ATtiny20 Atmel Corporation, ATtiny20 Datasheet - Page 10

ATtiny20
Manufacturer Part Number
ATtiny20
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATtiny20
Flash (kbytes)
2 Kbytes
Pin Count
14
Max. Operating Frequency
12 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
5
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
Yes
Max I/o Pins
12
Ext Interrupts
12
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
0.12
Self Program Memory
NO
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.8 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
2
Output Compare Channels
4
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
3
32khz Rtc
No
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ATtiny20-MMHR
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATtiny20-SSU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATtiny20-XU
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Quantity:
904
4.5
4.6
10
Stack Pointer
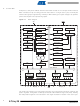
Instruction Execution Timing
ATtiny20
Figure 4-3.
In different addressing modes these address registers function as automatic increment and
automatic decrement (see document “AVR Instruction Set” and section
mary” on page 210
The stack is mainly used for storing temporary data, local variables and return addresses after
interrupts and subroutine calls. The Stack Pointer registers (SPH and SPL) always point to the
top of the stack. Note that the stack grows from higher memory locations to lower memory loca-
tions. This means that the PUSH instructions decreases and the POP instruction increases the
stack pointer value.
The stack pointer points to the area of data memory where subroutine and interrupt stacks are
located. This stack space must be defined by the program before any subroutine calls are exe-
cuted or interrupts are enabled.
The pointer is decremented by one when data is put on the stack with the PUSH instruction, and
incremented by one when data is fetched with the POP instruction. It is decremented by two
when the return address is put on the stack by a subroutine call or a jump to an interrupt service
routine, and incremented by two when data is fetched by a return from subroutine (the RET
instruction) or a return from interrupt service routine (the RETI instruction).
The AVR stack pointer is typically implemented as two 8-bit registers in the I/O register file. The
width of the stack pointer and the number of bits implemented is device dependent. In some
AVR devices all data memory can be addressed using SPL, only. In this case, the SPH register
is not implemented.
The stack pointer must be set to point above the I/O register areas, the minimum value being the
lowest address of SRAM. See
This section describes the general access timing concepts for instruction execution. The AVR
CPU is driven by the CPU clock clk
chip. No internal clock division is used.
X-register
Y-register
Z-register
The X-, Y-, and Z-registers
for details).
15
7
15
7
15
7
Figure 5-1 on page
CPU
R27
R29
R31
XH
YH
ZH
, directly generated from the selected clock source for the
16.
0
0
0
7
7
7
“Instruction Set Sum-
XL
YL
ZL
R26
R28
R30
8235B–AVR–04/11
0
0
0
0
0
0