PPC8567EVTAUJJ Freescale Semiconductor, PPC8567EVTAUJJ Datasheet - Page 62
PPC8567EVTAUJJ
Manufacturer Part Number
PPC8567EVTAUJJ
Description
MCU PWRQUICC III 1023-FCPBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MPC8567EVTAQGG.pdf
(139 pages)
Specifications of PPC8567EVTAUJJ
Processor Type
MPC85xx PowerQUICC III 32-Bit
Speed
1.333GHz
Voltage
1.1V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
1023-BBGA, FCBGA
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Features
-
- Current page: 62 of 139
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
High-Speed Serial Interfaces (HSSI)
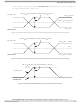
To illustrate these definitions using real values, consider the case of a CML (Current Mode Logic)
transmitter that has a common mode voltage of 2.25 V and each of its outputs, TD and TD, has a swing
that goes between 2.5 V and 2.0 V. Using these values, the peak-to-peak voltage swing of each signal (TD
or TD) is 500 mV p-p, which is referred as the single-ended swing for each signal. In this example, since
the differential signaling environment is fully symmetrical, the transmitter output’s differential swing
(V
62
OD
4. Differential Peak Voltage, V
5. Differential Peak-to-Peak, V
6. Common Mode Voltage, V
) has the same amplitude as each signal’s single-ended swing. The differential output signal ranges
two complimentary input voltages: V
negative.
each range from A – B to –(A – B) Volts, the peak-to-peak value of the differential transmitter
output signal or the differential receiver input signal is defined as Differential Peak-to-Peak
Voltage, V
amplitude, or twice of the differential peak. For example, the output differential peak-peak voltage
can also be calculated as V
of a balanced interchange circuit and ground. In this example, for SerDes output, V
+ V
within a differential pair. In a system, the common mode voltage may often differ from one
component’s output to the other’s input. Sometimes, it may be even different between the receiver
input and driver output circuits within the same component. It is also referred as the DC offset in
some occasion.
The Differential Input Voltage (or Swing) of the receiver, V
The peak value of the differential transmitter output signal or the differential receiver input signal
Since the differential output signal of the transmitter and the differential input signal of the receiver
The Common Mode Voltage is equal to one half of the sum of the voltages between each conductor
is defined as Differential Peak Voltage, V
A Volts
B Volts
SD_TX
MPC8568E/MPC8567E PowerQUICC III Integrated Processor Hardware Specifications, Rev. 1
DIFFp-p
= (A + B) / 2, which is the arithmetic mean of the two complimentary output voltages
Figure 39. Differential Voltage Definitions for Transmitter or Receiver
SD_TX or
SD_RX
SD_TX or
SD_RX
= 2*V
DIFFp
TX-DIFFp-p
Differential Peak-Peak Voltage, V
cm
DIFFp
= 2 * |(A – B)| Volts, which is twice of differential swing in
DIFFp-p
Differential Swing, V
Differential Peak Voltage, V
SD_RX
= 2*|V
DIFFp
– V
OD
= |A – B| Volts.
|.
SD_RX.
ID
or V
The V
DIFFpp
OD
DIFFp
ID
= 2*V
= A – B
ID
, is defined as the difference of the
= |A – B|
value can be either positive or
DIFFp
(not shown)
Freescale Semiconductor
V
cm
cm_out
= (A + B) / 2
= V
SD_TX
Related parts for PPC8567EVTAUJJ
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: