PIC16LF723A-I/ML Microchip Technology, PIC16LF723A-I/ML Datasheet - Page 157

PIC16LF723A-I/ML
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC16LF723A-I/ML
Description
MCU PIC 3.5K FLASH XLP 28-QFN
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® XLP™ 16Fr
Specifications of PIC16LF723A-I/ML
Core Size
8-Bit
Program Memory Size
7KB (4K x 14)
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Core Processor
PIC
Speed
20MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Number Of I /o
25
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
192 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.8 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 11x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
28-VQFN Exposed Pad, 28-HVQFN, 28-SQFN, 28-DHVQFN
Controller Family/series
PIC16LF
No. Of I/o's
25
Ram Memory Size
192Byte
Cpu Speed
20MHz
No. Of Timers
3
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant, Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 157 of 284
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
17.1.1
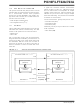
In Master mode, data transfer can be initiated at any
time because the master controls the SCK line. Master
mode determines when the slave (Figure 17-1,
Processor 2) transmits data via control of the SCK line.
17.1.1.1
The SSP consists of a transmit/receive shift register
(SSPSR) and a buffer register (SSPBUF). The SSPSR
register shifts the data in and out of the device, MSb
first. The SSPBUF register holds the data that is written
out of the master until the received data is ready. Once
the eight bits of data have been received, the byte is
moved to the SSPBUF register. The Buffer Full Status
bit, BF of the SSPSTAT register, and the SSP Interrupt
Flag bit, SSPIF of the PIR1 register, are then set.
Any write to the SSPBUF register during transmission/
reception of data will be ignored and the Write Collision
Detect bit, WCOL of the SSPCON register, will be set.
User software must clear the WCOL bit so that it can be
determined if the following write(s) to the SSPBUF
register completed successfully.
When the application software is expecting to receive
valid data, the SSPBUF should be read before the next
byte of data is written to the SSPBUF. The BF bit of the
SSPSTAT register is set when SSPBUF has been
loaded with the received data (transmission is
complete). When the SSPBUF is read, the BF bit is
cleared. This data may be irrelevant if the SPI is only a
transmitter. The SSP interrupt may be used to
determine
complete and the SSPBUF must be read and/or
written. If interrupts are not used, then software polling
can be done to ensure that a write collision does not
occur. Example 17-1 shows the loading of the SSPBUF
(SSPSR) for data transmission.
17.1.1.2
To enable the serial port, the SSPEN bit of the
SSPCON register, must be set. To reset or reconfigure
SPI mode, clear the SSPEN bit, re-initialize the
SSPCON register and then set the SSPEN bit. If a
Master mode of operation is selected in the SSPM bits
of the SSPCON register, the SDI, SDO and SCK pins
will be assigned as serial port pins.
For these pins to function as serial port pins, they must
have their corresponding data direction bits set or
cleared in the associated TRIS register as follows:
• SDI configured as input
• SDO configured as output
• SCK configured as output
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note:
MASTER MODE
The SSPSR is not directly readable or
writable and can only be accessed by
addressing the SSPBUF register.
when
Master Mode Operation
Enabling Master I/O
the
transmission/reception
is
PIC16F/LF722A/723A
17.1.1.3
In Master mode, the data is transmitted/received as
soon as the SSPBUF register is loaded with a byte
value. If the master is only going to receive, SDO output
could be disabled (programmed and used as an input).
The SSPSR register will continue to shift in the signal
present on the SDI pin at the programmed clock rate.
When initializing SPI Master mode operation, several
options need to be specified. This is accomplished by
programming the appropriate control bits in the
SSPCON and SSPSTAT registers. These control bits
allow the following to be specified:
• SCK as clock output
• Idle state of SCK (CKP bit)
• Data input sample phase (SMP bit)
• Output data on rising/falling edge of SCK (CKE bit)
• Clock bit rate
In Master mode, the SPI clock rate (bit rate) is user
selectable to be one of the following:
• F
• F
• F
• (Timer2 output)/2
This allows a maximum data rate of 5 Mbps
(at F
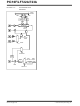
Figure 17-3 shows the waveforms for Master mode.
The clock polarity is selected by appropriately program-
ming the CKP bit of the SSPCON register. When the
CKE bit is set, the SDO data is valid before there is a
clock edge on SCK. The sample time of the input data
is shown based on the state of the SMP bit and can
occur at the middle or end of the data output time. The
time when the SSPBUF is loaded with the received
data is shown.
17.1.1.4
In Master mode, all module clocks are halted and the
transmission/reception will remain in their current state,
paused, until the device wakes from Sleep. After the
device wakes up from Sleep, the module will continue
to transmit/receive data.
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
/4 (or TCY)
/16 (or 4 TCY)
/64 (or 16 TCY)
= 20 MHz).
Master Mode Setup
Sleep in Master Mode
DS41417A-page 157
Related parts for PIC16LF723A-I/ML
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-SPDIP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-QFN
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-SPDIP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-QFN
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-SOIC
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-SSOP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX14 28-SSOP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
7 KB Flash, 16 MHz Int. Osc, NanoWatt XLP 28 SOIC .300in TUBE
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28SOIC
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28QFN
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28DIP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28SOIC
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28QFN
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 28SSOP
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC, 8BIT MCU, PIC16LF, 32MHZ, QFN-28
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet: