MC68HC908GP16CFB Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC908GP16CFB Datasheet - Page 172
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Description
MCU 8-BIT 16K FLASH 44-QFP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC08r
Datasheet
1.MC908EY16VFAR2.pdf
(278 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC908GP16CFB
Core Processor
HC08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Connectivity
SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM
Number Of I /o
33
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
512 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
44-QFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 172 of 278
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module
The SPI module allows full-duplex, synchronous, serial communication between the MCU and peripheral
devices, including other MCUs. Software can poll the SPI status flags or SPI operation can be interrupt
driven. All SPI interrupts can be serviced by the CPU.
The following paragraphs describe the operation of the SPI module.
15.4.1 Master Mode
The SPI operates in master mode when the SPI master bit, SPMSTR (SPCR $0010), is set.
Only a master SPI module can initiate transmissions. Software begins the transmission from a master SPI
module by writing to the SPI data register. If the shift register is empty, the byte immediately transfers to
the shift register, setting the SPI transmitter empty bit, SPTE (SPSCR $0011). The byte begins shifting
out on the MOSI pin under the control of the serial clock. (See
The SPR1 and SPR0 bits control the baud rate generator and determine the speed of the shift register.
(See
master also controls the shift register of the slave peripheral.
As the byte shifts out on the MOSI pin of the master, another byte shifts in from the slave on the master’s
MISO pin. The transmission ends when the receiver full bit, SPRF (SPSCR), becomes set. At the same
time that SPRF becomes set, the byte from the slave transfers to the receive data register. In normal
operation, SPRF signals the end of a transmission. Software clears SPRF by reading the SPI status and
control register and then reading the SPI data register. Writing to the SPI data register clears the SPTIE
bit.
15.4.2 Slave Mode
The SPI operates in slave mode when the SPMSTR bit (SPCR, $0010) is clear. In slave mode the SPSCK
pin is the input for the serial clock from the master MCU. Before a data transmission occurs, the SS pin
of the slave MCU must be at logic 0. SS must remain low until the transmission is complete. (See
Mode Fault
172
15.13.2 SPI Status and Control
Error.)
Configure the SPI modules as master and slave before enabling them.
Enable the master SPI before enabling the slave SPI. Disable the slave SPI
before disabling the master SPI. See
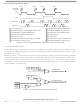
SHIFT REGISTER
GENERATOR
MASTER MCU
BAUD RATE
Figure 15-3. Full-Duplex Master-Slave Connections
MC68HC908EY16 • MC68HC908EY8 Data Sheet, Rev. 10
Register.) Through the SPSCK pin, the baud rate generator of the
MISO
MOSI
SPSCK
SS
NOTE
V
15.13.1 SPI Control
DD
SPSCK
MISO
MOSI
SS
Table
15-3).
Register.
SHIFT REGISTER
SLAVE MCU
Freescale Semiconductor
15.6.2
Related parts for MC68HC908GP16CFB
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: