NHE6300ESB S L7XJ Intel, NHE6300ESB S L7XJ Datasheet

NHE6300ESB S L7XJ
Specifications of NHE6300ESB S L7XJ
Related parts for NHE6300ESB S L7XJ
NHE6300ESB S L7XJ Summary of contents
Page 1
... Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Datasheet November 2007 ® Notice: The Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request. Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 2
... Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order. Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained by calling 1-800-548-4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com. ...
Page 3
... OS capability to call TCO BIOS Timers to detect improper CPU reset — Alert On Lan (AOL) to enable heartbeats and system event reporting via LAN controller — Supports CPU BIST — Supports ability to disable external devices ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 3 ...
Page 4
... Configurable granularity from 1µ min ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 4 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH— • SMBus — Flexible SMBus/SMLink architecture to optimize for ASF and eliminate board requirements of SMBus 2.0 compliance — Supports SMBus 2.0 Specification — Host interface allows CPU to communicate via SMBus — ...
Page 5
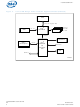
... AGP ® Intel 875P MCH HL 1.5 Hublink 1.5 LPC IDE IDE ® Intel PCI-X 6300ESB I/O SATA Controller PCI Hub SATA GPIO AC'97 Memory 1GB Hard Disk Hard Disk / CD-DVD Hard Disk Hard Disk B2475-02 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 5 ...
Page 6
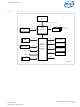
... I/O Controller Hub DS 6 CPU Processor System Bus ® Intel HL 1.5 875P MCH Hublink ® Intel PCI-X 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub ® Intel 6300ESB ICH— Memory 256 MB to 1GB Hard Disk GPIO's SIO B2476-02 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 7
... Processor System Bus ® Intel HL 1.5 E7210 MCH Hublink 1.5 PCI-X IDE IDE ® Intel 6300ESB PCI I/O SATA Controller Hub SATA GPIO LPC Memory 1GB Hard Disk Hard Disk Hard Disk Hard Disk B2477-03 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 7 ...
Page 8
... LPC Bridge (with System and Management Functions) (D31:F0)...............................97 5.2.1 LPC Cycle Types .....................................................................................98 5.2.1.1 Start Field Definition ..................................................................98 5.2.1.2 Cycle Type/Direction (CYCTYPE + DIR).........................................99 5.2.1.3 SIZE........................................................................................99 5.2.1.4 SYNC .......................................................................................99 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 8 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 9
... SYNC Error Indication .............................................................. 100 5.2.1.7 LFRAME# Usage ..................................................................... 101 5.2.1.8 I/O Cycles.............................................................................. 102 5.2.1.9 Bus Master Cycles ................................................................... 102 5.2.1.10 LPC Power Management........................................................... 102 5.2.1.11 Configuration and Intel 5.3 DMA Operation (D31:F0) .................................................................................. 103 5.3.1 DMA Overview ..................................................................................... 103 5.3.2 Channel Priority ................................................................................... 104 5.3.2.1 Fixed Priority .......................................................................... 104 5 ...
Page 10
... Signal Differences ................................................................... 143 5.10.2.2 Dual Processor Power Management............................................ 143 5.11 Power Management (D31:F0) ............................................................................ 145 5.11.1 Features .............................................................................................. 145 ® 5.11.2 Intel 6300ESB ICH Power States and Transition Rules ............................. 146 5.11.3 System Power Planes ............................................................................ 148 ® 5.11.4 Intel 6300ESB ICH Power Planes .......................................................... 148 5 ...
Page 11
... GPIO Mapping...................................................................................... 176 5.13.2 Power Wells......................................................................................... 178 5.13.3 SMI# and SCI Routing .......................................................................... 178 5.13.4 Triggering ........................................................................................... 178 5.14 IDE Controller (D31:F1) ................................................................................... 178 5.14.1 Overview ............................................................................................ 178 5.14.2 PIO Transfers ...................................................................................... 179 5.14.2.1 Overview ............................................................................... 179 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 11 ...
Page 12
... Command Register, Status Register, and TD Status Bit Interaction 204 5.17.3.4 Transfer Queuing .................................................................... 204 5.17.4 Data Encoding and Bit Stuffing ............................................................... 208 5.17.5 Bus Protocol......................................................................................... 208 5.17.5.1 Bit Ordering............................................................................ 208 5.17.5.2 SYNC Field ............................................................................. 208 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 12 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 13
... I 5.19.2.3 Heartbeat for Use with the External LAN Controller ...................... 249 5.19.3 Bus Arbitration..................................................................................... 249 5.19.4 Bus Timing .......................................................................................... 249 5.19.4.1 Clock Stretching ..................................................................... 249 5.19.4.2 Bus Time Out (Intel November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US C Behavior .......................................................................... 249 ® 6300ESB ICH as SMBus Master) ................. 250 ® ...
Page 14
... Offset 02 - 03h: DID—Device ID Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) .................... 288 7.1.3 Offset 04 - 05h: CMD—Command Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0)................... 289 7.1.4 Offset 06 - 07h: PD_STS—Primary Device Status Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) .. 290 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 14 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 15
... Offset 40 - 43h: HI_CMD—Hub Interface Command Control Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0).................................................................. 304 7.1.26 Offset 44 - 45h: DEVICE_HIDE—Secondary PCI Device Hiding Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) ........................................................ 305 7.1.27 Offset 50 - 51h: CNF—Intel D30:F0)306 7.1.28 Offset 58 - 5Bh: D30_PNE — PERR#_NMI_ENABLE Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) 307 7.1.29 Offset 70h: MTT—Multi-Transaction Timer Register (HUB-PCI— ...
Page 16
... I/F—D31:F0) ................................................................................ 341 8.1.35 Offset F0h: FWH_DEC_EN2—FWH Decode Enable 2 Register (LPC I/F—D31:F0) . 342 8.1.36 Offset F2h: FUNC_DIS—Function Disable Register (LPC I/F—D31:F0) ................................................................................ 343 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 16 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 17
... CPU Interface Registers.................................................................................... 381 8.7.1 NMI_SC—NMI Status and Control Register ............................................... 381 8.7.2 NMI_EN—NMI Enable (and Real Time Clock Index) ................................... 382 8.7.3 PORT92—Fast A20 and Init Register ....................................................... 382 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 17 ...
Page 18
... GPIO Register I/O Address Map .............................................................. 425 8.10.2 Offset GPIOBASE + 00h: GPIO_USE_SEL—GPIO Use Select Register ........... 426 8.10.3 Offset GPIOBASE + 04h: GP_IO_SEL—GPIO Input/Output Select Register .... 426 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 18 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 19
... Offset 00 - 01h: VID—Vendor Identification Register (USB—D29:F0/F1)................................................................................ 462 10.1.2 Offset 02 - 03h: DID—Device Identification Register (USB—D29:F0/F1)................................................................................ 462 10.1.3 Offset 04 - 05h: CMD—Command Register (USB—D29:F0/F1)................................................................................ 463 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 19 ...
Page 20
... Next Item Pointer #1............................................................ 493 11.1.16Offset 52 - 53h: Power Management Capabilities ...................................... 493 11.1.17Offset 54 - 55h: Power Management Control/Status .................................. 494 11.1.18Offset 58h: Debug Port Capability ID....................................................... 495 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 20 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 21
... Offset 68 - 6Bh: USB EHCI Legacy Support Extended Capability ................. 499 11.1.26 Offset 6C - 6Fh: USB EHCI Legacy Support Extended Control/Status ........... 500 11.1.27 Offset 70 - 73h: Intel Specific USB EHCI SMI ........................................... 501 11.1.28 Offset 80h: Access Control .................................................................... 503 11.1.29 HS_ Ref_V_USB HS Reference Voltage Register........................................ 503 11 ...
Page 22
... MMBAR—Mixer Base Address Register (Audio—D31:F5)...... 557 13.1.13Offset 1C - 1Fh: MBBAR—Bus Master Base Address Register (Audio—D31:F5).... 558 13.1.14Offset 2D - 2Ch: SVID—Subsystem Vendor ID Register (Audio—D31:F5) ..... 559 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 22 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 23
... Offset 2E - 2Fh: SID—Subsystem ID (Modem—D31:F6) ............................ 588 14.1.14 Offset 34h: CAP_PTR—Capabilities Pointer (Modem—D31:F6) ................................................................................ 589 14.1.15 Offset 3Ch: INTR_LN—Interrupt Line Register (Modem—D31:F6) ................................................................................ 589 14.1.16 Offset 3Dh: INT_PIN—Interrupt Pin (Modem—D31:F6) .............................. 590 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 23 ...
Page 24
... Base + 08h: General Interrupt Status Register ................................ 628 16.4.21Offset Base + 0Ch: Reload Register......................................................... 629 16.5 Theory Of Operation......................................................................................... 629 16.5.1 RTC Well and WDT_TOUT# Functionality.................................................. 629 16.5.2 Register Unlocking Sequence.................................................................. 629 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 24 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 25
... Prefetchable Memory Base and Limit Address Registers, Upper 32-Bit Registers .. 648 18.3 VGA Addressing .............................................................................................. 649 18.4 Configuration Addressing.................................................................................. 650 18.4.1 Type 0 Accesses to the Intel 18.4.2 Type 1 to Type 0 Translation.................................................................. 650 18.4.3 Type 1 to Type 1 Forwarding ................................................................. 651 18.4.4 Type 1 to Special Cycle Forwarding......................................................... 651 18.5 Transaction Ordering ....................................................................................... 652 18.5.1 Comparison of Rules vs. a PCI – ...
Page 26
... Transaction Termination ........................................................................ 686 18.7.7.1 Normal Master Termination....................................................... 686 18.7.7.2 Master Abort Termination ......................................................... 686 18.7.7.3 Target Termination Received by the Intel 18.7.7.4 Target Termination Initiated by the Intel 18.7.8 LOCK Cycles ........................................................................................ 687 18.7.9 Error Handling...................................................................................... 687 18.7.9.1 Data Parity Errors.................................................................... 689 18.7.9.2 System Errors......................................................................... 690 18 ...
Page 27
... LPC Transfers ...................................................................................... 707 19.4.3.1 I/O Transfers ......................................................................... 707 19.5 Logical Device 4 and 5: Serial Ports (UARTs) ....................................................... 707 19.5.1 Overview ............................................................................................ 707 19.5.1.1 UART Feature List ................................................................... 708 19.5.1.2 UART Operational Description ................................................... 709 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 27 ...
Page 28
... CAP—Capabilities Pointer Register (SATA–D31:F2) .................................................................................... 747 20.1.17Offset 3Ch: INTR_LN—Interrupt Line Register (SATA–D31:F2) .................................................................................... 747 20.1.18Offset 3Dh: INTR_PN—Interrupt Pin Register (SATA–D31:F2) .................................................................................... 748 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 28 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 29
... System Clocks and General Timing ......................................................... 815 22.5.3 IDE and Ultra ATA Timing ...................................................................... 817 22.5.4 USB.................................................................................................... 820 22.5.5 SMBus ................................................................................................ 821 22.5.6 Power and Reset .................................................................................. 822 22.5.7 AC’97 and Miscellaneous ....................................................................... 824 23 Testability ............................................................................................................. 825 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 29 ...
Page 30
... Test Mode Description ...................................................................................... 825 23.2 Tri-State Mode ................................................................................................ 826 23.3 XOR Chain Mode.............................................................................................. 826 23.3.1 XOR Chain Testability Algorithm Example................................................. 826 Index ..................................................................................................................... 835 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 30 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 31
... SDIN Wake Signaling.............................................................................................. 271 ® 28 Intel 6300ESB ICH Device Diagram ........................................................................ 277 29 WDT Block Diagram ............................................................................................... 616 ® 30 Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Appearance to Software ........................................ 650 31 Type ‘1’ to Type ‘0’ Translation ................................................................................ 651 32 SIU Block Diagram ................................................................................................ 704 33 Example UART Data Frame...................................................................................... 709 34 Start Frame Timing with Source Sampled a Low Pulse on IRQ1 ...
Page 32
... Timing ............................................................................................. 823 Timings............................................................................................ 824 65 AC’97 Data Input and Output Timings ....................................................................... 824 66 Test Mode Entry (XOR Chain Example) ...................................................................... 826 67 Example XOR Chain Circuitry ................................................................................... 826 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 32 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 33
... Arbitration Cycles................................................................................................... 126 48 APIC Message Formats ........................................................................................... 126 49 EOI Message ......................................................................................................... 127 50 Short Message....................................................................................................... 128 51 APIC Bus Status Cycle Definition .............................................................................. 129 52 Lowest Priority Message (Without Focus Processor)..................................................... 130 53 Remote Read Message ............................................................................................ 131 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 33 ...
Page 34
... Data Frame Format................................................................................................. 137 58 Configuration Bits Reset By RTCRST# Assertion.......................................................... 140 59 INIT# Going Active ................................................................................................. 141 60 NMI Sources .......................................................................................................... 143 61 DP Signal Differences .............................................................................................. 143 62 General Power States for Systems Using Intel 63 State Transition Rules for Intel 64 System Power Plane ............................................................................................... 148 65 Causes of SCI ........................................................................................................ 149 66 Causes of SMI#...................................................................................................... 150 67 Causes of TCO SMI# ...
Page 35
... Input Slot 1 Bit Definitions ...................................................................................... 267 140 Output Tag Slot 0 .................................................................................................. 269 141 AC-link State during PXPCIRST# .............................................................................. 273 142 PCI Devices and Functions....................................................................................... 276 143 Fixed I/O Ranges Decoded by Intel 144 Variable I/O Decode Ranges .................................................................................... 281 145 Memory Decode Ranges from CPU Perspective ........................................................... 283 146 ...
Page 36
... Offset 44 - 45h: DEVICE_HIDE—Secondary PCI Device Hiding Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) 305 173 Offset 50 - 51h: CNF—Intel® 6300ESB ICH Configuration Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) 174 Offset 58 - 5Bh: D30_PNE — PERR#_NMI_ENABLE Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0)............. 307 175 Offset 70h: MTT—Multi-Transaction Timer Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) 176 Offset 82h: PCI_MAST_STS— ...
Page 37
... NMI_EN—NMI Enable (and Real Time Clock Index) ..................................................... 382 268 PORT92—Fast A20 and Init Register ......................................................................... 382 269 COPROC_ERR—Coprocessor Error Register ................................................................ 383 270 RST_CNT—Reset Control Register ............................................................................ 383 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US .................................................................................. 345 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 37 ...
Page 38
... Offset GPIOBASE + 38h: GP_LVL2—GPIO Level for Input or Output 2 Register ............... 432 322 PCI Configuration Map (IDE-D31:F1)......................................................................... 435 323 Offset 00 - 01h: VID—Vendor ID Register (LPC I/F—D31:F1) ....................................... 436 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 38 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents (D31:F0)............................................ 384 ..................................... 392 Order Number: 300641-004US November 2007 ...
Page 39
... USB I/O Registers .................................................................................................. 473 371 Offset 00 - 01h: USBCMD—USB Command Register .................................................... 474 372 Run/Stop, Debug Bit Interaction SWDBG (Bit 5), Run/Stop (Bit 0) Operation ................. 477 373 Offset 02 - 03h: USBSTA—USB Status Register .......................................................... 478 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ....................................... 455 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 39 ...
Page 40
... Offset 68 - 6Bh: USB EHCI Legacy Support Extended Capability 404 Offset 6C - 6Fh: USB EHCI Legacy Support Extended Control/Status 405 Offset 70 - 73h: Intel Specific USB EHCI SMI ............................................................. 501 406 Offset 80h: Access Control....................................................................................... 503 407 HS_ Ref_V_USB HS Reference Voltage Register 408 Offset 00h: CAPLENGTH—Capability Registers Length.................................................. 504 409 Offset 02 - 03h: HCIVERSION— ...
Page 41
... Offset 41h: CFG—Configuration Register (Audio—D31:F5) ........................................... 562 480 Offset 50h: PID—PCI Power Management Capability ID Register (Audio—D31:F5)........... 562 481 Offset 52h: PC—Power Management Capabilities Register (Audio—D31:F5).................... 563 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 41 ...
Page 42
... Offset 54h: PCS—Power Management Control and Status Register (Audio—D31:F5) ........ 563 ® 483 Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Audio Mixer Register Configuration .......................... 565 484 Native Audio Bus Master Control Registers ................................................................. 566 485 x_BDBAR—Buffer Descriptor Base Address Register .................................................... 568 486 x_CIV— ...
Page 43
... Offset 06: PSTS—Primary Status .............................................................................. 657 588 Offset 08: RID—Revision ID .................................................................................... 658 589 Offset 09: CC—Class Code ...................................................................................... 659 590 Offset 0C: CLS—Cache Line Size .............................................................................. 659 591 Offset 0D: PLT—Primary Latency Timer ..................................................................... 660 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 43 ...
Page 44
... Offset 58: PX_USTC - PCI-X Upstream Split Transaction Control ................................... 678 613 Offset 5C: PX_DSTC - PCI-X Downstream Split Transaction Control ............................... 679 614 Offset E0: ACNF – Additional Intel® 6300ESB ICH Configuration................................... 680 615 Offset E4: PCR - PCI Compensation Register .............................................................. 681 616 Offset F0: HCCR - Hub Interface Command/Control Register ........................................ 682 617 Offset F8h: PC33 - Prefetch Control – ...
Page 45
... Offset A4h - A7h: SRD—SATA Registers Data (SATA–D31:F2) ...................................... 761 695 STTT—SATA TX Termination Test Register A (SATA–D31:F2) ....................................... 762 696 STOT — SATA TX Output Test Register (SATA–D31:F2) ............................................... 762 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 45 ...
Page 46
... XOR Chain #6 (RTCRST# asserted for 52 PCI clocks while PWROK active)...................... 834 739 XOR Chain #7 (RTCRST# asserted for 60 PCI clocks while PWROK active)...................... 834 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 46 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 47
... RSM_PWROK signals which do not exist in 6300ESB Table 731, Figure 66: Updated to correct timing requirements for entering test mode. Section 5.7 and Section 8.5: Removed PCI register references for APIC0. APIC0 registers are purely memory mapped. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 47 ...
Page 48
... A change bar to left of text, a table row or a figure heading indicates this item is either new or modified from the previous version of the document. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 48 Description register bits. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 49
... About This Document This datasheet is intended for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and BIOS vendors creating products based on the Intel manual assumes a working knowledge of the vocabulary and principles of USB, IDE, AC’97, SMBus, PCI, ACPI, and LPC. Although some details of these features are described herein, refer to the individual industry specifications listed in complete details ...
Page 50
... F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6 and F7. For example Device 31 Function 5 is abbreviated as D31:F5, Bus 1 Device 8 Function 0 is abbreviated as B1:D8:F0. Generally, the bus number will not be used, and may be considered to be Bus 0. Note that the Intel 6300ESB ICH’s external PCI bus is typically Bus 1, but may be assigned a different number depending upon system configuration. Chapter 6, “ ...
Page 51
... SIU, its features, LPC interface, serial ports provides a detailed description provides ballout information, signal lists and provides AC and DC characteristics and AC provides information on test modes and scan chains. provides a detailed ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 51 ...
Page 52
... Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 52 This page intentionally left blank. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—1 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 53
... UART clock must use a 14.7456 MHz discrete clock frequency; most clock chips do not circuit. provide this frequency. An option will be to use the 48.0 MHz clock. Main Clock 1.5 GHz clock generated internal to the Intel Generator 6300ESB ICH for use by SATA phy. 2 Figure 4 shows the assumed Usage 6300ESB ICH, PCI, LPC I/F. This ® ...
Page 54
... XTAL ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub MHz 33 MHz Clock 14.31818 MHz Gen. 48 MHz 100 MHz Diff. Pair 12.288 MHz AC’97 Codec(s) SUSCLK# (32 kHz) ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—2 PCI Clocks (33 MHz) 14.31818 MHz 48 MHz November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 55
... Hub Interface 1.5 mode this signal is not differential and is the first of the two strobe signals. Hub Interface Compensation: Used for Hub Interface buffer compensation. ® NOTE: The Intel 6300ESB ICH will only support RCOMP, not the ZCOMP mode. Hub Interface Clock: 66 MHz clock input for Hub Interface also I used for some other internal units ...
Page 56
... Hub Interface mode. Description Firmware Hub Signals. Muxed with LPC address signals. Internal pull-ups are provided. Firmware Hub Signals. Muxed with LPC LFRAME# signal. LFRAME#: Indicates the start of an LPC cycle abort. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—3 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 57
... Device Select: The Intel 6300ESB ICH asserts DEVSEL# to claim a PCI ® transaction output, the Intel when a PCI master peripheral attempts an access to an internal Intel 6300ESB ICH address or an address destined for Hub Interface (main memory or AGP input, DEVSEL# indicates the response to an ® ...
Page 58
... Initiator of PCI read transactions and when it is the Target of PCI write transactions. It also checks parity on the address phase when it is the target of PCI transitions parity error is detected, the Intel ICH will set the appropriate internal status bits, and has the option to generate an NMI# or SMI# ...
Page 59
... PCI Power Management Event: Driven by PCI peripherals to wake the system from low-power states S1-S5. If can also cause an SCI from the S0 state. Note that in some cases the Intel PME# active (low) due to an internal wake event. It will not drive PME# high (but it may be pulled up using the internal pull-up resistor). ...
Page 60
... Memory Read Line Memory Write and Invalidate All command encodings not shown are reserved. The Intel ICH does not decode reserved values, and therefore will not respond when a PCI-X master generates a cycle using one of the reserved values. Bus Command and Byte enables upper 4 bits: These signals are a multiplexed command field and byte enable field ...
Page 61
... ICH Target is prepared to latch data PXTRDY input to the Intel ® the Intel 6300ESB ICH is the Initiator and an output from the Intel ® 6300ESB ICH when the Intel 6300ESB ICH is a Target. PXTRDY# is tri-stated from the leading edge of PXPCIRST#. PXTRDY# remains ® ...
Page 62
... If one of these errors is active, the pin is low. If none are active, then the pin is high. PCI/PCI-X Reset: The Intel reset devices that reside on the PCI-X bus. The Intel asserts PXPCIRST# during power-up and when S/W initiates a hard reset sequence through the RC (CF9h) register. The Intel ...
Page 63
... It has the same timing as PXFRAME#. When the Intel 6300ESB ICH is the initiator, this signal is an output. When the Intel 6300ESB ICH is the target this signal is an input PCI-X interface acknowledge 64-bit transfer: This is asserted by the target only when PXREQ64# is asserted by the initiator, to indicate the target’ ...
Page 64
... IDE connector asserted by the IDE device to request a I data transfer, and used in conjunction with the PCI bus master IDE function and are not associated with any AT compatible DMA channel. There is a weak internal pull-down resistor on these signals. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—3 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 65
... Primary and Secondary Disk I/O Read (PIO and Non-Ultra DMA): This is the command to the IDE device that it may drive data onto the PDD or SDD lines. Data is latched by the Intel ICH on the deassertion edge of PDIOR# or SDIOR#. The IDE device is selected either by the ATA register file chip selects (PDCS1# or SDCS1#, PDCS3# or SDCS3#) and the PDA or SDA lines, or the IDE DMA acknowledge (PDDAK# or SDDAK#) ...
Page 66
... Route Control Register. In APIC mode, these signals are connected to the internal I/O APIC in the following fashion: I PIRQ[A]# IRQ16 PIRQ[B]# IRQ17 PIRQ[C]# IRQ18 PIRQ[D]# IRQ19 This frees the legacy interrupts. These signals are 5V tolerant. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—3 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 67
... USB Resistor Bias: Analog connection point for an external O resistor to ground. USBRBIAS should be connected to USBRBIAS# as close to the resistor as possible. USB Resistor Bias Complement: Analog connection point for I an external resistor to ground. USBRBIAS# should be connected to USBRBIAS as close to the resistor as possible. Description ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 67 ...
Page 68
... The signal is used to shut power off to all non-critical systems when in the S5 (Soft Off) state. Power OK: When asserted, PWROK is an indication to the Intel 6300ESB ICH that core power and PCICLK have been stable for at least 1 ms. PWROK may be driven asynchronously. When PWROK is ® ...
Page 69
... CPUSLP# signal when going to the S1 state. It will go active for all other sleep states. Numeric Coprocessor Error: This signal is tied to the coprocessor error signal on the processor. FERR# is only used when the Intel 6300ESB ICH coprocessor error reporting function is enabled in the General Control Register (D31:F0:Offset D0.bit 5). When FERR# is ® ...
Page 70
... DS 70 Description Ignore Numeric Error: This signal is connected to the ignore error pin on the CPU. IGNNE# is only used when the Intel coprocessor error reporting function is enabled in the General Control Register (D31:F0:Offset D0.bit 5). When FERR# is active, indicating a O coprocessor error, a write to the Coprocessor Error Register (F0h) causes the IGNNE asserted ...
Page 71
... RTCX1 may be driven with the desired clock rate. Crystal Input 2: Connected to the 32.768 KHz crystal. When no external crystal is used, then RTCX2 should be left floating. Bias Voltage for Oscillator: Sets the proper biasing for the oscillator. I Expected voltage 200 mV. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 71 ...
Page 72
... RTC Reset: When asserted, this signal resets register bits in the RTC well and sets the RTC_PWR_STS bit (bit 2 in GEN_PMCON3 register). NOTES: ® 1. Clearing CMOS in an Intel I done by using a jumper on RTCRST# or GPI, or using SAFEMODE strap. Implementations should not attempt to clear CMOS by using a jumper to pull VccRTC low ...
Page 73
... MARKING condition (logic ‘1’ state). CLEAR TO SEND: Active low, this pin indicates that data may be ® exchanged between the Intel These pins have no effect on the transmitter. NOTE: These pins could be used as Modem Status Input whose condition may be tested by the processor by reading bit 4 (CTS the Modem Status register (MSR) ...
Page 74
... Description DATA SET READY for UART 0, 1: Active low, this pin indicates that the external agent is ready to communicate with the Intel ICH UARTS. These pins have no effect on the transmitter. NOTE: These pins could be used as Modem Status Input whose condition may be tested by the processor by reading bit 5 I (DSR) of the Modem Status register ...
Page 75
... Reserved. These GPIO are not implemented. Fixed as Output only. Core power well. May instead be used for O WDT_TOUT#. May be input or output. Core power well. May instead be used for I/O PXIRQ[0:3]#. I/O May be input or output. Core power well. GPIO[37,39] are unmuxed. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 75 ...
Page 76
... RTC battery is removed or completely drained. NOTE: Implementations should not attempt to clear CMOS by using a jumper to pull VccRTC low. Clearing CMOS in an Intel ICH-based platform may be done by using a jumper on RTCRST# or GPI, or using SAFEMODE strap. ® ...
Page 77
... PWROK strapping definition. The status of this strap is readable via the SAFE_MODE bit (bit 2, D31: F0, Offset D4h). This signal has a weak internal pull-up. The Intel Rising Edge 6300ESB ICH starts driving it when PXPCIRST# of PWROK goes high. The status of this strap is readable via D31: F0, Offset D5h, bit 5) ...
Page 78
... D29:F5 IOxAPIC D29, F7 USB EHCI Hub interface to D28:F0 PCI-X Bridge D31:F2 RAID Controller NOTE: Refer to the latest Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Specification Update for the value of the Revision Identification Registers. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 78 Device A0 ID ...
Page 79
... S3, S4, S5 state, this plane is assumed to be shut off. VccRTC: When other power is available (from the main supply), external diode coupling will provide power to reduce the drain on the RTC battery. Assumed to operate from 3.3 V down to 2 Figure 5. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 79 ...
Page 80
... Lithium Coin Cell 2.0 – 3.0V Resistor Type pull-down pull-down pull-down pull-down pull-down pull-down pull-up pull-up pull-up pull-up pull-up pull-up pull-up pull-down ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—4 1.5 V Core Well FET Switch 1.5 V Suspend Well VccRTC RTC Well 3.3 V Nominal Value Notes 20K 1 ...
Page 81
... ICH IDE signals that have integrated series Integrated Series Termination Resistor Value approximately 33 Ω (See Note) shows the power plane associated with the output and I/O ® Tri-state. The Intel 6300ESB ICH is not driving the signal high or low. ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH is driving the signal to a logic ‘ ...
Page 82
... Note: The signal levels are the same in S4 and S5. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 82 The power plane is off, so the Intel driving. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—4 ® 6300ESB ICH is not November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 83
... I/O NOTES: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH sets these signals at reset for CPU frequency strap. 2. The states of main I/O signals are taken at the times during PXPCIRST# and immediately after PXPCIRST#. 3. The states of resume I/O signals are taken at the times during RSMRST# and immediately after RSMRST# 4 ...
Page 84
... I/OD NOTES: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH sets these signals at reset for CPU frequency strap. 2. The states of main I/O signals are taken at the times during PXPCIRST# and immediately after PXPCIRST#. 3. The states of resume I/O signals are taken at the times during RSMRST# and immediately after RSMRST# 4 ...
Page 85
... SDA[2:0] NOTES: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH sets these signals at reset for CPU frequency strap. 2. The states of main I/O signals are taken at the times during PXPCIRST# and immediately after PXPCIRST#. 3. The states of resume I/O signals are taken at the times during RSMRST# and immediately after RSMRST# 4 ...
Page 86
... I NOTES: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH sets these signals at reset for CPU frequency strap. 2. The states of main I/O signals are taken at the times during PXPCIRST# and immediately after PXPCIRST#. 3. The states of resume I/O signals are taken at the times during RSMRST# and immediately after RSMRST# 4 ...
Page 87
... O NOTES: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH sets these signals at reset for CPU frequency strap. 2. The states of main I/O signals are taken at the times during PXPCIRST# and immediately after PXPCIRST#. 3. The states of resume I/O signals are taken at the times during RSMRST# and immediately after RSMRST# 4 ...
Page 88
... I/O NOTES: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH sets these signals at reset for CPU frequency strap. 2. The states of main I/O signals are taken at the times during PXPCIRST# and immediately after PXPCIRST#. 3. The states of resume I/O signals are taken at the times during RSMRST# and immediately after RSMRST# 4 ...
Page 89
... I/O NOTES: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH sets these signals at reset for CPU frequency strap. 2. The states of main I/O signals are taken at the times during PXPCIRST# and immediately after PXPCIRST#. 3. The states of resume I/O signals are taken at the times during RSMRST# and immediately after RSMRST# 4 ...
Page 90
... Main I/O IDE Drive Main I/O PCI Bus Peripherals Main I/O IDE Drive External Pull-Up External Circuit Main I/O Thermal Sensor CPU I/O Thermal Sensor External Pull-Down ® Intel 6300ESB ICH— Static Low Low Low Low Low Low Low Low ...
Page 91
... USB, IDE or AC’97 will appear on the PCI bus. When the Intel programmed for positive decode, the Intel appearing on the external PCI bus in medium decode time. When the Intel ICH is programmed for subtractive decode, the Intel cycles in subtractive time. When the Intel subtractive decode, these cycles may be claimed by another positive decode agent out on PCI ...
Page 92
... The NMI may also be routed to instead cause an SMI#. Note: Note that the Intel active onto the PCI bus. The external SERR# signal is an input into the Intel ICH driven only by external PCI devices. The conceptual logic diagrams in Figure 7 illustrate all sources of SERR#, along with their respective enable and status bits ...
Page 93
... SERR_EN (D30:04h.8) D30:3Eh.0 AND D30:3Eh.1 AND PCI Address Parity Error SERR_EN (D30:04h.8) AND AND OR AND SERR_RTA (D30:92h.2) AND OR AND (D28:04h.8) AND PX_SERR#_ENABLE AND AND Pre-latch P_SSE (To T-Unit) P_SSE (D30:06h.14) OR AND SSE for PCI-X (D28:06h.14) AND ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 93 ...
Page 94
... Receive DO_SERR message from HL MCHSERR_STS (TCOBASE+04h.bit 12) SERR_RTA_EN (D31:88h.2) ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 94 AND ERROR from XL-Unit IOCHK# via SERIRQ AND Received Target Abort ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 Pre-latch S_SSE (To T-Unit) S_SSE (D31:F0.06h.14) AND OR November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 95
... ICH may be programmed to cause an NMI (or SMI# when NMI is routed to SMI#) based on detecting a parity error. The conceptual logic diagram in Figure 8 details all the parity errors that the Intel with their respective enable bits, status bits, and the results. ® Note: The Intel 6300ESB ICH does not escalate a data parity mismatch reported by a PCI device (PERR#) across the P2P bridge ...
Page 96
... ICH logic will generate single D-word configuration read and write cycles on the PCI bus. The Intel cycle for configurations to the bus number matching the PCI bus. When the cycle is targeting a device behind an external bridge, the Intel cycle on the PCI bus. 5.1.6.2 ...
Page 97
... The rest of the cycle proceeds normally. 5.2 LPC Bridge (with System and Management Functions) (D31:F0) The LPC Bridge function of the Intel 0. In addition to the LPC bridge function, D31:F0 contains other functional units including DMA, Interrupt Controllers, Timers, Power Management, System Management, GPIO, and RTC. ...
Page 98
... Bus Master Write NOTES: 1. For memory cycles below 16M which do not target enabled FWH ranges, the Intel ICH will perform standard LPC memory cycles. It will only attempt 8-bit transfers. When the cycle appears on PCI as a 16-bit transfer, it will appear as two consecutive 8-bit transfers on LPC ...
Page 99
... Ready: SYNC achieved with no error. For DMA transfers, this also indicates DMA 0000 request deassertion and no more transfers desired for that channel. Short Wait: Part indicating wait-states. For bus master cycles, the Intel 0101 6300ESB ICH will not use this encoding. It will instead use the Long Wait encoding (see next encoding below) ...
Page 100
... In the case of multiple byte cycles, such as for memory and DMA cycles, an error SYNC terminates the cycle. Therefore, when the Intel bytes from a device, and if the device returns the error SYNC in the first byte, the other three bytes will not be transferred. ...
Page 101
... ICH Upon recognizing the SYNC field indicating an error, the Intel this the same as IOCHK# going active on the ISA bus. 5.2.1.7 LFRAME# Usage Start of Cycle For Memory, I/O, and DMA cycles, the Intel clock at the beginning of the cycle ICH will drive LAD[3:0] with the proper START field. ...
Page 102
... ICH will break the cycle up into multiple 8-bit transfers to consecutive I/O addresses. Note: When the cycle is not claimed by any peripheral (and subsequently aborted), the Intel 6300ESB ICH will return a value of all ones (FFh) to the processor. This is to maintain compatibility with ISA I/O cycles where pull-up resistors would keep the bus high when no device responds ...
Page 103
... ICH Bus Master Device Mapping and START Fields Bus Masters must have a unique START field. In the case of the Intel which supports two LPC bus masters, it will drive 0010 for the START field for grants to bus master #0 (requested through LDRQ[0]#) and 0011 for grants to bus master #1 (requested through LDRQ[1]# ...
Page 104
... CPURST is valid. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 104 Section 8.2, “DMA I/O Registers” Section 8.4.9, “OCW3—Operational Control Word 3 (Section 8.2, “DMA I/O Registers”). Table 37. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 for more November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 105
... I/O, Count By Words (Address Shifted) ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH maintains compatibility with the implementation of the DMA in the PC-AT which used the 8237. The DMA shifts the addresses for transfers to/from a 16-bit device count-by-words. Note that the least significant bit of the Low Page Register is dropped in 16-bit shifted mode ...
Page 106
... LDRQ# signal. To simplify the protocol, each peripheral on the LPC I/F has its own dedicated LDRQ# signal (they may not be shared between two separate peripherals). ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH has two LDRQ# inputs, allowing at least two devices to support DMA or bus mastering. ...
Page 107
... DMA cycle may still occur. The peripheral may choose not to respond to this cycle, in which case the host will abort it may choose to complete the cycle normally with any random data. This method of DMA deassertion should be prevented whenever possible, to limit boundary conditions both on the Intel November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Start ...
Page 108
... LPC interface. However, the host will not transfer this data into main memory. 5.4.6 DMA Request Deassertion An end of transfer is communicated to the Intel field transmitted by the peripheral. An LPC device must not attempt to signal the end of a transfer by deasserting LDREQ#. When a DMA transfer is several bytes, such as a transfer from a demand mode device, the Intel deassert the DMA request based on the data currently being transferred. ® ...
Page 109
... Intel 6300ESB ICH indicated a 16 bit transfer, the peripheral may end the transfer after one byte by indicating a SYNC value of ‘0000b’ or ‘1010b’. The Intel ICH will not attempt to transfer the second byte, and will deassert the DMA request internally. This also holds true for any byte bit transfer. This allows the peripheral, therefore, to terminate a DMA burst. When the peripheral indicates a ‘ ...
Page 110
... Timers (D31:F0) ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH contains three counters which have fixed uses. All registers and functions associated with the 8254 timers are in the core well. The 8254 unit is clocked by a 14.31818 MHz clock. The 14.31818 MHz clock will stop during the S3-S5 and G3 states ...
Page 111
... Output is ‘1’. Output goes to ‘0’ when count expires for one clock period. Output is ‘1’. Output goes to ‘0’ when count expires for one clock period. for more information. Description ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 111 ...
Page 112
... When a Counter is latched and then, some time later, latched again before the count is read, the second Counter Latch command is ignored. The count read will be the count at the time the first Counter Latch command was issued. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 112 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 113
... Interrupt Controllers (PIC) (D31:F0) ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH incorporates the functionality of two 8259 interrupt controllers that provide system interrupts for the ISA compatible interrupts. These interrupts are: system timer, keyboard controller, serial ports, parallel ports, floppy disk, IDE, mouse, and DMA channels ...
Page 114
... Interrupts may individually be programmed to be edge or level, except for IRQ0, IRQ2 and IRQ8#. Note that previous PIIXn devices internally latched IRQ12 and IRQ1 and required a port 60h read to clear the latch. The Intel IRQ12 or IRQ1 (see bit 11 and bit 12 in General Control Register, D31:F0, offset D0h). 5.6.1 Interrupt Handling 5 ...
Page 115
... EOI command is issued at the end of the interrupt subroutine. 5.6.2 Initialization Command Words (ICWx) Before operation may begin, each 8259 must be initialized. In the Intel this is a four byte sequence. The four initialization command words are referred to by their acronyms: ICW1, ICW2, ICW3, and ICW4. ...
Page 116
... ICW1 An I/O write to the master or slave controller base address with data bit 4 equal interpreted as a write to ICW1. Upon sensing this write, the Intel expects three more byte writes to 21h for the master controller, or A1h for the slave controller, to complete the ICW sequence. ...
Page 117
... IRQ5 is programmed as the bottom priority device, IRQ6 will be the highest priority device. The Set Priority Command is issued in OCW2 to accomplish this, where: R=1, SL=1, and LO-L2 is the binary priority level code of the bottom priority device. November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 117 ...
Page 118
... Edge and Level Triggered Mode In ISA systems this mode is programmed using bit 3 in ICW1, which sets level or edge for the entire controller. In the Intel register for edge and level triggered mode selection, per interrupt input, is included. This is the Edge/Level control Registers ELCR1 and ELCR2. ...
Page 119
... Specific and Non-Specific. When a Non-Specific EOI command is issued, the PIC will clear the highest ISR bit of those that are set to one. Non-Specific EOI is the normal mode of operation of the PIC within the Intel serviced currently is the interrupt entered with the interrupt acknowledge. When the PIC is operated in modes which preserve the fully nested structure, software may determine which ISR bit to clear by issuing a Specific EOI ...
Page 120
... Figure 13. Note that the signal which indicates that a port 60 read occurred is only one PCI clock wide. This cannot be a handshake signal because the Intel 6300ESB ICH is not necessarily responding to the cycle. Figure 13. Port 60 Read Clearing IRQ1 AND IRQ12 Latch 0ns ...
Page 121
... The I/O APIC handles interrupts very differently than the 8259. Briefly, these differences are: • Method of Interrupt Transmission. Interrupts are handled without the need for the processor to run an interrupt acknowledge cycle. The Intel® 6300ESB ICH only supports FSB delivery of interrupts. • Interrupt Priority. The priority of interrupts in the I/O APIC is independent of the interrupt number ...
Page 122
... Boot Interrupt ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH’s APIC1 contains a capability to logically OR several of its interrupt inputs together to generate a single interrupt through PIC. This is necessary for systems that do not support the APIC, and for boot. The generated interrupt is routed to IRQ 9. This interrupt is generated when the following conditions met: • ...
Page 123
... IRQ 14 and 15 can only be driven directly from the pins when in Legacy IDE mode IRQ11 is used for MMT #2, software should ensure IRQ 11 is not shared with any other devices to ensure the proper operation of MMT #2. The Intel prevent sharing of IRQ 11. 5. SW: Boot interrupt may optionally be routed to PIRQG# output for programmable PIRQx# mapping ...
Page 124
... When IRQ11 is used for MMT #2, software should ensure IRQ 11 is not shared with any other devices to ensure the proper operation of MMT #2. The Intel sharing of IRQ 11. 7. PCI Message interrupts are not prevented by hardware in these cases. However, the system ...
Page 125
... From PCI Pin Message PXIRQ0 Yes PXIRQ1 Yes PXIRQ2 Yes PXIRQ3 Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes WDT No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Internal Modules ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 125 ...
Page 126
... I/O Controller Hub DS 126 ® 6300ESB ICH will sample the state of Bit 1 on the APIC ® 6300ESB ICH did not drive Bit 1 (ARBID[27] = ‘0’), and it 6300ESB ICH, and it has higher priority. The Intel Table 47 describes the arbitration cycles. Bit 0 0 Bit Normal Arbitration ID ...
Page 127
... November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Bit 1 Bit EOI message 1 Arbitration ID Interrupt vector bits from redirection NOT(V6) table register NOT(V4) NOT(V2) NOT(V0) NOT(C0) Check Sum from Cycles Postamble NOT(A) Status Cycle 0 NOT(A1) Status Cycle Idle Comments ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 127 ...
Page 128
... NOT(V2) NOT(V0) NOT(D6) NOT(D4) Destination field from bits 63:56 of redirection table 1 register NOT(D2) NOT(D0) NOT(C0) Checksum for Cycles Postamble NOT(A) Status Cycle 0. See Table NOT(A1) Status Cycle 1. See Table 1 Idle ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 2 51. 51. November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 129
... Checksum OK: No Focus 11 1x Processor Error xx Checksum OK: Focus 01 xx Processor 00 Checksum Error xx 11 Checksum Error xx 01 Error xx 00 Checksum Error xx Comments Error Accepted Retry Error Accepted Error Error End and Retry Go for Low Priority Arbitration ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 129 ...
Page 130
... NOT(V2) NOT(V0) NOT(D6) NOT(D4) Destination field from bits 63:56 of redirection table register. NOT(D2) NOT(D0) NOT(C0) Checksum for Cycles Postamble NOT(A) Status Cycle 0. NOT(A1) Status Cycle Inverted Processor Priority Status 1 Idle ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 131
... ICH Remote Read Message Remote read message is used when a local APIC wishes to read the register in another local APIC. The I/O APIC in the Intel this cycle. The message format is same as short message for the first 21 cycles. Table 53. Remote Read Message (Sheet ...
Page 132
... The MESSAGE_DATA will be a 32-bit value, although only the lower 5 bits are used. 3. When the PRQ bit in the APIC Version Register is set, the Intel positively decodes the cycles (as a slave) in Medium time. ® ...
Page 133
... Processor System Bus Interrupt Delivery 5.7.7.1 Theory of Operation For processors that support Processor System Bus interrupt delivery, the Intel 6300ESB ICH has an option to let the integrated I/O APIC behave as an I/O (x) APIC. In this case, it will deliver interrupt messages to the processor in a parallel manner, rather than using the I/O APIC serial scheme ...
Page 134
... The local APIC (in the processor) has a delivery mode option to interpret Processor System Bus messages as a SMI in which case the processor treats the incoming interrupt as a SMI instead interrupt. This does not mean that the Intel 6300ESB ICH has any way to have a SMI source from the Intel management logic cause the I/OAPIC to send an SMI message (there is no way to do ® ...
Page 135
... ICH supports a serial IRQ scheme. This allows a single signal to be used to report interrupt requests. The signal used to transmit this information is shared between the host, the Intel interrupts. The signal line, SERIRQ, is synchronous to PCI clock, and follows the sustained tri-state protocol that is used by all PCI signals. This means that when a device has driven SERIRQ low, it will first drive it high synchronous to PCI clock and release it the following PCI clock ...
Page 136
... Start Frame. Since the first PCI clock of the start frame was driven by the peripheral in this mode, the Intel ICH will drive the SERIRQ line low for 1 PCI clock less than in continuous mode. This mode of operation allows for a quiet, and therefore lower power, operation ...
Page 137
... ICH 5.8.3 Stop Frame After all data frames, a Stop Frame is driven by the Intel signal is driven low by the Intel clocks is determined by the SERIRQ configuration register. The number of clocks determines the next mode: Table 56. Stop Frame Explanation Stop Frame Width ...
Page 138
... Ignored. IRQ13 may only be generated from FERR not include in BM IDE interrupt logic not include in BM IDE interrupt logic. 50 Same as ISA IOCHCK# going active. 53 Drive PIRQA# 56 Drive PIRQB# 59 Drive PIRQC# 62 Drive PIRQD# ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 Comment November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 139
... The Intel 6300ESB ICH will detect a rollover when the Year byte (RTC I/O space, index offset 09h) transitions form 99 to 00. Upon detecting the rollover, the Intel 6300ESB ICH will set the NEWCENTURY_STS bit (TCOBASE + 04h, bit 7). When the system state, this will cause an SMI#. The SMI# handler may update registers in the RTC RAM that are associated with century value ...
Page 140
... Clearing Battery-Backed RTC RAM Clearing CMOS RAM in an Intel jumper on RTCRST# or GPI, or using SAFEMODE strap. Implementations should not attempt to clear CMOS by using a jumper to pull VccRTC low. Using RTCRST# to clear CMOS: A jumper on RTCRST# may be used to clear CMOS values, as well as reset to default, the state of those configuration bits that reside in the RTC power well ...
Page 141
... ICH does not support the processor’s FRC mode. 5.10.1 Processor Interface Signals This section describes each of the signals that interface between the Intel ICH and the processor(s). 5.10.1.1 A20M# The A20M# signal will be active (low) when both of the following conditions are true: • ...
Page 142
... Offset D0, bit 13). FERR# is tied directly to the Coprocessor Error signal of the processor. When FERR# is driven active by the processor, IRQ13 goes active (internally). When it detects a write to the COPROC_ERR register, the Intel ICH negates the internal IRQ13 and drives IGNNE# active. IGNNE# remains active until FERR# is driven inactive ...
Page 143
... Generally not used, but still supported by the Intel Used for S1 State as well as preparation for entry to S3-S5. Also allows for THERM# based throttling (not through ACPI control methods). Should be connected to both processors. Generally not used, but still supported by the Intel Comment ® 6300ESB ICH. ...
Page 144
... C1 state for dual-processor designs. In going to the S1 state, multiple Stop-Grant cycles will be generated by the CPUs. The Intel 6300ESB also has the option to assert the CPU’s SLP# signal (CPUSLP#). It is assumed that prior to setting the SLP_EN bit (which causes the transition to the S1 state), the CPUs will not be executing code that is likely to delay the Stop-Grant cycles ...
Page 145
... ACPI G2/S5 state - Soft Off(SOFF) — Power Failure Detection and Recovery — Supports new output signal - SLP_S4# • Streamlined Legacy Power Management Support for APM-Based Systems • Support for Prescott Processor November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 145 ...
Page 146
... GEN_PMCON3 register (D31:F0, offset A4). Refer to ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 146 ® Legacy Name / Description ® 63. Within the C0 state, the Intel 6300ESB ICH may throttle the STPCLK# C1. processors. A full boot is required when waking. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 6300ESB ICH-based platforms. The ® ...
Page 147
... For example, in going from S0 to S1, it may appear to pass through the G0/S0/ C2 states. These intermediate transitions and states are not listed in the table. Table 63. State Transition Rules for Intel Present State • Processor halt instruction • ...
Page 148
... The Intel 6300ESB ICH power planes were previously defined in Planes”. Although not specific power planes within the Intel interface signals that go to devices that may be powered down. These include: • IDE: Output signals may be tri-stated or driven low and all input buffers may be shut off • ...
Page 149
... ICH 5.11.5 SMI#/SCI Generation Upon any SMI# event, the Intel which will cause it to enter SMM space. SMI# remains active until the EOS bit is set. When the EOS bit (bit 1) is set, SMI# will go inactive for a minimum of four PCI clocks. ...
Page 150
... NMI GBL_RLS written to 1 Write to B2h register Periodic timer expires 64 ms timer expires Enhanced USB Legacy Support Event Enhanced USB Intel-Specific Event Classic USB Legacy logic (Port 64/60 R/W, End of pass through) Classic USB Legacy logic (IRQ) Serial IRQ SMI Reported NOTES: 1 ...
Page 151
... MCSMI_STS SMI_ON_SLP_EN_S SMI_ON_SLP_EN = 1 WDT_ENABLE = 1, WDT_SMI_STS WDT_INT_TYPE = ‘10’ Additional Enables None NEWCENTURY_STS None TIMEOUT None OS_TCO_SMI None MCHSMI_STS NMI2SMI_EN = 1 NMI2SMI_STS INTRD_SEL = 10 INTRD_DET BLD = 1 BIOSWR_STS BIOSWP = 1 BIOSWR_STS for details on the TCO SMI# ® Intel Synch Where Reported 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 151 ...
Page 152
... The C2 state is entered based on the processor reading the Level 2 register in the ® Intel 6300ESB ICH state ends due to a break event. Based on the break event, the Intel 6300ESB ICH returns the system to C0 state. from C2 states. The break events from C1 are indicated in the processor’s datasheet. Table 68. ...
Page 153
... C0 state. 5.11.6.1 Throttling Using STPCLK# Throttling is used to lower power consumption or reduce heat. The Intel asserts STPCLK# to throttle the processor clock and the processor appears to temporarily enter a C2 state. After a programmable time, the Intel deasserts STPCLK# and the processor appears to return to the C0 state ...
Page 154
... The Host controller must post Stop-Grant cycles in such a way that the processor gets an indication of the end of the special cycle prior to the Intel observing the Stop-Grant cycle. This ensures that the STPCLK# signals stays active for a sufficient period after the processor observes the response phase. ...
Page 155
... Exception: For SMI#s that are caused by a processor I/O cycle, when STPCLK# is ® active, the Intel STPCLK# was obviously too late to be recognized at the instruction boundary. The I/O cycles that may cause SMI# include: writes to the APM register (B2h), accesses to 60/ 64h when “ ...
Page 156
... The Intel S4 shut off the power to the memory subsystem. Only devices needed to wake from this state should be powered. Same power state as S4. The Intel S5 SLP_S5#. Other Assumptions: • Entry state is mutually exclusive with entry to a Sleep state. This is because the processor may only perform one register access at a time ...
Page 157
... S5 state (unless previously in S4). There are only three possible events that will wake the system after a power failure. 1. PWRBTN#: PWRBTN# is always enabled as a wake event. When RSMRST# is low (G3 state), the PWRBTN_STS bit is reset. When the Intel after power returns (RSMRST# goes high), the PWRBTN# signal is already high (because V ...
Page 158
... When the THRM# signal remains active for some time greater than two seconds and ® the Intel 6300ESB ICH is in the S0/G0/C0 state, then the Intel an auto-throttling mode, in which it provides a duty cycle on the STPCLK# signal. This will reduce the overall power consumption by the system, and should cool the system. ...
Page 159
... THRM# Override Software Bit The FORCE_THTL bit allows the BIOS to force passive cooling, just as though the THRM# signal had been active for two seconds. When this bit is set, the Intel 6300ESB ICH will start throttling using the ratio in the THRM_DTY field. ...
Page 160
... PWRBTN_LVL bit. Note: The four second PWRBTN# assertion should only be used when a system lock-up has occurred. The four second timer starts counting when the Intel S0 state. When the PWRBTN# signal is asserted and held active when the system suspend state (S1–S5), the assertion will cause a wake event. Once the system has resumed to the S0 state, the four second timer will start ...
Page 161
... S5 state, drive SLP_S3#, SLP_S4#, SLP_S5# low, and set the CTS bit. The transition will look like a power button override extremely important that when a THRMTRIP# event occurs, the Intel ICH power down immediately without following the normal S0 -> S5 path. This path may be taken in parallel, but the Intel down state ...
Page 162
... Until sleep machine enters the S5 state, SLP_S3#, SLP_S4#, and SLP_S5# stay active, even when THRMTRIP# is now inactive. This is the equivalent of “latching” the thermal trip event. 4. When S5 state reached step #1, otherwise stay here. When the Intel 6300ESB ICH never reaches S5, the Intel is cycled. ...
Page 163
... DMA Chan 5 base address low 1 byte DMA Chan 5 base address high 2 byte 1 DMA Chan 5 base count low byte 2 DMA Chan 5 base count high byte DMA Chan 6 base address low 1 byte DMA Chan 6 base address high 2 byte ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 163 ...
Page 164
... Add CAh 2 CCh 2 CEh 2 D0h ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 Restore Data Data s 1 DMA Chan 6 base count low byte 2 DMA Chan 6 base count high byte DMA Chan 7 base address low 1 byte DMA Chan 7 base address high 2 byte 1 DMA Chan 7 base count low byte ...
Page 165
... The SLP_S3# output signal may be used to cut power to the system core supply, since it will only go active for the STR state (typically mapped to ACPI S3). Power must be maintained to system memory, the Intel circuits that need to generate Wake signals from the STR state. Cutting power to the core may be done through the power supply external FETs to the motherboard ...
Page 166
... PWROK goes high, then this is a full power failure and the reboot policy is controlled by the AFTERG3 bit. 2. PWROK and RSMRST# are sampled using the RTC clock. Therefore, low times that are less than one RTC clock period may not be detected by the Intel ICH. 5.11.11.3VRMPWRGD Signal The VRMPWRGD signal is not implemented in the Intel need to be pulled up to Vcc in order to disable internal legacy logic ...
Page 167
... Main Clock Generator ® the Intel 6300ESB ICH. This clock may be stopped in S3 states. This signal is not 5V tolerant. Free-running PCI Clock to the Intel ICH. Provides timing for all transactions on the internal primary PCI-X bus, as well as units inside Main Clock Generator ® the Intel 6300ESB ICH ...
Page 168
... However, the OS is assumed least APM enabled. Without APM calls, there is no quick way to know when the system is idle between keystrokes. The Intel ICH does not support the burst modes found in previous components. 5.11.13.2APM Feature Notes ® ...
Page 169
... ICH supports TCO compatible mode connectivity. The Intel 6300ESB ICH supports LAN controllers. A LAN controller can be used to receive or retrieve TCO message or information on Host SMBus if needed. In Legacy TCO mode messages will be driven via SMLink. For the Intel will use SMBus protocol at the rates described in (D31:F0)” ...
Page 170
... Intel 6300ESB ICH will assert PXPCIRST#. When TCO Reboots are not enabled, then the Intel • The SMLink will still send out the first 8 bits of the message. After the eighth bit, the logic will stall because there is no integrated LAN controller to send the ACK. ...
Page 171
... Note: The INTRD_DET bit resides in the Intel cleared synchronously with the RTC clock. Thus, when software attempts to clear INTRD_DET (by writing a ‘1’ to the bit location) there may be as much as two RTC clocks (about 65 µ ...
Page 172
... NOTE: The GPIO[11]/SMBALERT# pin will trigger an event message (when enabled by the GPIO11_ALERT_DISABLE bit) regardless of whether it is configured as a GPI or not. Whenever an event occurs that causes the Intel message, it will increment its SEQ[3:0] field. For Heartbeat messages, the sequence number will not increment. ...
Page 173
... ICH will continue sending messages every heartbeat period until the BIOS clears the SECOND_TO_STS bit. 7. When step 5 (power button press) is unsuccessful in waking the system, the Intel 6300ESB ICH will continue sending a message every heartbeat period. The Intel 6300ESB ICH will not attempt to automatically reboot again. The Intel ICH will start sending a message every heartbeat period (30-32 seconds) ...
Page 174
... PWROK low or through the message on the SMBus slave I/F), the Intel ICH will attempt to reset the system. 9. When step 8 (reset attempt) is successful, then the BIOS will be run. The Intel 6300ESB ICH will continue sending heartbeats until the BIOS clears the SECOND_TO_STS bit. ...
Page 175
... The Intel 6300ESB ICH will send a Heartbeat message every Heartbeat Period (30-32 seconds). 2. When an event occurs prior to the system being shut down, the Intel ICH will immediately send another Event message with the next (incremented) sequence number. 3. After the event, it will resume sending Heartbeat messages. ...
Page 176
... V e Input active high/low set through GPI_INV register bit 12. Input active status read from GPE0_STS register bit Resum 29. 3 Input active high/low set through GPI_INV register bit 13. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 Notes Section 8.8.3.7 GPI_INV November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 177
... Output controlled through GP_LVL register bits e [27:28] TTL driver output Core 3.3 V Core 3.3 V Core 3.3 V These GPIOs have high strength output capability (for Core 3.3 V driving LEDs) Resum e and 3.3 V RTC Notes Section 8.10.4 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 177 ...
Page 178
... Triggering GPIO[0:15] have “sticky” bits on the input. See register. As long as the signal goes active for at least 2 clocks, the Intel will keep the sticky status bit active. The active level (high or low) can be selected via the GP_INV register. If the system S1-D state, the GPI are sampled at 33 MHz, so the signal only needs to be active for about latched ...
Page 179
... PIO Transfers 5.14.2.1 Overview ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH IDE controller includes both compatible and fast timing modes. The fast timing modes may be enabled only for the IDE data ports. All other transactions to the IDE registers are run in single transaction mode with compatible timings ...
Page 180
... Drive 07h Status NOTE: For accesses to the Alt Status register in the Control Block, the Intel must always force the upper address bit (PDA[2] or SDA[2 order to ensure proper native mode decode by the IDE device. Unlike the legacy mode fixed address location, the native mode address for this register may contain address bit 2 when ...
Page 181
... The demand read and all prefetch reads much be of the same size ( bits). Data posting is performed for writes to the IDE data ports. The transaction is completed on the PCI bus after the data is received by the Intel 6300ESB ICH will then run the IDE cycle to transfer the data to the drive. When the ® ...
Page 182
... Descriptor (PRD). The PRDs are stored sequentially in a Descriptor Table in memory. The data transfer proceeds until all regions described by the PRDs in the table have been transferred. Note that the Intel support memory regions or descriptor tables located on ISA. Descriptor Tables must not cross a 64-Kbyte boundary. Each PRD entry in the table is 8 bytes in length ...
Page 183
... IDE device drives an interrupt but the interrupt is masked in the system. • Bus Master IDE devices are connected directly off of the Intel interrupts cannot be communicated through PCI devices or the serial stream. Caution:In this mode, the Intel associated with this function. That is only used in native mode. ...
Page 184
... Table 82 describes how to interpret the Interrupt and Active bits in the Status Register after a DMA transfer has started. During concurrent DMA or Ultra ATA transfers, the Intel will arbitrate between the primary and secondary IDE cables when a PRD expires. ® Intel ...
Page 185
... These pins have similar characteristics to their ISA counterparts in terms of when data is valid relative to strobe edges, and the polarity of the strobes, however ® the Intel 6300ESB ICH does not use the 8237 for this mode. November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Description DMA transfer is in progress ...
Page 186
... The DIOR# signal is redefined as STROBE for transferring data from the Intel ICH to the IDE device (write the data strobe signal driven by the Intel ICH on which data is transferred during each rising and falling edge transition. ...
Page 187
... The CRC value is calculated for all data by both the Intel the IDE device over the duration of the Ultra ATA/33 burst transfer segment. This segment is defined as all data transferred with a valid STROBE edge from DDACK# assertion to DDACK# deassertion. At the end of the transfer burst segment, the Intel November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® ...
Page 188
... When the ATA_FAST bit is set for any of the four IDE devices, then the timings for the transfers to and from the corresponding device run at a higher rate. The Intel 6300ESB ICH Ultra ATA/100 logic may achieve read transfer rates up to 100 Mbytes/s, and write transfer rates ...
Page 189
... Power Management Operation Power management of the Intel operations of the host controller and the SATA wire. November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ® ...
Page 190
... Power State Mappings The following PCI power management states for devices are supported by the Intel 6300ESB ICH SATA Controller: D0 – working D3 – very deep sleep. This state is split into two sub-states, D3 PCI configuration accesses) and D3 accesses). These two sub-states are considered the same, where D3 D3 does not ...
Page 191
... To block accesses to the native IDE ranges, software must use the generic Power Management control registers described in CAh: MON[n]_TRP_RNG—I/O Monitor [4:7] Trap Range Register for Devices 4-7 (PM— D31:F0)”. November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Section 8.8.1.7, “Offset C4h, C6h, C8h, ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 191 ...
Page 192
... OS (see OS will move the location of these timers once it is set by the BIOS. ® In the Intel 6300ESB ICH, one timer block is implemented. The timer block has one counter and three timers (comparators). Future devices may have a different number of implemented timers. Various capabilities registers indicate the number of timers and the capabilities of each. ® ...
Page 193
... Section 15.1.3, “Offset 010-017h: General Config Register” APIC Mapping In this case, the 8254 timer will not cause any IRQ2 interrupts. IRQ8 In this case, the RTC will not cause any interrupts. As per IRQ Routing Field for Comment for LEG_RT_CNF details. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 193 ...
Page 194
... Set the lower 32 bits of the Timer0 Comparator Value register 3. Set TIMER0_VAL_SET_CNF bit 4. Set the upper 32 bits of the Timer0 Comparator Value register ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 194 Section 15, “Multimedia Timer Registers” ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—5 for register and November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 195
... When a 32-bit processor needs to access a 64-bit timer, it must first halt the timer before reading both the upper and lower 32-bits of the timer. November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Section 5.7, “Advanced for information regarding the polarity ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 195 ...
Page 196
... TD (Transfer Descriptor (Queue Head). This allows the ® Intel 6300ESB ICH to perform the proper type of processing on the item after fetched Terminate (T): This bit indicates to the Intel this frame has valid entries in it Empty Frame (pointer is invalid Pointer is valid (points TD). ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub ...
Page 197
... Terminate (T): This bit informs the Intel does not point to another valid entry. When encountered in a queue context, this bit indicates to the Intel A TD encountered outside of a queue context with the T bit set informs the Intel 0 6300ESB ICH that this is the last TD in the frame. ...
Page 198
... Low Speed Device (LS): This bit indicates that the target device (USB data source or sink low speed device, running at 1.5 Mb/s, instead of at full speed (12 Mb/s). There are special restrictions on schedule placement for low speed TDs. When an Intel 6300ESB ICH root hub port is connected to a full speed device and this bit is set ...
Page 199
... ICH sets this bit to 0 indicating that the descriptor should not be executed 23 when it is next encountered in the schedule. The Active bit is also set to 0 when a stall handshake is received from the endpoint Set software to enable the execution of a message transaction by the Intel 6300ESB ICH. Stalled Set the Intel serious error has occurred at the device/endpoint addressed by this TD ...
Page 200
... SE0-to-IDE transition of previous End of Packet (EOP). 15:11 Reserved Actual Length (ACTLEN): The Actual Length field is written by the Intel ICH at the conclusion of a USB transaction to indicate the actual number of bytes that 10:0 were transferred. It may be used by the software to maintain data integrity. The value programmed in this register is encoded as n-1 (see Maximum Length field description in the TD Token) ...