ATAM862P-TNSY4D Atmel, ATAM862P-TNSY4D Datasheet - Page 18

ATAM862P-TNSY4D
Manufacturer Part Number
ATAM862P-TNSY4D
Description
IC MCU FLASH 4K TX 433MHZ 24SSOP
Manufacturer
Atmel
Datasheet
1.ATAM862P-TNQY4D.pdf
(110 pages)
Specifications of ATAM862P-TNSY4D
Applications
UHF ASK/FSK
Core Processor
MARC4
Program Memory Type
FLASH (4 kB)
Controller Series
MARC4 4-Bit
Ram Size
256 x 4
Interface
SSI
Number Of I /o
11
Voltage - Supply
1.8 V ~ 4 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
24-SSOP
Processor Series
ATAM862x
Core
MARC4
Data Bus Width
4 bit
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
16.3.2
16.3.3
16.3.4
16.3.5
16.3.6
16.3.7
16.3.8
16.3.9
18
ATAM862-4
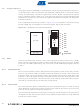
RAM Address Registers
Expression Stack Pointer (SP)
Return Stack Pointer (RP)
RAM Address Registers (X and Y)
Top of Stack (TOS)
Condition Code Register (CCR)
Carry/Borrow (C)
Branch (B)
The RAM is addressed with the four 8-bit wide RAM address registers: SP, RP, X and Y. These
registers allow access to any of the 256 RAM nibbles.
The stack pointer contains the address of the next-to-top 4-bit item (TOS-1) of the expression
stack. The pointer is automatically pre-incremented if a nibble is moved onto the stack or
post-decremented if a nibble is removed from the stack. Every post-decrement operation moves
the item (TOS-1) to the TOS register before the SP is decremented. After a reset, the stack
pointer has to be initialized with >SP S0 to allocate the start address of the expression stack
area.
The return stack pointer points to the top element of the 12-bit wide return stack. The pointer
automatically pre-increments if an element is moved onto the stack, or it post-decrements if an
element is removed from the stack. The return stack pointer increments and decrements in
steps of 4. This means that every time a 12-bit element is stacked, a 4-bit RAM location is left
unwritten. This location is used by the qFORTH compiler to allocate 4-bit variables. After a reset
the return stack pointer has to be initialized via >RP FCh.
The X and Y registers are used to address any 4-bit item in the RAM. A fetch operation moves
the addressed nibble onto the TOS. A store operation moves the TOS to the addressed RAM
location. By using either the pre-increment or post-decrement addressing mode arrays in the
RAM can be compared, filled or moved.
The top of stack register is the accumulator of the microcontroller block. All arithmetic/logic,
memory reference and I/O operations use this register. The TOS register receives data from the
ALU, EEPROM, RAM or I/O bus.
The 4-bit wide condition code register contains the branch, the carry and the interrupt enable
flag. These bits indicate the current state of the CPU. The CCR flags are set or reset by ALU
operations. The instructions SET_BCF, TOG_BF, CCR! and DI allow direct manipulation of the
condition code register.
The carry/borrow flag indicates that the borrowing or carrying out of arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
occurred during the last arithmetic operation. During shift and rotate operations, this bit is used
as a fifth bit. Boolean operations have no effect on the C-flag.
The branch flag controls the conditional program branching. Should the branch flag has been set
by a previous instruction, a conditional branch will cause a jump. This flag is affected by arith-
metic, logic, shift, and rotate operations.
4551G–4BMCU–07/07