M30240ECFP MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor], M30240ECFP Datasheet - Page 53

M30240ECFP
Manufacturer Part Number
M30240ECFP
Description
M30240 Group Specification
Manufacturer
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet
1.M30240ECFP.pdf
(142 pages)
- Current page: 53 of 142
- Download datasheet (902Kb)
Preliminary Specifications REV. E
Specifications in this manual are tentative and subject to change
Universal Serial Bus
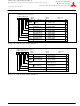
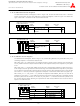
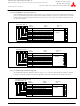
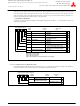
Figure 1.35: USB Interrupt Status Register 2
2.18.4.6 Clearing of the USB Interrupt Status Registers
2.18.4.7 The USB Function Interrupt Enable Registers 1 and 2
The USB Interrupt Status Register 1 and 2 are used to indicate pending interrupts for a given source. The
USB FCU sets the interrupt status bits. The CPU writes a “1” to each status bit to clear it.
Because the USB Function Interrupt has multiple sources that can generate an interrupt, it is recommended
that the user first read the two status registers and store them in variables then write back the same value for
clearing all the existing interrupts that were pending when the status registers were read. This procedure pre-
vents any interrupt that occurs after the status registers are read from being cleared by the ‘write-back’ oper-
ation. The CPU must read, then write both status registers, writing to status register 1 first and status register
2 second to guarantee proper operation. The upper three bits of the value written back to USBIS2 should al-
ways be “000” to prevent any of the USB Reset, Suspend and Resume Status Flags from being cleared.
The USB Reset, Suspend and Resume Status Flags are contained in USBIS2 along with the USB Endpoint
4 In/Out Interrupt Status Flags and the USB Overrun/Underrun Interrupts Status Flag. Because the flags are
not all sources for the same interrupt, use caution when clearing one or more of the flags to avoid inadvertently
clearing other flags. The Reset, Suspend and Resume Status Flags should be cleared individually by writing
a byte value with at “1” only at the position corresponding to the flag to be cleared. The USB Endpoint 4 In/
Out Interrupt status Flags and the USB Overrun/Underrun Interrupt Status Flag should be cleared as de-
scribed in the preceding paragraph because they are sourced for the USB Function Interrupt.
“Read-modify-write’ instructions, such as “BCLR’ and ‘BSET’, should not be used to clear any of the interrupt
status bits in USBIS1 or USBIS2. Using these instructions could cause pending interrupts to be cleared with-
out the firmware’s knowledge.
The USB Function Interrupt Enable Registers 1 and 2, shown in Figure 1.36 and Figure 1.37, are used to en-
able the corresponding interrupt status conditions that can generate a USB Function Interrupt. When the bit
to a corresponding interrupt condition is “0”, that condition does not generate a USB function interrupt. When
the bit is a “1”, that condition can generate a USB function interrupt. At reset, all USB function interrupt status
conditions are enabled.
USB Interrupt Status Register 2
b7
b6
b5
b4
b3
0 0
b2
b1
b0
Bit symbol
Reserved
Reserved
INTST8
INTST9
INTST12
INTST13
INTST14
INTST15
Symbol
USBIS2
USB Reset
Interrupt Status Flag
USB Suspend Signaling
Interrupt Status Flag
USB Overrun/Underrun
Interrupt Status Flag
USB Resume Signaling
Interrupt Status Flag
USB Endpoint 4 IN
Interrupt Status Flag
USB Endpoint 4 OUT
Interrupt Status Flag
1-53
Bit name
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Address
0303
Must always be set to "0"
0 : No interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
0 : No interrupt request issued
1 : Interrupt request issued
16
Function
Mitsubishi microcomputers
M30240 Group
When reset
00
16
R
W
Related parts for M30240ECFP
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Designer's Kits Unicoil 7/10 mm Tunable Inductors
Manufacturer:
Coilcraft

Part Number:
Description:
VCXO 200Mhz to 1000Mhz
Manufacturer:
Micro Networks
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128 x 8-BIT x 2 MAIL-BOX
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PROGRAMMABLE BUFFERED I/0 EXPANDER
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
ELECTRONIC SOUND CONTROL WITH ELECTRONIC VOLUME FOR MULTIPLE SOURCES
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2CH 4 MODE PRESET EQUALIZER
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SERIAL DATA CONTROL DUAL ELECTRONIC VOLUME
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SCREEN CHARACTER and PATTERN DISPLAY CONTROLLERS?????
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
M51996P
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER??
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SINGLE-CHIP 4-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR (TRIAC) MEDIUM POWER USE INSULATED TYPE, PLANAR PASSIVATION TYPE
Manufacturer:
Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor

Part Number:
Description:
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR (TRIAC) LOW POWER USE GLASS PASSIVATION TYPE
Manufacturer:
Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor

Part Number:
Description:
SINGLE-CHIP 4-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER?
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Datasheet: