ATmega168P Atmel Corporation, ATmega168P Datasheet - Page 215

ATmega168P
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega168P
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega168P
Flash (kbytes)
16 Kbytes
Pin Count
32
Max. Operating Frequency
20 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
23
Ext Interrupts
24
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
1
Eeprom (bytes)
512
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
Yes
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.8 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
6
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
6
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega168P-20AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
1 250
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega168P-20MU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
12 000
Part Number:
ATmega168P-20MU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega168PA-15AZ
Manufacturer:
VAC
Quantity:
120
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega168PA-15MZ
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA
Quantity:
1 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega168PA-AU
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Quantity:
2 902
Part Number:
ATmega168PA-AU
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATmega168PA-MMH
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
22.3.3
22.3.4
8025M–AVR–6/11
Address Packet Format
Data Packet Format
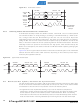
All address packets transmitted on the TWI bus are 9 bits long, consisting of 7 address bits, one
READ/WRITE control bit and an acknowledge bit. If the READ/WRITE bit is set, a read opera-
tion is to be performed, otherwise a write operation should be performed. When a Slave
recognizes that it is being addressed, it should acknowledge by pulling SDA low in the ninth SCL
(ACK) cycle. If the addressed Slave is busy, or for some other reason can not service the Mas-
ter’s request, the SDA line should be left high in the ACK clock cycle. The Master can then
transmit a STOP condition, or a REPEATED START condition to initiate a new transmission. An
address packet consisting of a slave address and a READ or a WRITE bit is called SLA+R or
SLA+W, respectively.
The MSB of the address byte is transmitted first. Slave addresses can freely be allocated by the
designer, but the address 0000 000 is reserved for a general call.
When a general call is issued, all slaves should respond by pulling the SDA line low in the ACK
cycle. A general call is used when a Master wishes to transmit the same message to several
slaves in the system. When the general call address followed by a Write bit is transmitted on the
bus, all slaves set up to acknowledge the general call will pull the SDA line low in the ack cycle.
The following data packets will then be received by all the slaves that acknowledged the general
call. Note that transmitting the general call address followed by a Read bit is meaningless, as
this would cause contention if several slaves started transmitting different data.
All addresses of the format 1111 xxx should be reserved for future purposes.
Figure 22-4. Address Packet Format
All data packets transmitted on the TWI bus are nine bits long, consisting of one data byte and
an acknowledge bit. During a data transfer, the Master generates the clock and the START and
STOP conditions, while the Receiver is responsible for acknowledging the reception. An
Acknowledge (ACK) is signalled by the Receiver pulling the SDA line low during the ninth SCL
cycle. If the Receiver leaves the SDA line high, a NACK is signalled. When the Receiver has
received the last byte, or for some reason cannot receive any more bytes, it should inform the
Transmitter by sending a NACK after the final byte. The MSB of the data byte is transmitted first.
SDA
SCL
START
Addr MSB
1
2
ATmega48P/88P/168P
Addr LSB
7
R/W
8
ACK
9
215