MC8640DTHX1067NE Freescale Semiconductor, MC8640DTHX1067NE Datasheet - Page 59
MC8640DTHX1067NE
Manufacturer Part Number
MC8640DTHX1067NE
Description
IC MPU DUAL CORE E600 1023FCCBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MC8640HX1067NE.pdf
(130 pages)
Specifications of MC8640DTHX1067NE
Processor Type
MPC86xx PowerPC 32-Bit
Speed
1.067GHz
Voltage
0.95V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
1023-FCCBGA
Processor Series
MPC8xxx
Core
e600
Development Tools By Supplier
MCEVALHPCN-8641D
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
No
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC8640DTHX1067NE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
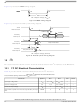
Differential Waveform
Common Mode Voltage, V
To illustrate these definitions using real values, consider the case of a current mode logic (CML)
transmitter that has a common mode voltage of 2.25 V and each of its outputs, TD and TD, has a swing
that goes between 2.5 V and 2.0 V. Using these values, the peak-to-peak voltage swing of each signal (TD
or TD) is 500 mV p-p, which is referred as the single-ended swing for each signal. In this example, since
the differential signaling environment is fully symmetrical, the transmitter output’s differential swing
(V
between 500 mV and –500 mV, in other words, V
phase. The peak differential voltage (V
is 1000 mV p-p.
13.2
The SerDes reference clock inputs are applied to an internal PLL whose output creates the clock used by
the corresponding SerDes lanes. The SerDes reference clocks inputs are SDn_REF_CLK and
SDn_REF_CLK for PCI Express and Serial RapidIO.
The following sections describe the SerDes reference clock requirements and some application
information.
Freescale Semiconductor
OD
) has the same amplitude as each signal’s single-ended swing. The differential output signal ranges
SerDes Reference Clocks
MPC8640 and MPC8640D Integrated Host Processor Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
signal is defined as differential peak-to-peak voltage,
V
amplitude, or twice of the differential peak. For example, the output differential
peak-peak voltage can also be calculated as V
The differential waveform is constructed by subtracting the inverting signal
(SDn_TX, for example) from the non-inverting signal (SDn_TX, for example)
within a differential pair. There is only one signal trace curve in a differential
waveform. The voltage represented in the differential waveform is not referenced
to ground. Refer to
The common mode voltage is equal to one half of the sum of the voltages between
each conductor of a balanced interchange circuit and ground. In this example, for
SerDes output, V
arithmetic mean of the two complimentary output voltages within a differential
pair. In a system, the common mode voltage may often differ from one
component’s output to the other’s input. Sometimes, it may be even different
between the receiver input and driver output circuits within the same component.
It is also referred as the DC offset in some occasion.
DIFFp-p
cm
= 2 × V
DIFFp
DIFFp
cm_out
Figure 47
) is 500 mV. The peak-to-peak differential voltage (V
= 2 × |(A – B)| volts, which is twice of differential swing in
= (V
OD
SDn_TX
is 500 mV in one phase and –500 mV in the other
as an example for differential waveform.
+ V
SDn_TX
TX-DIFFp-p
) ÷ 2 = (A + B) ÷ 2, which is the
High-Speed Serial Interfaces (HSSI)
= 2 × |V
OD
|.
DIFFp-p
59
)