ST72C334J4T6 STMicroelectronics, ST72C334J4T6 Datasheet - Page 33

ST72C334J4T6
Manufacturer Part Number
ST72C334J4T6
Description
MCU 8BIT FLASH SPI SCI 44TQFP
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Series
ST7r
Datasheet
1.ST72C124J2T6.pdf
(153 pages)
Specifications of ST72C334J4T6
Core Processor
ST7
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
32
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
256 x 8
Ram Size
512 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3.2 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 6x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
44-TQFP, 44-VQFP
Processor Series
ST72C3x
Core
ST7
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
512 B
Interface Type
SCI, SPI
Maximum Clock Frequency
8 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
32
Number Of Timers
4 bit
Operating Supply Voltage
3.2 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Development Tools By Supplier
ST7C334-INDART, ST7MDT2-EPB2/US
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
8 bit
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
497-4838
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ST72C334J4T6
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Quantity:
10 000
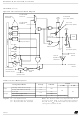
10 INTERRUPTS
The ST7 core may be interrupted by one of two dif-
ferent methods: maskable hardware interrupts as
listed in the Interrupt Mapping Table and a non-
maskable software interrupt (TRAP). The Interrupt
processing flowchart is shown in
The maskable interrupts must be enabled by
clearing the I bit in order to be serviced. However,
disabled interrupts may be latched and processed
when they are enabled (see external interrupts
subsection).
Note: After reset, all interrupts are disabled.
When an interrupt has to be serviced:
– Normal processing is suspended at the end of
– The PC, X, A and CC registers are saved onto
– The I bit of the CC register is set to prevent addi-
– The PC is then loaded with the interrupt vector of
The interrupt service routine should finish with the
IRET instruction which causes the contents of the
saved registers to be recovered from the stack.
Note: As a consequence of the IRET instruction,
the I bit will be cleared and the main program will
resume.
Priority Management
By default, a servicing interrupt cannot be inter-
rupted because the I bit is set by hardware enter-
ing in interrupt routine.
In the case when several interrupts are simultane-
ously pending, an hardware priority defines which
one will be serviced first (see the Interrupt Map-
ping Table).
Interrupts and Low Power Mode
All interrupts allow the processor to leave the
WAIT low power mode. Only external and specifi-
cally mentioned interrupts allow the processor to
leave the HALT low power mode (refer to the “Exit
from HALT“ column in the Interrupt Mapping Ta-
ble).
10.1
INTERRUPT
This interrupt is entered when the TRAP instruc-
tion is executed regardless of the state of the I bit.
the current instruction execution.
the stack.
tional interrupts.
the interrupt to service and the first instruction of
the interrupt service routine is fetched (refer to
the Interrupt Mapping Table for vector address-
es).
NON
MASKABLE
Figure
SOFTWARE
18.
It will be serviced according to the flowchart on
Figure
10.2 EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS
External interrupt vectors can be loaded into the
PC register if the corresponding external interrupt
occurred and if the I bit is cleared. These interrupts
allow the processor to leave the Halt low power
mode.
The external interrupt polarity is selected through
the miscellaneous register or interrupt register (if
available).
An external interrupt triggered on edge will be
latched and the interrupt request automatically
cleared upon entering the interrupt service routine.
If several input pins, connected to the same inter-
rupt vector, are configured as interrupts, their sig-
nals are logically NANDed before entering the
edge/level detection block.
Caution: The type of sensitivity defined in the Mis-
cellaneous or Interrupt register (if available) ap-
plies to the ei source. In case of a NANDed source
(as described on the I/O ports section), a low level
on an I/O pin configured as input with interrupt,
masks the interrupt request even in case of rising-
edge sensitivity.
10.3 PERIPHERAL INTERRUPTS
Different peripheral interrupt flags in the status
register are able to cause an interrupt when they
are active if both:
– The I bit of the CC register is cleared.
– The corresponding enable bit is set in the control
If any of these two conditions is false, the interrupt
is latched and thus remains pending.
Clearing an interrupt request is done by:
– Writing “0” to the corresponding bit in the status
– Access to the status register while the flag is set
Note: the clearing sequence resets the internal
latch. A pending interrupt (i.e. waiting for being en-
abled) will therefore be lost if the clear sequence is
executed.
register.
register or
followed by a read or write of an associated reg-
ister.
ST72334J/N, ST72314J/N, ST72124J
18.
33/153