DSPIC33FJ128MC804-H/ML Microchip Technology, DSPIC33FJ128MC804-H/ML Datasheet - Page 247
DSPIC33FJ128MC804-H/ML
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC33FJ128MC804-H/ML
Description
16-bit DSC, 128KB Flash, Motor, CAN, DMA, 40 MIPS, NanoWatt 44 QFN 8x8x0.9mm TUB
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
dsPIC™ 33Fr
Datasheet
1.DSPIC33FJ32MC302-ISO.pdf
(436 pages)
Specifications of DSPIC33FJ128MC804-H/ML
Core Processor
dsPIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
20 MIPS
Connectivity
CAN, I²C, IrDA, LIN, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, Motor Control PWM, QEI, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
35
Program Memory Size
128KB (128K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
16K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 9x10b/12b, D/A 6x16b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 140°C
Package / Case
44-QFN
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 247 of 436
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
21.0
21.1
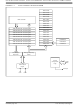
The Enhanced Controller Area Network (ECAN)
module is a serial interface, useful for communicating
with other CAN modules or microcontroller devices.
This
communications within noisy environments. The
dsPIC33FJ32MC302/304,
and dsPIC33FJ128MCX02/X04 devices contain up to
two ECAN modules.
The ECAN module is a communication controller
implementing the CAN 2.0 A/B protocol, as defined in
the BOSCH CAN specification. The module supports
CAN 1.2, CAN 2.0A, CAN 2.0B Passive and CAN 2.0B
Active versions of the protocol. The module implementa-
tion is a full CAN system. The CAN specification is not
covered within this data sheet. The reader can refer to
the BOSCH CAN specification for further details.
The module features are as follows:
• Implementation of the CAN protocol, CAN 1.2,
• Standard and extended data frames
• 0-8 bytes data length
• Programmable bit rate up to 1 Mbit/sec
• Automatic response to remote transmission
• Up to eight transmit buffers with application
• Up to 32 receive buffers (each buffer can contain
• Up to 16 full (standard/extended identifier)
• Three full acceptance filter masks
• DeviceNet™ addressing support
• Programmable wake-up functionality with
© 2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
dsPIC33FJ32MC302/304, dsPIC33FJ64MCX02/X04 AND dsPIC33FJ128MCX02/X04
CAN 2.0A and CAN 2.0B
requests
specified prioritization and abort capability (each
buffer can contain up to 8 bytes of data)
up to 8 bytes of data)
acceptance filters
integrated low-pass filter
Note 1: This data sheet summarizes the features
interface/protocol
2: Some registers and associated bits
ENHANCED CAN (ECAN™)
MODULE
Overview
of
dsPIC33FJ64MCX02/X04
dsPIC33FJ128MCX02/X04
devices. It is not intended to be a
comprehensive reference source. To
complement the information in this data
sheet, refer to “Section 21. Enhanced
Controller Area Network (ECAN™)”
(DS70185) of the “dsPIC33F/PIC24H
Family Reference Manual”, which is
available from the Microchip web site
(www.microchip.com).
described in this section may not be
available on all devices. Refer to
Section 4.0 “Memory Organization”
this data sheet for device-specific register
and bit information.
the
was
dsPIC33FJ32MC302/304,
dsPIC33FJ64MCX02/X04
designed
family
to
allow
and
of
in
• Programmable Loopback mode supports self-test
• Signaling via interrupt capabilities for all CAN
• Programmable clock source
• Programmable link to input capture module (IC2
• Low-power Sleep and Idle mode
The CAN bus module consists of a protocol engine and
message buffering/control. The CAN protocol engine
handles all functions for receiving and transmitting
messages on the CAN bus. Messages are transmitted
by first loading the appropriate data registers. Status
and errors can be checked by reading the appropriate
registers. Any message detected on the CAN bus is
checked for errors and then matched against filters to
see if it should be received and stored in one of the
receive registers.
21.2
The ECAN module transmits various types of frames
which include data messages, or remote transmission
requests initiated by the user, as other frames that are
automatically generated for control purposes. The
following frame types are supported:
• Standard Data Frame:
• Extended Data Frame:
• Remote Frame:
• Error Frame:
• Overload Frame:
• Interframe Space:
operation
receiver and transmitter error states
for CAN1) for time-stamping and network
synchronization
A standard data frame is generated by a node when
the node wishes to transmit data. It includes an 11-bit
Standard Identifier (SID), but not an 18-bit Extended
Identifier (EID).
It is possible for a destination node to request the
data from the source. For this purpose, the
destination node sends a remote frame with an iden-
tifier that matches the identifier of the required data
frame. The appropriate data source node sends a
data frame as a response to this remote request.
An error frame is generated by any node that detects
a bus error. An error frame consists of two fields: an
error flag field and an error delimiter field.
An overload frame can be generated by a node as a
result of two conditions. First, the node detects a
dominant bit during interframe space which is an ille-
gal condition. Second, due to internal conditions, the
node is not yet able to start reception of the next
message. A node can generate a maximum of 2
sequential overload frames to delay the start of the
next message.
Interframe space separates a proceeding frame (of
whatever type) from a following data or remote
frame.
An extended data frame is similar to a standard
data frame, but includes an extended identifier as
well.
Frame Types
DS70291E-page 247
Related parts for DSPIC33FJ128MC804-H/ML
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: