COP8SA-DM National Semiconductor, COP8SA-DM Datasheet - Page 18
COP8SA-DM
Manufacturer Part Number
COP8SA-DM
Description
MODULE DEBUGGING FOR COP8SA
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.DM-COP820D.pdf
(254 pages)
Specifications of COP8SA-DM
Module/board Type
Debugger Module
For Use With/related Products
Cop 8
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
*COP8SA-DM
- Current page: 18 of 254
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
1.4
The broad category of microcomputers is divide into two areas: microcontrollers and
microprocessors. This distinction is made because these are really two different types of
devices. Microcontrollers generally have a dual-bus architecture rather than the memory
mapped von Neumann architecture common in most microprocessors. For control
applications, microcontrollers are generally more memory efficient than microprocessors.
The microcontroller instruction set is quite different in nature than the microprocessor
instruction set. Microcontrollers are invariably single-chip devices and microprocessors
are, generally, multi-chip devices. Microcontrollers dominate the microcomputer
marketplace in terms of volume. To be sure, the division between microcontroller and
microprocessor is sometimes blurred but the distinction is real nonetheless.
1.5
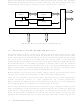
Microcontrollers have two types of architecture: Von Neumann or Harvard.
1.5.1
The Von Neumann architecture was named after John Von Neumann, an early pioneer
in the computer field at Princeton. In this architecture, a CPU and memory are
interconnected by a common address bus and data bus. Positive aspects of this approach
include convenient access to tables stored in program memory (ROM or OTP/EPROM)
and a more orthogonal instruction set. The address bus is used to identify which memory
location is being accessed, while the data bus is used to transfer information either from
the CPU to the selected memory location or vice versa. Von Neumann was the first to
realize that his architecture model could have the memory serve as either program
memory or data memory. In earlier computers (both electronic and electromechanical),
the program store (often a program patchboard) had been completely separate from the
data store (often a bank of vacuum tubes or relays).
1-6
Automotive
Market Segment
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A MICROCONTROLLER AND A
MICROPROCESSOR?
WHAT IS THE ARCHITECTURE OF A MICROCONTROLLER
MICROCONTROLLER BASICS
Von Neumann Architecture
Radio/Tape Deck
Window, Seat, Mirror,
Climate Controls
Headlight/Antenna
Power Steering
Anti Theft
Slave Controllers
Controls
and Door Controls
Applications
Timing
Motion Control
Display Control
Soft Runaway/Trap
EMI/Noise Immunity
Serial Interfaces
Standby Modes
Wide Temp Range
Recovery (safety
considerations)
Features/Functions
Applications
Flexible PWM Timers
Power Saving Modes
Multi-Input Wakeup
WATCHDOG Software
UART
CAN Interface
Special Features for
Control (counters, capture
Reduced EMI
Wide Temp Range
Trap
Dashboard
modules, MUL/DIV)
Features Required
Microcontroller
Related parts for COP8SA-DM
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
PROGRAMING UNIT FOR COP8SA PARTS
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor

Part Number:
Description:
ADAPTER SOIC 16,20,28,44 PLCC
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Part Number:
Description:
8-Bit CMOS ROM Based and One-Time Programmable OTP Microcontroller with 1k to 4k Memory/ Power On Reset/ and Very Small Packaging
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
National Semiconductor [8-Bit D/A Converter]
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
National Semiconductor [Media Coprocessor]
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Digitally Controlled Tone and Volume Circuit with Stereo Audio Power Amplifier, Microphone Preamp Stage and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Digitally Controlled Tone and Volume Circuit with Stereo Audio Power Amplifier, Microphone Preamp Stage and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
AC97 Rev 2 Codec with Sample Rate Conversion and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
General Purpose, Low Voltage, Low Power, Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
8-bit 20 MSPS flash A/D converter.
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Low Noise Quad Operational Amplifier
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Quad Differential Line Receivers
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet: