COP8SA-DM National Semiconductor, COP8SA-DM Datasheet - Page 79
COP8SA-DM
Manufacturer Part Number
COP8SA-DM
Description
MODULE DEBUGGING FOR COP8SA
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.DM-COP820D.pdf
(254 pages)
Specifications of COP8SA-DM
Module/board Type
Debugger Module
For Use With/related Products
Cop 8
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
*COP8SA-DM
- Current page: 79 of 254
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
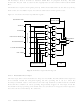
2.13.4 Non-maskable Interrupt
Pending Flag
There is a pending flag bit associated with the non-maskable interrupt, called STPND.
This pending flag is not memory-mapped and cannot be accessed directly by the software.
The pending flag is reset to zero when a device Reset occurs. When the non-maskable
interrupt occurs, the associated pending bit is set to 1. The interrupt service routine
should contain an RPND instruction to reset the pending flag to zero. The RPND
instruction always resets the STPND flag
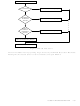
Software Trap
The Software Trap is a special kind of non-maskable interrupt which occurs when the
INTR instruction (used to acknowledge interrupts) is fetched from program memory and
placed in the instruction register. This can happen in a variety of ways, usually because
of an error condition. Some examples of causes are listed below.
If the program counter incorrectly points to a memory location beyond the available
program memory space, the non-existent or unused memory location returns zeros which
is interpreted as the INTR instruction.
If the stack is popped beyond the allowed limit (address 02F or 06F Hex), a Software Trap
is triggered.
A Software Trap can be triggered by a temporary hardware condition such as a brownout
or power supply glitch.
The Software Trap has the highest priority of all interrupts. When a Software Trap
occurs, the STPND bit is set. The GIE bit is not affected and the pending bit (not
accessible by the user) is used to inhibit other interrupts and to direct the program to the
ST service routine with the VIS instruction. Nothing can interrupt a Software Trap
service routine except for another Software Trap. The STPND can be reset only by the
RPND instruction or a chip Reset.
The Software Trap indicates an unusual or unknown error condition. Generally,
returning to normal execution at the point where the Software Trap occurred cannot be
done reliably. Therefore, the Software Trap service routine should re-initialize the stack
pointer and perform a recovery procedure that re-starts the software at some known
point, similar to a device Reset, but not necessarily performing all the same functions as
a device Reset. The routine must also execute the RPND instruction to reset the STPND
flag. Otherwise, all other interrupts will be locked out. To the extent possible, the
interrupt routine should record or indicate the context of the device so that the cause of
the Software Trap can be determined.
If the user wishes to return to normal execution from the point at which the Software
Trap was triggered, the user must first execute RPND, followed by RETSK rather tan
RETI or RET. This is because the return address stored on the stack is the address of the
INTR instruction that triggered the interrupt. The program must skip that instruction
in order to proceed with the next one. Otherwise, an infinite loop of Software Traps and
returns will occur.
COP8SAx7 MICROCONTROLLER
2-41
Related parts for COP8SA-DM
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
PROGRAMING UNIT FOR COP8SA PARTS
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor

Part Number:
Description:
ADAPTER SOIC 16,20,28,44 PLCC
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Part Number:
Description:
8-Bit CMOS ROM Based and One-Time Programmable OTP Microcontroller with 1k to 4k Memory/ Power On Reset/ and Very Small Packaging
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
National Semiconductor [8-Bit D/A Converter]
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
National Semiconductor [Media Coprocessor]
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Digitally Controlled Tone and Volume Circuit with Stereo Audio Power Amplifier, Microphone Preamp Stage and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Digitally Controlled Tone and Volume Circuit with Stereo Audio Power Amplifier, Microphone Preamp Stage and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
AC97 Rev 2 Codec with Sample Rate Conversion and National 3D Sound
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
General Purpose, Low Voltage, Low Power, Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
8-bit 20 MSPS flash A/D converter.
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Low Noise Quad Operational Amplifier
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Quad Differential Line Receivers
Manufacturer:
National Semiconductor
Datasheet: