ST72C334J4T6 STMicroelectronics, ST72C334J4T6 Datasheet - Page 76

ST72C334J4T6
Manufacturer Part Number
ST72C334J4T6
Description
MCU 8BIT FLASH SPI SCI 44TQFP
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Series
ST7r
Datasheet
1.ST72C124J2T6.pdf
(153 pages)
Specifications of ST72C334J4T6
Core Processor
ST7
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
32
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
256 x 8
Ram Size
512 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3.2 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 6x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
44-TQFP, 44-VQFP
Processor Series
ST72C3x
Core
ST7
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
512 B
Interface Type
SCI, SPI
Maximum Clock Frequency
8 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
32
Number Of Timers
4 bit
Operating Supply Voltage
3.2 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Development Tools By Supplier
ST7C334-INDART, ST7MDT2-EPB2/US
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
8 bit
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
497-4838
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ST72C334J4T6
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Quantity:
10 000
ST72334J/N, ST72314J/N, ST72124J
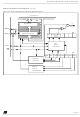
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d)
14.4.4.3 Data Transfer Format
During an SPI transfer, data is simultaneously
transmitted (shifted out serially) and received
(shifted in serially). The serial clock is used to syn-
chronize the data transfer during a sequence of
eight clock pulses.
The SS pin allows individual selection of a slave
device; the other slave devices that are not select-
ed do not interfere with the SPI transfer.
Clock Phase and Clock Polarity
Four possible timing relationships may be chosen
by software, using the CPOL and CPHA bits.
The CPOL (clock polarity) bit controls the steady
state value of the clock when no data is being
transferred. This bit affects both master and slave
modes.
The combination between the CPOL and CPHA
(clock phase) bits selects the data capture clock
edge.
Figure
combinations of the CPHA and CPOL bits. The di-
agram may be interpreted as a master or slave
timing diagram where the SCK pin, the MISO pin,
the MOSI pin are directly connected between the
master and the slave device.
The SS pin is the slave device select input and can
be driven by the master device.
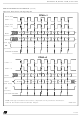
Figure 44. CPHA / SS Timing Diagram
76/153
45, shows an SPI transfer with the four
MOSI/MISO
Master
(CPHA=0)
(CPHA=1)
Slave
Slave
SS
SS
SS
Byte 1
The master device applies data to its MOSI pin-
clock edge before the capture clock edge.
CPHA bit is set
The second edge on the SCK pin (falling edge if
the CPOL bit is reset, rising edge if the CPOL bit is
set) is the MSBit capture strobe. Data is latched on
the occurrence of the second clock transition.
No write collision should occur even if the SS pin
stays low during a transfer of several bytes (see
Figure
CPHA bit is reset
The first edge on the SCK pin (falling edge if CPOL
bit is set, rising edge if CPOL bit is reset) is the
MSBit capture strobe. Data is latched on the oc-
currence of the first clock transition.
The SS pin must be toggled high and low between
each byte transmitted (see
To protect the transmission from a write collision a
low value on the SS pin of a slave device freezes
the data in its DR register and does not allow it to
be altered. Therefore the SS pin must be high to
write a new data byte in the DR without producing
a write collision.
Byte 2
44).
Byte 3
Figure
44).
VR02131A