AT90CAN32 Automotive Atmel Corporation, AT90CAN32 Automotive Datasheet - Page 235

AT90CAN32 Automotive
Manufacturer Part Number
AT90CAN32 Automotive
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Datasheets
1.AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE.pdf
(431 pages)
2.AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE.pdf
(16 pages)
3.AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE.pdf
(225 pages)
Specifications of AT90CAN32 Automotive
Flash (kbytes)
32 Kbytes
Pin Count
64
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
53
Ext Interrupts
8
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
2
Can
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
2
Eeprom (bytes)
1024
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 125
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
4
Output Compare Channels
8
Input Capture Channels
2
Pwm Channels
7
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
- AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE PDF datasheet
- AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE PDF datasheet #2
- AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE PDF datasheet #3
- Current page: 235 of 431
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
19.2.2.2
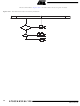
Figure 19-2. CAN Extended Frames
19.2.2.3
19.2.3
19.2.3.1
7682C–AUTO–04/08
Interframe
Interframe
Bus Idle
Bus Idle
Data Frame
Remote Frame
Space
Space
CAN Bit Timing
SOF
SOF
SOF
SOF
CAN Extended Frame
Format Co-existence
Bit Construction
11-bit base identifier
11-bit base identifier
IDT28..18
IDT28..18
A message in the CAN extended frame format is likely the same as a message in CAN standard
frame format. The difference is the length of the identifier used. The identifier is made up of the
existing 11-bit identifier (base identifier) and an 18-bit extension (identifier extension). The dis-
tinction between CAN standard frame format and CAN extended frame format is made by using
the IDE bit which is transmitted as dominant in case of a frame in CAN standard frame format,
and transmitted as recessive in the other case.
As the two formats have to co-exist on one bus, it is laid down which message has higher priority
on the bus in the case of bus access collision with different formats and the same identifier /
base identifier: The message in CAN standard frame format always has priority over the mes-
sage in extended format.
There are three different types of CAN modules available:
To ensure correct sampling up to the last bit, a CAN node needs to re-synchronize throughout
the entire frame. This is done at the beginning of each message with the falling edge SOF and
on each recessive to dominant edge.
One CAN bit time is specified as four non-overlapping time segments. Each segment is con-
structed from an integer multiple of the Time Quantum. The Time Quantum or TQ is the smallest
discrete timing resolution used by a CAN node.
SRR IDE
SRR IDE
Arbitration
Arbitration
Field
Field
– 2.0A - Considers 29 bit ID as an error
– 2.0B Passive - Ignores 29 bit ID messages
– 2.0B Active - Handles both 11 and 29 bit ID Messages
18-bit identifier extension
18-bit identifier extension
ID17..0
ID17..0
RTR
RTR
r1
r1
Control
Control
Field
Field
r0
r0
4-bit DLC
4-bit DLC
DLC4..0
DLC4..0
15-bit CRC
CRC
Field
0 - 8 bytes
Data
Field
CRC
del.
ACK
ACK
Field
ACK
del.
15-bit CRC
End of
Frame
AT90CAN32/64/128
7 bits
CRC
Field
CRC
Intermission
del.
3 bits
ACK
ACK
Field
Interframe
ACK
Space
del.
(Indefinite)
Bus Idle
End of
Frame
7 bits
Intermission
3 bits
Interframe
Space
(Indefini
Bus Idle
235
Related parts for AT90CAN32 Automotive
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU AVR 32K FLASH 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU AVR 32K FLASH 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 32K FLASH 16MHZ 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontroller with 32K/64K/128K Bytes of ISP Flash and CAN Controller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Microcontroller with 16K/32K/64K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash8-bit Microcontroller with 32K/64K/128K Bytes of ISP Flash and CAN Controller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: