
11.1
Timer0 can operate as either a timer or a counter; the
mode is selected with the T0CS bit (T0CON<5>). In
Timer mode (T0CS = 0), the module increments on
every clock by default unless a different prescaler value
is selected (see Section 11.3 “Prescaler”). If the
TMR0 register is written to, the increment is inhibited
for the following two instruction cycles. The user can
work around this by writing an adjusted value to the
TMR0 register.
The Counter mode is selected by setting the T0CS bit
(= 1). In this mode, Timer0 increments either on every
rising or falling edge of pin RA4/T0CKI. The increment-
ing edge is determined by the Timer0 Source Edge
Select bit, T0SE (T0CON<4>); clearing this bit selects
the rising edge. Restrictions on the external clock input
are discussed below.
An external clock source can be used to drive Timer0;
however, it must meet certain requirements to ensure
that the external clock can be synchronized with the
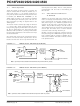
FIGURE 11-1:
FIGURE 11-2:
DS39631A-page 124
Note: Upon Reset, Timer0 is enabled in 8-bit mode with clock input from T0CKI max. prescale.
T0CKI pin
T0CKI pin
Note:
Timer0 Operation
T0SE
T0CS
T0PS2:T0PS0
PSA
Upon Reset, Timer0 is enabled in 8-bit mode with clock input from T0CKI max. prescale.
F
OSC
T0SE
T0CS
T0PS2:T0PS0
PSA
/4
F
OSC
TIMER0 BLOCK DIAGRAM (8-BIT MODE)
TIMER0 BLOCK DIAGRAM (16-BIT MODE)
/4
0
1
0
1
Programmable
Prescaler
Programmable
3
Prescaler
3
0
1
Preliminary
0
1
(2 T
Sync with
Internal
Clocks
CY
(2 T
Delay)
Sync with
Internal
Clocks
CY
internal phase clock (T
synchronization and the onset of incrementing the
timer/counter.
11.2
TMR0H is not the actual high byte of Timer0 in 16-bit
mode; it is actually a buffered version of the real high
byte of Timer0 which is not directly readable nor writ-
able (refer to Figure 11-2). TMR0H is updated with the
contents of the high byte of Timer0 during a read of
TMR0L. This provides the ability to read all 16 bits of
Timer0 without having to verify that the read of the high
and low byte were valid, due to a rollover between
successive reads of the high and low byte.
Similarly, a write to the high byte of Timer0 must also
take place through the TMR0H Buffer register. The high
byte is updated with the contents of TMR0H when a
write occurs to TMR0L. This allows all 16 bits of Timer0
to be updated at once.
Delay)
Timer0 Reads and Writes in
16-Bit Mode
TMR0L
8
8
TMR0L
8
8
OSC
2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
High Byte
TMR0H
TMR0
8
). There is a delay between
8
Set
TMR0IF
on Overflow
Internal Data Bus
8
Set
TMR0IF
on Overflow
Read TMR0L
Write TMR0L
Internal Data Bus
Related parts for PIC18F4520-I/P
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
40 PIN, 32 KB FLASH, 1536 RAM, 34 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
44 PIN, 32 KB FLASH, 1536 RAM, 34 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
44 PIN, 32 KB FLASH, 1536 RAM, 34 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
44 PIN, 32 KB FLASH, 1536 RAM, 34 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 48KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 64KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 TQFP 10x10x1mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128kB Flash, 4kB RAM, 1kB EE, 16MIPS, NanoWatt XLP, LCD, 5V 80 TQFP 12x12x1mm T/
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm TUBE
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet: