PIC18F45K22-I/P Microchip Technology Inc., PIC18F45K22-I/P Datasheet - Page 38

PIC18F45K22-I/P
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F45K22-I/P
Description
40 PDIP .600in TUBE, 32KB, Flash, 1536bytes-RAM, 8-bit Family, nanoWatt XLP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet
1.PIC18F45K22-IP.pdf
(496 pages)
Specifications of PIC18F45K22-I/P
A/d Inputs
28-Channel, 10-Bit
Comparators
2
Cpu Speed
16 MIPS
Eeprom Memory
256 Bytes
Input Output
35
Interface
I2C/SPI/UART/USART
Memory Type
Flash
Number Of Bits
8
Package Type
40-pin PDIP
Programmable Memory
32K Bytes
Ram Size
1.5K Bytes
Speed
64 MHz
Temperature Range
–40 to 125 °C
Timers
3-8-bit, 4-16-bit
Voltage, Range
1.8-5.5 V
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
RoHS Compliant part
Electrostatic Device
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
3 400
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/PT
Manufacturer:
SST
Quantity:
3 400
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
PIC18F45K22-I/PT
Manufacturer:
MIC
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 38 of 496
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
PIC18(L)F2X/4XK22
2.5.2
The Low-Frequency Internal Oscillator (LFINTOSC) is
a 31.25 kHz internal clock source. The LFINTOSC is
not tunable, but is designed to be stable across temper-
ature and voltage. See
acteristics”
specifications.
The output of the LFINTOSC can be a clock source to
the primary clock or the INTOSC clock (see
The LFINTOSC is also the clock source for the Power-
up Timer (PWRT), Watchdog Timer (WDT) and Fail-
Safe Clock Monitor (FSCM).
2.5.3
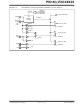
The HFINTOSC (16 MHz) and MFINTOSC (500 MHz)
outputs connect to a divide circuit that provides
frequencies of 16 MHz to 31.25 kHz. These divide
circuit
LFINTOSC output, are multiplexed to provide a single
INTOSC clock output (see
bits of the OSCCON register, the MFIOSEL bit of the
OSCCON2 register and the INTSRC bit of the
OSCTUNE register, select the output frequency of the
internal oscillators. One of eight frequencies can be
selected via software:
• 16 MHz
• 8 MHz
• 4 MHz
• 2 MHz
• 1 MHz (Default after Reset)
• 500 kHz (MFINTOSC or HFINTOSC)
• 250 kHz (MFINTOSC or HFINTOSC)
• 31 kHz (LFINTOSC, MFINTOSC or HFINTOSC)
2.5.4
The factory calibrates the internal oscillator block outputs
(HFINTOSC/MFINTOSC) for 16 MHz/500 kHz. However,
this frequency may drift as V
It is possible to adjust the HFINTOSC/MFINTOSC fre-
quency by modifying the value of the TUN<5:0> bits in the
OSCTUNE register. This has no effect on the LFINTOSC
clock source frequency.
Tuning the HFINTOSC/MFINTOSC source requires
knowing when to make the adjustment, in which direc-
tion it should be made and, in some cases, how large a
change is needed. Three possible compensation tech-
niques are discussed in the following sections. However,
other techniques may be used.
DS41412D-page 38
frequencies,
LFINTOSC
FREQUENCY SELECT BITS (IRCF)
INTOSC FREQUENCY DRIFT
for
Section 27.0 “Electrical Char-
the
along
Figure
DD
LFINTOSC
or temperature changes.
with
2-1). The IRCF<2:0>
the
Figure
31.25 kHz
accuracy
2-1).
Preliminary
2.5.4.1
An adjustment may be required when the EUSART
begins to generate framing errors or receives data with
errors while in Asynchronous mode. Framing errors
indicate that the device clock frequency is too high; to
adjust for this, decrement the value in OSCTUNE to
reduce the clock frequency. On the other hand, errors
in data may suggest that the clock speed is too low; to
compensate, increment OSCTUNE to increase the
clock frequency.
2.5.4.2
This technique compares device clock speed to some
reference clock. Two timers may be used; one timer is
clocked by the peripheral clock, while the other is
clocked by a fixed reference source, such as the
Timer1 oscillator.
Both timers are cleared, but the timer clocked by the
reference generates interrupts. When an interrupt
occurs, the internally clocked timer is read and both
timers are cleared. If the internally clocked timer value
is greater than expected, then the internal oscillator
block is running too fast. To adjust for this, decrement
the OSCTUNE register.
2.5.4.3
A CCP module can use free running Timer1, Timer3 or
Timer5 clocked by the internal oscillator block and an
external event with a known period (i.e., AC power
frequency). The time of the first event is captured in the
CCPRxH:CCPRxL registers and is recorded for use later.
When the second event causes a capture, the time of the
first event is subtracted from the time of the second
event. Since the period of the external event is known,
the time difference between events can be calculated.
If the measured time is much greater than the calcu-
lated time, the internal oscillator block is running too
fast; to compensate, decrement the OSCTUNE register.
If the measured time is much less than the calculated
time, the internal oscillator block is running too slow; to
compensate, increment the OSCTUNE register.
Compensating with the EUSART
Compensating with the Timers
Compensating with the CCP Module
in Capture Mode
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Related parts for PIC18F45K22-I/P
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
20-Pin USB Flash Microcontrollers
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP [Microchip Technology]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 48KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 64KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 TQFP 10x10x1mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128kB Flash, 4kB RAM, 1kB EE, 16MIPS, NanoWatt XLP, LCD, 5V 80 TQFP 12x12x1mm T/
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm TUBE
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 TQFP 10x10x1mm TRAY
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
128kB Flash, 4kB RAM, 1kB EE, 16MIPS, NanoWatt XLP, LCD, 5V 80 TQFP 12x12x1mm TR
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology