ATTINY43U-MU Atmel, ATTINY43U-MU Datasheet - Page 62
ATTINY43U-MU
Manufacturer Part Number
ATTINY43U-MU
Description
MCU AVR 4K FLASH 8MHZ 20-QFN
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
AVR® ATtinyr
Specifications of ATTINY43U-MU
Core Processor
AVR
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Connectivity
USI
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, Temp Sensor, WDT
Number Of I /o
16
Program Memory Size
4KB (2K x 16)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
64 x 8
Ram Size
256 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.8 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 4x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
20-MLF®, QFN
Processor Series
ATTINY4x
Core
AVR8
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
256 B
Interface Type
SPI
Maximum Clock Frequency
8 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
16
Number Of Timers
2
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
EWAVR, EWAVR-BL
Development Tools By Supplier
ATAVRDRAGON, ATSTK500, ATSTK600, ATAVRISP2, ATAVRONEKIT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 4 Channel
For Use With
ATSTK600-TINYX3U - STK600 SOCKET/ADAPTER TINYX3U
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 62 of 182
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
11. I/O Ports
11.1
62
Introduction
ATtiny43U
All AVR ports have true Read-Modify-Write functionality when used as general digital I/O ports.
This means that the direction of one port pin can be changed without unintentionally changing
the direction of any other pin with the SBI and CBI instructions. The same applies when chang-
ing drive value (if configured as output) or enabling/disabling of pull-up resistors (if configured as
input). Each output buffer has symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. The pin driver is strong enough to drive LED displays directly. All port pins have indi-
vidually selectable pull-up resistors with a supply-voltage invariant resistance. All I/O pins have
protection diodes to both V
cal Characteristics” on page 155
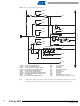
Figure 11-1. I/O Pin Equivalent Schematic
All registers and bit references in this section are written in general form. A lower case “x” repre-
sents the numbering letter for the port, and a lower case “n” represents the bit number. However,
when using the register or bit defines in a program, the precise form must be used. For example,
PORTB3 for bit no. 3 in Port B, here documented generally as PORTxn.
Three I/O memory address locations are allocated for each port, one each for the Data Register
– PORTx, Data Direction Register – DDRx, and the Port Input Pins – PINx. The Port Input Pins
I/O location is read only, while the Data Register and the Data Direction Register are read/write.
However, writing a logic one to a bit in the PINx Register, will result in a toggle in the correspond-
ing bit in the Data Register. In addition, the Pull-up Disable – PUD bit in MCUCR disables the
pull-up function for all pins in all ports when set.
Using the I/O port as General Digital I/O is described in
63. Most port pins are multiplexed with alternate functions for the peripheral features on the
device. How each alternate function interferes with the port pin is described in
Functions” on page
nate functions.
Note that enabling the alternate function of some of the port pins does not affect the use of the
other pins in the port as general digital I/O.
Pxn
67. Refer to the individual module sections for a full description of the alter-
CC
and Ground as indicated in
for a complete list of parameters.
C
pin
“Ports as General Digital I/O” on page
Figure 11-1 on page
"General Digital I/O" for
See Figure
R
Details
pu
Logic
62. See
“Alternate Port
8048B–AVR–03/09
“Electri-
Related parts for ATTINY43U-MU
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 512B FL 32B SRAM TIMER ATTINY4 12MHz
Manufacturer:
Atmel

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU AVR 512B FLASH SOT-23-6
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU AVR 512B FLASH SOT-23-6
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR AVR/AVR32
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: