ST7FMC1K2B3 STMICROELECTRONICS [STMicroelectronics], ST7FMC1K2B3 Datasheet - Page 52

ST7FMC1K2B3
Manufacturer Part Number
ST7FMC1K2B3
Description
Manufacturer
STMICROELECTRONICS [STMicroelectronics]
Datasheet
1.ST7FMC1K2B3.pdf
(309 pages)
- Current page: 52 of 309
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
ST7MC1xx/ST7MC2xx
POWER SAVING MODES (Cont’d)
8.4 ACTIVE-HALT AND HALT MODES
Active-halt and Halt modes are the two lowest
power consumption modes of the MCU. They are
both entered by executing the ‘HALT’ instruction.
The decision to enter either in Active-halt or Halt
mode is given by the MCC/RTC interrupt enable
flag (OIE bit in MCCSR register).
8.4.1 ACTIVE-HALT MODE
Active-halt mode is the lowest power consumption
mode of the MCU with a real-time clock available.
It is entered by executing the ‘HALT’ instruction
when the OIE bit of the Main Clock Controller Sta-
tus register (MCCSR) is set (see
page 37
The MCU can exit Active-halt mode on reception
of either an MCC/RTC interrupt, a specific inter-
rupt (see Table 8, “Interrupt Mapping,” on
page 44) or a RESET. When exiting Active-halt
mode by means of an interrupt, no 256 or 4096
CPU cycle delay occurs. The CPU resumes oper-
ation by servicing the interrupt or by fetching the
reset vector which woke it up (see
When entering Active-halt mode, the I[1:0] bits in
the CC register are forced to ‘10b’ to enable inter-
rupts. Therefore, if an interrupt is pending, the
MCU wakes up immediately.
In Active-halt mode, only the main oscillator and its
associated counter (MCC/RTC) are running to
keep a wake-up time base. All other peripherals
are not clocked except those which get their clock
supply from another clock generator (such as ex-
ternal or auxiliary oscillator).
The safeguard against staying locked in Active-
halt mode is provided by the oscillator interrupt.
Note: As soon as the interrupt capability of one of
the oscillators is selected (MCCSR.OIE bit set),
entering Active-halt mode while the Watchdog is
active does not generate a RESET.
This means that the device cannot spend more
than a defined delay in this power saving mode.
52/309
1
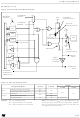
MCCSR
OIE bit
0
1
for more details on the MCCSR register).
Halt mode
Active-halt mode
Power Saving Mode entered when HALT
instruction is executed
Figure
section 6.4 on
29).
Figure 28. Active-halt Timing Overview
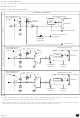
Figure 29. Active-halt Mode Flow-chart
Notes:
1. This delay occurs only if the MCU exits Active-
halt mode by means of a RESET.
2. Peripheral clocked with an external clock source
can still be active.
3. Only the MCC/RTC interrupt and some specific
interrupts can exit the MCU from Active-halt mode
(such as external interrupt). Refer to Table 8, “In-
terrupt Mapping,” on page 44 for more details.
4. Before servicing an interrupt, the CC register is
pushed on the stack. The I[1:0] bits of the CC reg-
ister are set to the current software priority level of
the interrupt routine and restored when the CC
register is popped.
[MCCSR.OIE=1]
INSTRUCTION
HALT INSTRUCTION
RUN
N
(MCCSR.OIE=1)
HALT
INTERRUPT
ACTIVE
HALT
Y
256 OR 4096 CPU
CYCLE DELAY
INTERRUPT
3)
RESET
256 OR 4096 CPU CLOCK
OR SERVICE INTERRUPT
FETCH RESET VECTOR
OR
OSCILLATOR
PERIPHERALS
OSCILLATOR
PERIPHERALS
OSCILLATOR
PERIPHERALS
CPU
I[1:0] BITS
CPU
I[1:0] BITS
CPU
I[1:0] BITS
N
CYCLE DELAY
RESET
Y
1)
VECTOR
FETCH
RUN
2)
XX
XX
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
10
4)
4)
Related parts for ST7FMC1K2B3
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [RIPPLE-CARRY BINARY COUNTER/DIVIDERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BOARD EVAL FOR MEMS SENSORS
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN TRANSISTOR POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TURBOSWITCH ULTRA-FAST HIGH VOLTAGE DIODE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> STE16N100
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search ---> STE53NA50
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN Transistor Power Module
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet: