ST7FMC1K2B3 STMICROELECTRONICS [STMicroelectronics], ST7FMC1K2B3 Datasheet - Page 130

ST7FMC1K2B3
Manufacturer Part Number
ST7FMC1K2B3
Description
Manufacturer
STMICROELECTRONICS [STMicroelectronics]
Datasheet
1.ST7FMC1K2B3.pdf
(309 pages)
- Current page: 130 of 309
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
ST7MC1xx/ST7MC2xx
LINSCI™ SERIAL COMMUNICATION INTERFACE (LIN Mode) (cont’d)
10.5.9.7 LINSCI Clock Tolerance
LINSCI Clock Tolerance when unsynchronized
When LIN slaves are unsynchronized (meaning no
characters have been transmitted for a relatively
long time), the maximum tolerated deviation of the
LINSCI clock is +/-15%.
If the deviation is within this range then the LIN
Synch Break is detected properly when a new re-
ception occurs.
This is made possible by the fact that masters
send 13 low bits for the LIN Synch Break, which
can be interpreted as 11 low bits (13 bits -15% =
11.05) by a “fast” slave and then considered as a
LIN Synch Break. According to the LIN specifica-
tion, a LIN Synch Break is valid when its duration
is greater than t
LIN Synch Break must last at least 11 low bits.
Note: If the period desynchronization of the slave
is +15% (slave too slow), the character “00h”
which represents a sequence of 9 low bits must
not be interpreted as a break character (9 bits +
15% = 10.35). Consequently, a valid LIN Synch
break must last at least 11 low bits.
LINSCI Clock Tolerance when Synchronized
When synchronization has been performed, fol-
lowing reception of a LIN Synch Break, the LINS-
CI, in LIN mode, has the same clock deviation tol-
erance as in SCI mode, which is explained below:
During reception, each bit is oversampled 16
times. The mean of the 8th, 9th and 10th samples
is considered as the bit value.
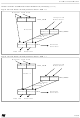
Figure 71.Bit Sampling in Reception Mode
130/309
1
RDI LINE
Sample
clock
SBRKTS
1
= 10. This means that the
2
3
4
7/16
5
6
7
sampled values
Consequently, the clock frequency should not vary
more than 6/16 (37.5%) within one bit.
The sampling clock is resynchronized at each start
bit, so that when receiving 10 bits (one start bit, 1
data byte, 1 stop bit), the clock deviation should
not exceed 3.75%.
10.5.9.8 Clock Deviation Causes
The causes which contribute to the total deviation
are:
All the deviations of the system should be added
and compared to the LINSCI clock tolerance:
D
8
One bit time
TRA
– D
– D
– D
– D
– D
Note: The transmitter can be either a master
or a slave (in case of a slave listening to the
response of another slave).
ment performed by the receiver.
tion of the receiver.
receiver: This deviation can occur during the
reception of one complete LIN message as-
suming that the deviation has been compen-
sated at the beginning of the message.
(generally due to the transceivers)
9
+ D
TRA
MEAS
QUANT
REC
TCL
: Deviation due to the transmission line
MEAS
: Deviation due to transmitter error.
: Deviation of the local oscillator of the
10
: Error due to the LIN Synch measure-
: Error due to the baud rate quantiza-
+D
11
QUANT
12
+ D
6/16
7/16
13
REC
14
+ D
15
TCL
< 3.75%
16
Related parts for ST7FMC1K2B3
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [RIPPLE-CARRY BINARY COUNTER/DIVIDERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BOARD EVAL FOR MEMS SENSORS
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN TRANSISTOR POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TURBOSWITCH ULTRA-FAST HIGH VOLTAGE DIODE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> STE16N100
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search ---> STE53NA50
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN Transistor Power Module
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet: