ST7FMC1K2B3 STMICROELECTRONICS [STMicroelectronics], ST7FMC1K2B3 Datasheet - Page 140

ST7FMC1K2B3
Manufacturer Part Number
ST7FMC1K2B3
Description
Manufacturer
STMICROELECTRONICS [STMicroelectronics]
Datasheet
1.ST7FMC1K2B3.pdf
(309 pages)
- Current page: 140 of 309
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
ST7MC1xx/ST7MC2xx
MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d)
10.6.3 Application Example: PM BLDC motor
drive
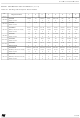
This example shows a six-step command se-
quence for a 3-phase permanent magnet DC
brushless motor (PM BLDC motor).
shows the phase steps and voltage, while
24
To run this kind of motor efficiently, an autoswitch-
ing mode has to be used, i.e. the position of the ro-
tor must self-generate the powered winding com-
mutation. The BEMF zero crossing (Z event) on
the non-excited winding is used by the MTC as a
rotor position sensor. The delay between this
event and the commutation is computed by the
MTC and the hardware commutation event C
automatically generated after this delay.
After the commutation occurs, the MTC waits until
the winding is completely demagnetized by the
free-wheeling diode: during this phase the winding
is tied to 0V or to the HV high voltage rail and no
BEMF can be read. At the end of this phase a new
BEMF zero-crossing detection is enabled.
140/309
1
shows the relevant phase configurations.
Figure 74
Table
n
is
The end of demagnetization event (D), is also de-
tected by the MTC or simulated with a timer com-
pare feature when no detection is possible.
The MTC manages these three events always in
the same order: Z generates C after a delay com-
puted in realtime, then waits for D in order to ena-
ble the peripheral to detect another Z event.
The BEMF zero-crossing event (Z), can also be
detected by the MTC or simulated with a timer
compare feature when no detection is possible.
The speed regulation is managed by the micro-
controller, by means of an adjustable reference
current level in case of current control, or by direct
PWM duty-cycle adjustment in case of voltage
control.
Related parts for ST7FMC1K2B3
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [RIPPLE-CARRY BINARY COUNTER/DIVIDERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BOARD EVAL FOR MEMS SENSORS
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN TRANSISTOR POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TURBOSWITCH ULTRA-FAST HIGH VOLTAGE DIODE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> STE16N100
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search ---> STE53NA50
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN Transistor Power Module
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet: