RC28F256P30TFB Micron Technology Inc, RC28F256P30TFB Datasheet - Page 47

RC28F256P30TFB
Manufacturer Part Number
RC28F256P30TFB
Description
Manufacturer
Micron Technology Inc
Datasheet
1.RC28F256P30TFB.pdf
(94 pages)
Specifications of RC28F256P30TFB
Cell Type
NOR
Density
256Mb
Access Time (max)
100ns
Interface Type
Parallel/Serial
Boot Type
Top
Address Bus
24b
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
1.8V
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Package Type
EZBGA
Sync/async
Async/Sync
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
1.7V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
2V
Word Size
16b
Number Of Words
16M
Supply Current
31mA
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
64
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
P30-65nm
11.3.2
Note:
11.3.3
Caution:
Datasheet
47
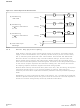
perform a read operation using the address offset corresponding to the register to be
read.
the OTP Registers and Lock Registers. PR data is read 16 bits at a time.
Programming the OTP Registers
To program an OTP Register, first issue the Program OTP Register command at the
parameter’s base address plus the offset of the desired OTP Register location (see
Section 6.0, “Command Set” on page
the same OTP Register address (see
The device programs the 64-bit and 128-bit user-programmable OTP Register data 16
bits at a time (see
page
address space causes a program error (SR.4 set). Attempting to program a locked OTP
Register causes a program error (SR.4 set) and a lock error (SR.1 set).
When programming the OTP bits in the OTP registers for a Top Parameter Device,
the following upper address bits must also be driven properly: A[Max:17] driven high
(V
SCSP.
Locking the OTP Registers
Each OTP Register can be locked by programming its respective lock bit in the Lock
Register. To lock a OTP Register, program the corresponding bit in the Lock Register by
issuing the Program Lock Register command, followed by the desired Lock Register
data (see
Registers are 0x80 for register 0 and 0x89 for register 1. These addresses are used
when programming the lock registers (see
page
Bit 0 of Lock Register 0 is already programmed during the manufacturing process by
Numonyx factory, locking the lower half segment of the first 128-bit OTP Register. Bit 1
of Lock Register 0 can be programmed by user to the upper half segment of the first
128-bit OTP Register. When programming Bit 1 of Lock Register 0, all other bits need to
be left as ‘1’ such that the data programmed is 0xFFFD.
Lock Register 1 controls the locking of the upper sixteen 128-bit OTP Registers. Each
bit of Lock Register 1 corresponds to a specific 128-bit OTP Register. Programming a bit
in Lock Register 1 locks the corresponding 128-bit OTP Register; e.g., programming
LR1.0 locks the corresponding OTP Register 1.
After being locked, the OTP Registers cannot be unlocked.
IH
) for TSOP and Easy BGA packages, and A[Max:16] driven high (V
85). Issuing the Program OTP Register command outside of the OTP Register’s
26).
Table 10, “Device Identifier Information” on page 26
Section 6.0, “Command Set” on page
Figure 42, “Protection Register Programming Flowchart” on
Figure 16, “OTP Register Map” on page
21). Next, write the desired OTP Register data to
Table 10, “Device Identifier Information” on
21). The physical addresses of the Lock
shows the address offsets of
Order Number: 320002-10
IH
) for QUAD+
46).
Mar 2010