MC68HC908GP16CFB Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC908GP16CFB Datasheet - Page 88
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Description
MCU 8-BIT 16K FLASH 44-QFP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC08r
Datasheet
1.MC908EY16VFAR2.pdf
(278 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC908GP16CFB
Core Processor
HC08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Connectivity
SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM
Number Of I /o
33
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
512 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
44-QFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 88 of 278
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
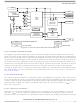
Internal Clock Generator (ICG) Module
asynchronously to the clocks. The unpredictably of the transition period is a necessary result of the
asynchronicity.
The switch automatically selects ICLK during reset. When the clock monitor is on (CMON is set) and it
determines one of the clock sources is inactive (as indicated by the IOFF or EOFF signals), the circuit is
forced to select the active clock. There are no clocks for the inactive side of the synchronizer to properly
operate, so that side is forced deselected. However, the active side will not be selected until one to two
clock cycles after the IOFF or EOFF signal transitions.
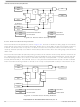
8.4 Usage Notes
The ICG has several features which can provide protection to the microcontroller if properly used. Other
features can greatly simplify usage of the ICG if certain techniques are employed. This section describes
several possible ways to use the ICG and its features. These techniques are not the only ways to use the
ICG and may not be optimum for all environments. In any case, these techniques should be used only as
a template, and the user should modify them according to the application’s requirements.
These notes include:
8.4.1 Switching Clock Sources
Switching from one clock source to another requires both clock sources to be enabled and stable. A
simple flow requires:
The key point to remember in this flow is that the clock source cannot be switched (CS cannot be written)
unless the desired clock is on and stable. A short assembly code example of how to employ this flow is
shown in
particular assembler.
88
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Switching clock sources
Enabling the clock monitor
Using clock monitor interrupts
Quantization error in digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) output
Switching internal clock frequencies
Nominal frequency settling time
Improving frequency settling time
Trimming frequency
Enable desired clock source
Wait for it to become stable
Switch clocks
Disable previous clock source
Figure
8-9. This code is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent valid syntax for any
MC68HC908EY16 • MC68HC908EY8 Data Sheet, Rev. 10
Freescale Semiconductor
Related parts for MC68HC908GP16CFB
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: