MT48LC64M4A2 Micron Technology, MT48LC64M4A2 Datasheet - Page 12

MT48LC64M4A2
Manufacturer Part Number
MT48LC64M4A2
Description
(MT48Lxxxx) SYNCHRONOUS DRAM
Manufacturer
Micron Technology
Datasheet
1.MT48LC64M4A2.pdf
(62 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2BB-75
Manufacturer:
MICRON
Quantity:
6 966
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2BB-75D
Manufacturer:
MICRON/美光
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2BB-7E
Manufacturer:
MICRON
Quantity:
7 000
Company:
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2FB-6
Manufacturer:
MICRON
Quantity:
7 000
Company:
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2FB-75
Manufacturer:
MICRON
Quantity:
6 695
Company:
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2FB-75:C
Manufacturer:
MICRON
Quantity:
4 000
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2TG-75
Manufacturer:
MICRON/美光
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
MT48LC64M4A2TG-7E:D
Manufacturer:
MICRON/美光
Quantity:
20 000
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
8 Meg x 8 x 4 banks and 4 Meg x 16 x 4 banks) are quad-
bank DRAMs that operate at 3.3V and include a syn-
chronous interface (all signals are registered on the
positive edge of the clock signal, CLK). Each of the x4’s
67,108,864-bit banks is organized as 8,192 rows by 2,048
columns by 4 bits. Each of the x8’s 67,108,864-bit banks
is organized as 8,192 rows by 1,024 columns by 8 bits.
Each of the x16’s 67,108,864-bit banks is organized as
8,192 rows by 512 columns by 16 bits.
oriented; accesses start at a selected location and con-
tinue for a programmed number of locations in a pro-
grammed sequence. Accesses begin with the registra-
tion of an ACTIVE command, which is then followed by
a READ or WRITE command. The address bits regis-
tered coincident with the ACTIVE command are used
to select the bank and row to be accessed (BA0 and BA1
select the bank, A0–A12 select the row). The address
bits (x4: A0–A9, A11; x8: A0–A9; x16: A0–A8) registered
coincident with the READ or WRITE command are used
to select the starting column location for the burst ac-
cess.
tialized. The following sections provide detailed infor-
mation covering device initialization, register defini-
tion, command descriptions and device operation.
Initialization
predefined manner. Operational procedures other
than those specified may result in undefined opera-
tion. Once power is applied to V
neously) and the clock is stable (stable clock is defined
as a signal cycling within timing constraints specified
for the clock pin), the SDRAM requires a 100µs delay
prior to issuing any command other than a
COMMAND INHIBIT or NOP. Starting at some point
during this 100µs period and continuing at least
through the end of this period, COMMAND INHIBIT or
NOP commands should be applied.
least one COMMAND INHIBIT or NOP command hav-
ing been applied, a PRECHARGE command should be
applied. All banks must then be precharged, thereby
placing the device in the all banks idle state.
must be performed. After the AUTO REFRESH cycles
are complete, the SDRAM is ready for mode register
programming. Because the mode register will power
up in an unknown state, it should be loaded prior to
applying any operational command.
256Mb: x4, x8, x16 SDRAM
256MSDRAM_E.p65 – Rev. E; Pub. 3/02
In general, the 256Mb SDRAMs (16 Meg x 4 x 4 banks,
Read and write accesses to the SDRAM are burst
Prior to normal operation, the SDRAM must be ini-
SDRAMs must be powered up and initialized in a
Once in the idle state, two AUTO REFRESH cycles
Once the 100µs delay has been satisfied with at
DD
and V
DD
Q (simulta-
12
Register Definition
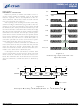
MODE REGISTER
of operation of the SDRAM. This definition includes
the selection of a burst length, a burst type, a CAS
latency, an operating mode and a write burst mode, as
shown in Figure 1. The mode register is programmed
via the LOAD MODE REGISTER command and will re-
tain the stored information until it is programmed again
or the device loses power.
M3 specifies the type of burst (sequential or inter-
leaved), M4–M6 specify the CAS latency, M7 and M8
specify the operating mode, M9 specifies the write burst
mode, and M10 and M11 are reserved for future use.
Address A12 (M12) is undefined but should be driven
LOW during loading of the mode register.
are idle, and the controller must wait the specified time
before initiating the subsequent operation. Violating
either of these requirements will result in unspecified
operation.
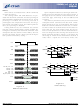
Burst Length
oriented, with the burst length being programmable,
as shown in Figure 1. The burst length determines the
maximum number of column locations that can be ac-
cessed for a given READ or WRITE command. Burst
lengths of 1, 2, 4 or 8 locations are available for both the
sequential and the interleaved burst types, and a full-
page burst is available for the sequential type. The
full-page burst is used in conjunction with the BURST
TERMINATE command to generate arbitrary burst
lengths.
operation or incompatibility with future versions may
result.
of columns equal to the burst length is effectively se-
lected. All accesses for that burst take place within this
block, meaning that the burst will wrap within the block
if a boundary is reached. The block is uniquely se-
lected by A1–A9, A11 (x4), A1–A9 (x8) or A1–A8 (x16)
when the burst length is set to two; by A2–A9, A11 (x4),
A2–A9 (x8) or A2–A8 (x16) when the burst length is set
to four; and by A3–A9, A11 (x4), A3–A9 (x8) or A3–A8
(x16) when the burst length is set to eight. The remain-
ing (least significant) address bit(s) is (are) used to
select the starting location within the block. Full-page
bursts wrap within the page if the boundary is reached.
The mode register is used to define the specific mode
Mode register bits M0–M2 specify the burst length,
The mode register must be loaded when all banks
Read and write accesses to the SDRAM are burst
Reserved states should not be used, as unknown
When a READ or WRITE command is issued, a block
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
256Mb: x4, x8, x16
©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
SDRAM