COP8SA-DM National Semiconductor, COP8SA-DM Datasheet - Page 179
COP8SA-DM
Manufacturer Part Number
COP8SA-DM
Description
MODULE DEBUGGING FOR COP8SA
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.DM-COP820D.pdf
(254 pages)
Specifications of COP8SA-DM
Module/board Type
Debugger Module
For Use With/related Products
Cop 8
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
*COP8SA-DM
- Current page: 179 of 254
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
National’s design goal was to reshape the IC pin current waveforms from their original
values. A second goal was to provide separate power and ground bus systems on-chip for
each of the following groups: Chip digital logic, Chip I/O buffers, and if present a chip A/
D converter (or other analog intensive sections).
Inspection of these goals demanded the need to divide the chip into separate areas: the
nucleus, the perimeter and the analog. Also the partitioning of the nucleus (containing
the digital logic functions) and the perimeter (containing digital I/O and oscillator
functions) allowed the use of an on-chip device to choke the nucleus’ current, thereby
wave shaping the current. The current choke, however, causes the nucleus V
to dip by 0.5 to 1 Volt at each clock edge. These V
within the chip’s nucleus where the circuitry (digital logic) is tolerant and no significant
radiation antennae exist.
On-chip level shifting circuitry was inserted as interface between the nucleus and the
perimeter. It allowed the nucleus to operate at a lower V
Another challenge was to reduce EMI from the chip’s output drivers. CMOS output
drivers turn on fast, in about 1nS. This causes 2 problems. The first is called ‘shoot
through’ current which flows from DV
down drivers are on and the output load is small. The second is due to output current
magnitude increasing to maximum in about 1 nS when the output changes state. Both
problems were solved by using fast turn off, gradual turn on device drivers.
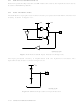
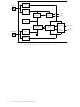
Figure 2-35 illustrates, in block diagram form, how the chip is partitioned for EMC. The
power/ground pads named DV
most of the chip), GND (a global GND to most of the chip) and DGND (driver ground) are
all available). To minimize package pin count, DV
GND & DGND is also bonded to the same pin, and the V
2.24.2 Conclusion
While electromagnetic emissions can be a problem for the designer of any electronic
system, it is particularly troublesome in the design of high speed CMOS systems. With
knowledge of the primary sources of noise, and the ways to combat that noise, it is
possible to design and build systems which are electromagnetically quiet.
Very few references to specific values of capacitance, resistance, or inductance have been
made in this document. The reason for this is that a value which works well in one
application may not be effective in another. The best way to determine the values which
will work well for a particular application is by experimentation.
CC
(Driver V
CC
to DGND when both the pull up and the pull
CC
), LV
CC
CC
CC
COP8SAx7 MICROCONTROLLER
and LV
(Logic V
voltage swings were confined to
CC
CC
CC
than the perimeter.
pad is not bonded.
is bonded to the same pin,
CC
),V
CC
(a global V
CC
voltage
CC
2-141
to
Related parts for COP8SA-DM
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
PROGRAMING UNIT FOR COP8SA PARTS
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor

Part Number:
Description:
ADAPTER SOIC 16,20,28,44 PLCC
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Part Number:
Description:
8-Bit CMOS ROM Based and One-Time Programmable OTP Microcontroller with 1k to 4k Memory/ Power On Reset/ and Very Small Packaging
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
National Semiconductor [8-Bit D/A Converter]
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
National Semiconductor [Media Coprocessor]
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Digitally Controlled Tone and Volume Circuit with Stereo Audio Power Amplifier, Microphone Preamp Stage and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Digitally Controlled Tone and Volume Circuit with Stereo Audio Power Amplifier, Microphone Preamp Stage and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
AC97 Rev 2 Codec with Sample Rate Conversion and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
General Purpose, Low Voltage, Low Power, Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
8-bit 20 MSPS flash A/D converter.
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Low Noise Quad Operational Amplifier
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Quad Differential Line Receivers
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet: