mcf51jf128 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, mcf51jf128 Datasheet - Page 927
mcf51jf128
Manufacturer Part Number
mcf51jf128
Description
Mcf51jf128 Reference Manual
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet
1.MCF51JF128.pdf
(1339 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
mcf51jf128VLH
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI
Quantity:
321
Company:
Part Number:
mcf51jf128VLH
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 927 of 1339
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
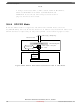
As long as no more than one slave device drives the system slave's serial data output line,
it is possible for several slaves to receive the same transmission from a master, although
the master would not receive return information from all of the receiving slaves.
If the CPHA bit in SPI Control Register 1 is clear, odd numbered edges on the SPSCK
input cause the data at the serial data input pin to be latched. Even numbered edges cause
the value previously latched from the serial data input pin to shift into the LSB or MSB
of the SPI shift register, depending on the LSBFE bit .
If the CPHA bit is set, even numbered edges on the SPSCK input cause the data at the
serial data input pin to be latched. Odd numbered edges cause the value previously
latched from the serial data input pin to shift into the LSB or MSB of the SPI shift
register, depending on the LSBFE bit.
When CPHA is set, the first edge is used to get the first data bit onto the serial data output
pin. When CPHA is clear and the SS input is low (slave selected), the first bit of the SPI
data is driven out of the serial data output pin. After the eighth (SPIMODE = 0) or
sixteenth (SPIMODE = 1) shift, the transfer is considered complete and the received data
is transferred into the SPI data registers. To indicate transfer is complete, the SPRF flag
in the SPI Status Register is set.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
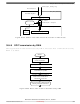
The SS pin is the slave select input. Before a data transmission occurs, the SS pin of
the slave SPI must be low. SS must remain low until the transmission is complete . If
SS goes high, the SPI is forced into idle state.
The SS input also controls the serial data output pin, if SS is high (not selected), the
serial data output pin is high impedance, and, if SS is low the first bit in the SPI Data
Register is driven out of the serial data output pin . Also, if the slave is not selected
(SS is high), then the SPSCK input is ignored and no internal shifting of the SPI shift
register takes place.
Although the SPI is capable of duplex operation, some SPI peripherals are capable of
only receiving SPI data in a slave mode. For these simpler devices, there is no serial
data out pin.
When peripherals with duplex capability are used, take care not
to simultaneously enable two receivers whose serial outputs
drive the same system slave's serial data output line.
MCF51JF128 Reference Manual, Rev. 2, 03/2011
Preliminary
Note
Chapter 38 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
927
Related parts for mcf51jf128
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: