MC68HC908GP16CFB Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC908GP16CFB Datasheet - Page 177
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Description
MCU 8-BIT 16K FLASH 44-QFP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC08r
Datasheet
1.MC908EY16VFAR2.pdf
(278 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC908GP16CFB
Core Processor
HC08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Connectivity
SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM
Number Of I /o
33
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
512 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
44-QFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC908GP16CFB
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 177 of 278
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
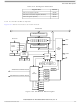
15.6.1 Overflow Error
The overflow flag (OVRF in SPSCR) becomes set if the SPI receive data register still has unread data
from a previous transmission when the capture strobe of bit 1 of the next transmission occurs. (See
Figure 15-4
receive data register so that the unread data can still be read. Therefore, an overflow error always
indicates the loss of data.
OVRF generates a receiver/error CPU interrupt request if the error interrupt enable bit (ERRIE in SPSCR)
is also set. MODF and OVRF can generate a receiver/error CPU interrupt request. (See
is not possible to enable only MODF or OVRF to generate a receiver/error CPU interrupt request.
However, leaving MODFEN low prevents MODF from being set.
If an end-of-block transmission interrupt was meant to pull the MCU out of wait, having an overflow
condition without overflow interrupts enabled causes the MCU to hang in wait mode. If the OVRF is
enabled to generate an interrupt, it can pull the MCU out of wait mode instead.
If the CPU SPRF interrupt is enabled and the OVRF interrupt is not, watch for an overflow condition.
Figure 15-7
The first part of
problems. However, as illustrated by the second transmission example, the OVRF flag can be set in
between the time that SPSCR and SPDR are read.
In this case, an overflow can be easily missed. Since no more SPRF interrupts can be generated until this
OVRF is serviced, it will not be obvious that bytes are being lost as more transmissions are completed.
To prevent this, either enable the OVRF interrupt or do another read of the SPSCR after the read of the
SPDR. This ensures that the OVRF was not set before the SPRF was cleared and that future
transmissions will complete with an SPRF interrupt.
avoid this second SPSCR read, enable the OVRF to the CPU by setting the ERRIE bit (SPSCR).
Freescale Semiconductor
1
2
3
4
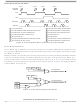
BYTE 1 SETS SPRF BIT.
CPU READS SPSCR WITH SPRF BIT SET AND OVRF BIT CLEAR.
CPU READS BYTE 1 IN SPDR, CLEARING SPRF BIT.
BYTE 2 SETS SPRF BIT.
and
shows how it is possible to miss an overflow.
READ SPSCR
READ SPDR
Figure 15-7
Figure
OVRF
SPRF
15-5.) If an overflow occurs, the data being received is not transferred to the
BYTE 1
Figure 15-7. Missed Read of Overflow Condition
MC68HC908EY16 • MC68HC908EY8 Data Sheet, Rev. 10
shows how to read the SPSCR and SPDR to clear the SPRF without
1
2
3
BYTE 2
4
5
6
7
8
CPU READS SPSCRW WITH SPRF BIT SET AND OVRF BIT CLEAR.
BYTE 3 SETS OVRF BIT. BYTE 3 IS LOST.
CPU READS BYTE 2 IN SPDR, CLEARING SPRF BIT, BUT NOT OVRF BIT.
BYTE 4 FAILS TO SET SPRF BIT BECAUSE OVRF BIT IS SET. BYTE 4 IS LOST.
Figure 15-8
BYTE 3
5
6
7
illustrates this process. Generally, to
BYTE 4
8
Figure
Error Conditions
15-9.) It
177
Related parts for MC68HC908GP16CFB
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: